NVIDIA AI Infrastructure and Operations Fundamentals
Comprehensive guide to NVIDIA AI infrastructure covering GPU architecture, accelerated computing, training vs inference workloads, data center networking, storage design, virtualization, and operational best practices.
Syllabus:
1️⃣ Essential AI Knowledge (38%)
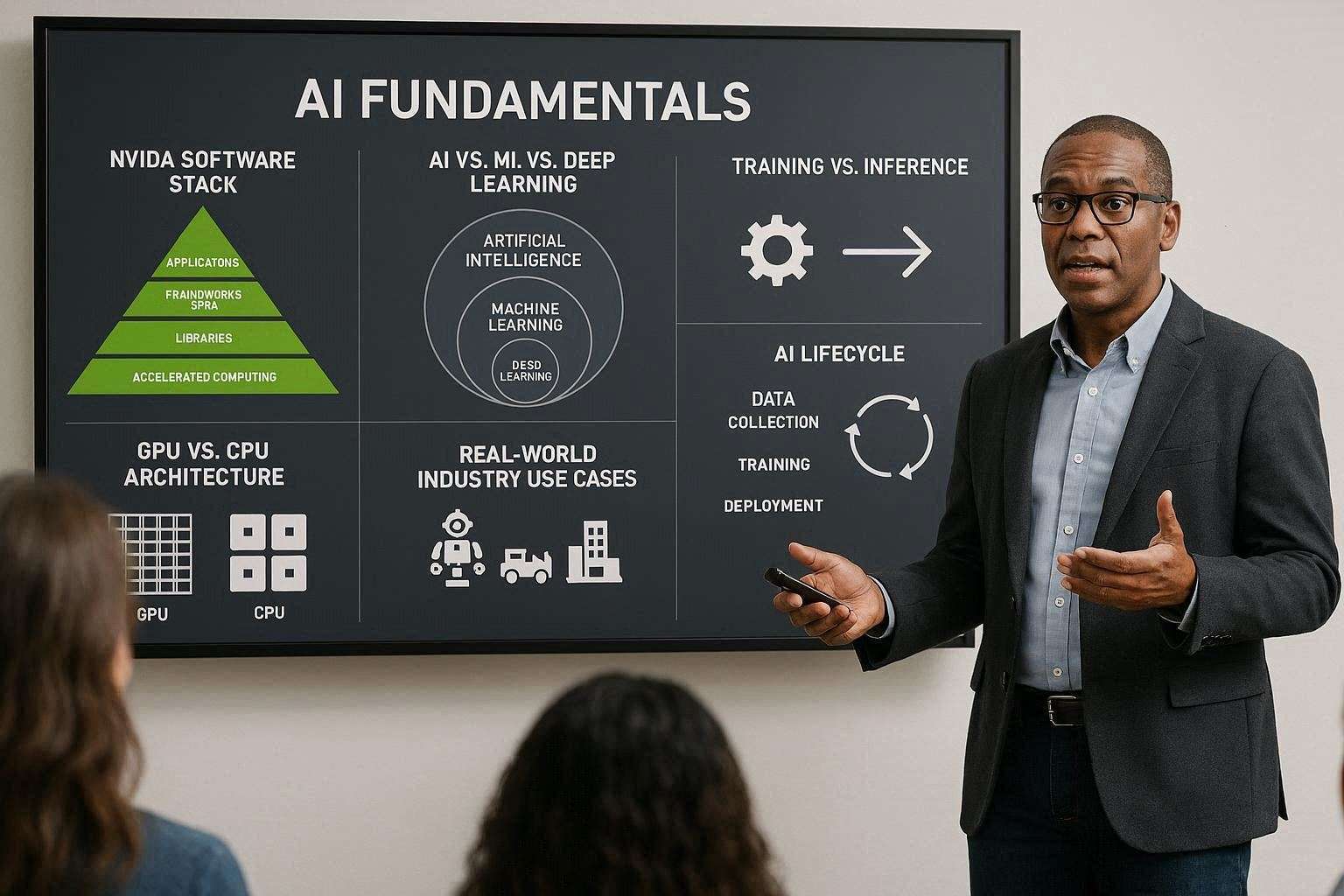
AI vs ML vs DL
- Deep Learning (DL) → ML using neural networks with many layers
- Machine Learning (ML) → Systems that learn from data
- AI → Broad concept of machines performing intelligent tasks
- AgenticAI → Broad concept of machines performing intelligent tasks
- PhysicalAI → Broad concept of machines performing intelligent tasks
Relationship: DL ⊂ ML ⊂ AI ⊂ GenAI ⊂ Agentic AI ⊂ Physical AI
GPU vs CPU Architecture
| CPU | GPU |
|---|---|
| Few powerful cores | Thousands of smaller cores |
| Optimized for sequential tasks | Optimized for parallel workloads |
| Lower throughput | Massive parallel throughput |
| Best for control logic | Best for matrix operations |
Key Point: GPUs excel at matrix multiplications used in neural networks.
Training vs Inference
AI Workflow:
Data Preperation
|--> Model Training
|--> Optimization
|--> Inference/Deployment
| Training | Inference |
|---|---|
| Model learning | Model usage |
| High compute + memory | Lower latency focus |
| Batch workloads | Real-time workloads |
| Multi-GPU scaling | Edge + cloud deployment |
Training = compute intensive
Inference = latency optimized
NVIDIA Software Stack (High-Level)
- CUDA → GPU programming platform
- cuDNN → Deep learning primitives
- TensorRT → Inference optimization
- NCCL → Multi-GPU communication
- RAPIDS → GPU data science
- NVIDIA AI Enterprise → Production AI platform
Why AI Adoption Accelerated
- GPU performance improvements
- Large datasets
- Cloud scalability
- Transformer architectures
- Pretrained models
- Open-source frameworks
2️⃣ AI Infrastructure (40%)
Scaling GPU Infrastructure
Scale-Up
- More GPUs per node
NVLinkNVSwitch
Scale-Out
- More nodes
InfiniBand- Ethernet
RDMA
Data Center Requirements
Power
- High rack density (30–80kW+ per rack)
Cooling
- Air cooling
- Liquid cooling
- Rear door heat exchangers
- Direct-to-chip cooling
Networking Requirements
Important concepts:
RDMARoCEInfiniBand- East-west traffic
- Spine-leaf architecture
High-speed DC options:
- 100G / 200G / 400G Ethernet
InfiniBand HDR/NDR
DPU (Data Processing Unit)
Purpose:
- Networking offload
- Security isolation
- Storage acceleration
- Free CPU resources
Architecture roles:
- CPU → General compute
- GPU → AI compute
- DPU → Infrastructure acceleration
On-Prem vs Cloud
| On-Prem | Cloud |
|---|---|
| CapEx | OpEx |
| Full control | Elastic scaling |
| Long-term cost efficiency | Fast deployment |
| Hardware management required | Managed infrastructure |
3️⃣ AI Operations (22%)
Monitoring GPUs
Key Metrics:
- GPU utilization
- Memory utilization
- Temperature
- Power usage
- ECC errors
- SM occupancy
Tools:
NVIDIA DCGM- Prometheus
- Grafana
- nvidia-smi
Cluster Orchestration
- Kubernetes
Slurm- Workload scheduling
- Job prioritization
- Multi-tenant isolation
Virtualization
- NVIDIA
vGPU MIG(Multi-Instance GPU)- GPU partitioning
- Isolation vs performance trade-offs