Provision Tools
1. AWS ELASTIC BEANSTALK
Platform as Service Developer Centric Fully Manged Cloud service to deploy code.
- Free Service but need to pay for underlying hardware.
- Internally use Cloudformation
- We can jump start using pre configured loader.
- Application code + configuration to auto deploy infrastructure in dev environment
- Support creating multiple Environments: Dev, Prod etc along with Cloning to create similar environment
- Built in Health & Monitoring
- Logs & Events for tracing
BeanStalk CLI (eb cli)
help speed up deployment to beanstalk using cli
-
Basic command:
eb create, status, health, events, logs, open, deploy, config, terminate
Beanstalk LifeCycle Policy
- EB can store at most
1000app versions - Old versions must phase out using
timeorspaceconstrains - Current live version cant be deleted
EB Extensions
Set UI parameters using code
- JSON/YAML file reside in
.ebextensions/directory of root of source code zip. - Must have extension
.config(eg. logging.config) - Modify default settings & Environment variables in EB Console using code
- Can add resources eg RDS, ElastiCache, DynamoDB
- Added resources gets auto deleted when eb env goes away
Adding SSL Support Can be done in 2 ways
- Directly from Console in ALB config
- Using Extension
.ebextension/securelistener-alb.config
Using Worker Schedule tasks to run periodically and asynchronously away from EB. These tasks typically take more than 1 hour to complete.
- Use Worker environment &
cron.yaml
Creating Custom EB Platform
Define custom platform : OS + Software + Scripts of EB
- Define AMI using
Platform.yaml& build the platform AMI usingPacker
- Used to create a whole new platform or tweak programming languages
- Use Case: Run Incompatible language on eb & does not support docker.
Deployment Modes
1. All at Once:
Deploy all instance at the same time
- Result in downtime
- Fastest
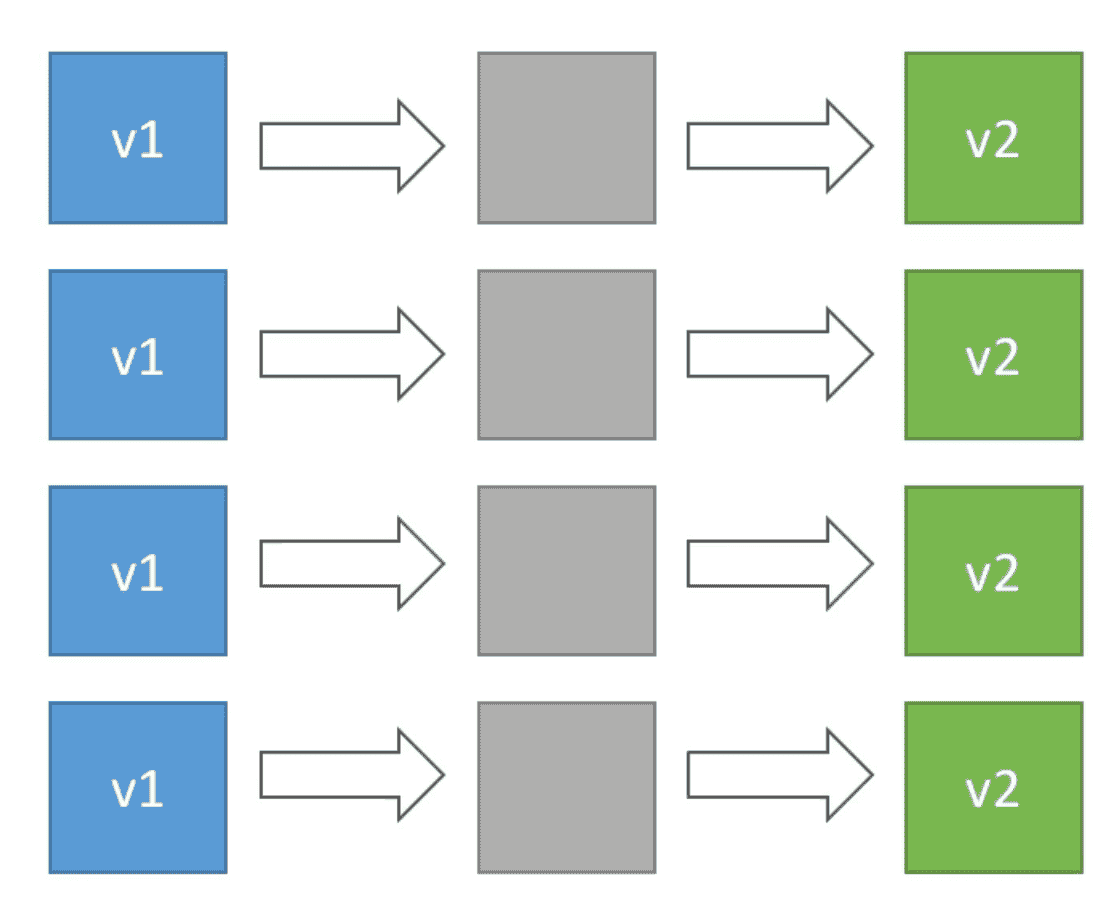
2. Rolling
Roll update on a fix number of host called
Bucket Size
- No Additional Cost=> Number of EC2 stays the same
- App Run new & old version at some time of update
- App run below Capacity during deployment
- Can take a long time to deploy
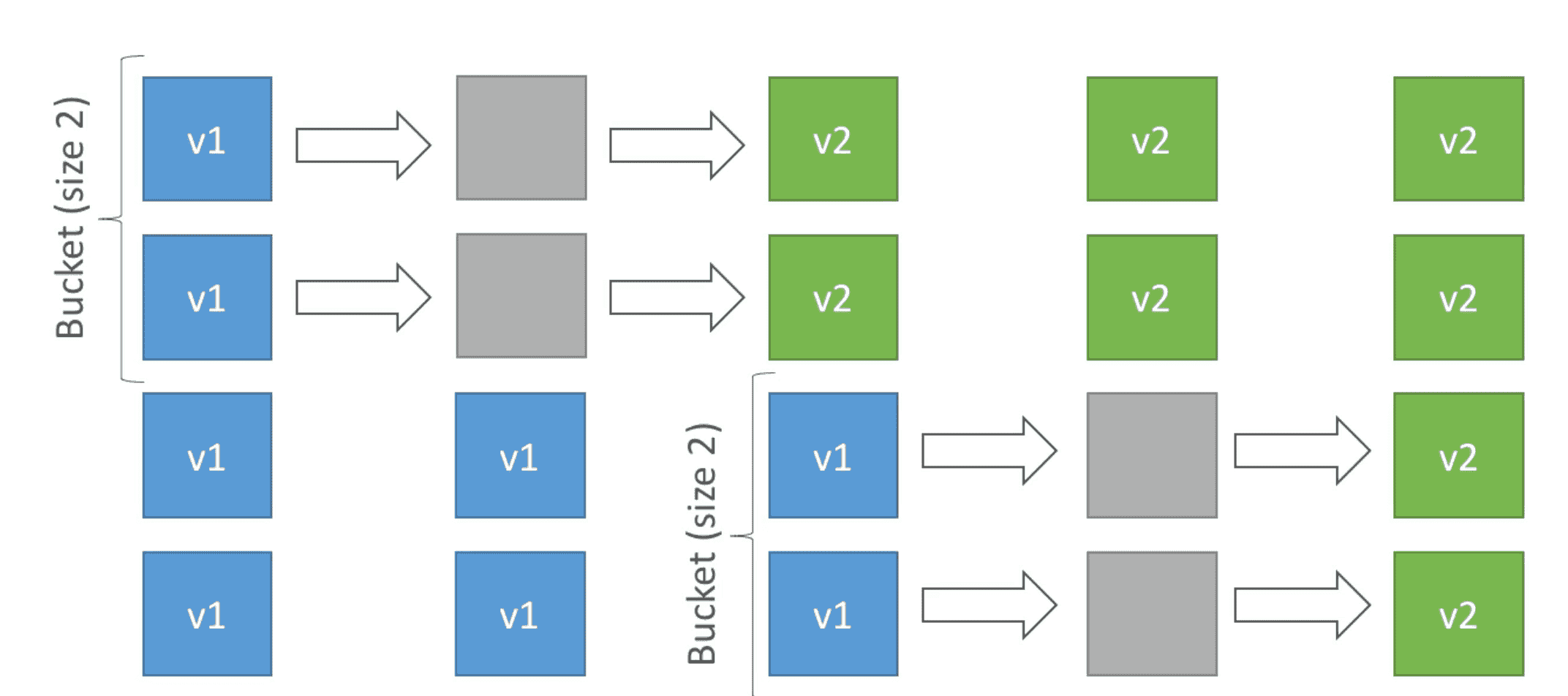
3. Rolling with additional Batch
Roll update with additional EC2 Batch
- Small Additional Cost
- App Run new & old version at some time of update
- App always run at Capacity even during deployment
- Good for production
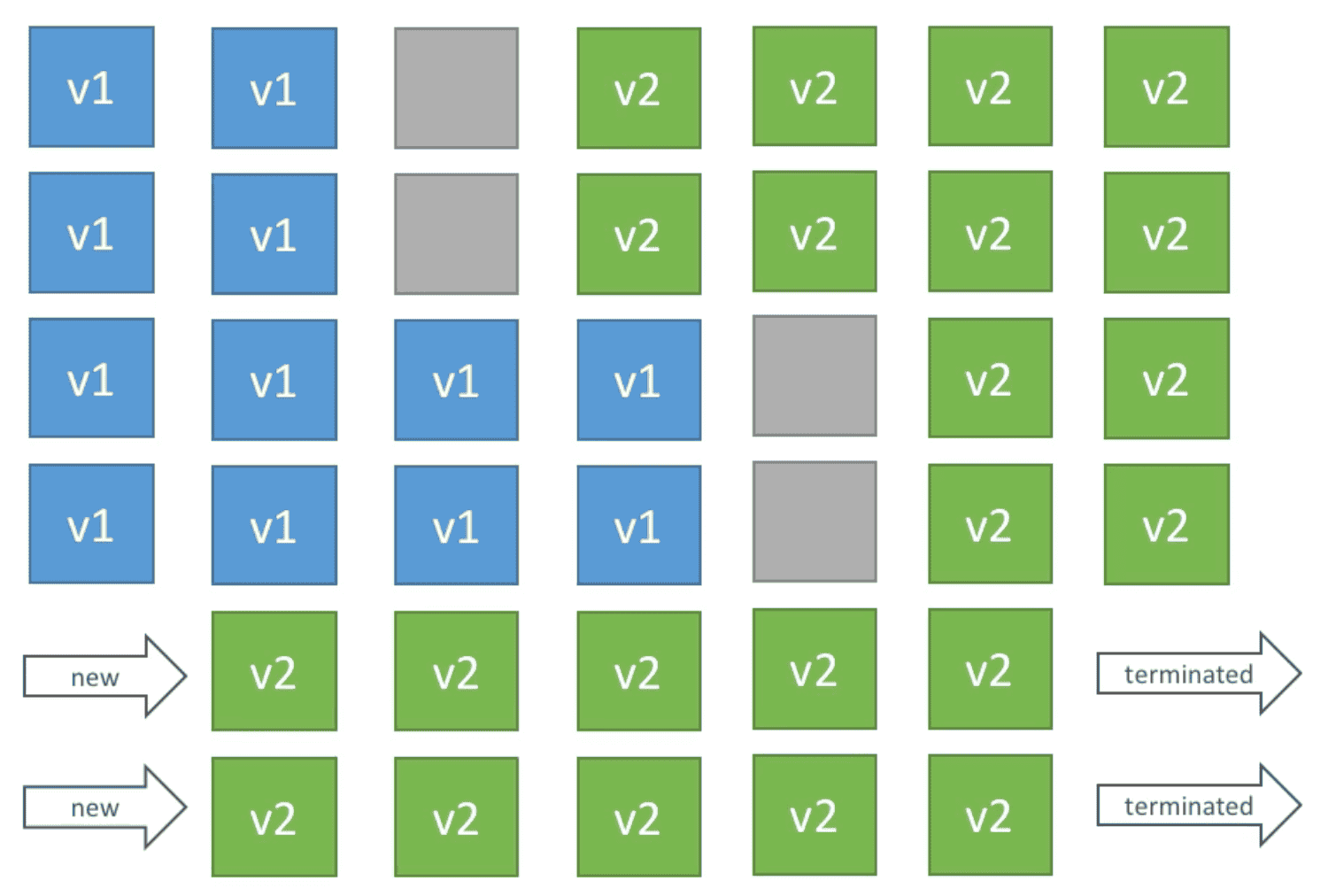
4. Immutable Deployment
Duplicate deployment on new ASG with new version
- Costly because of duplication of resources
- Quick Rollback in case of Failure
- Zero Downtime
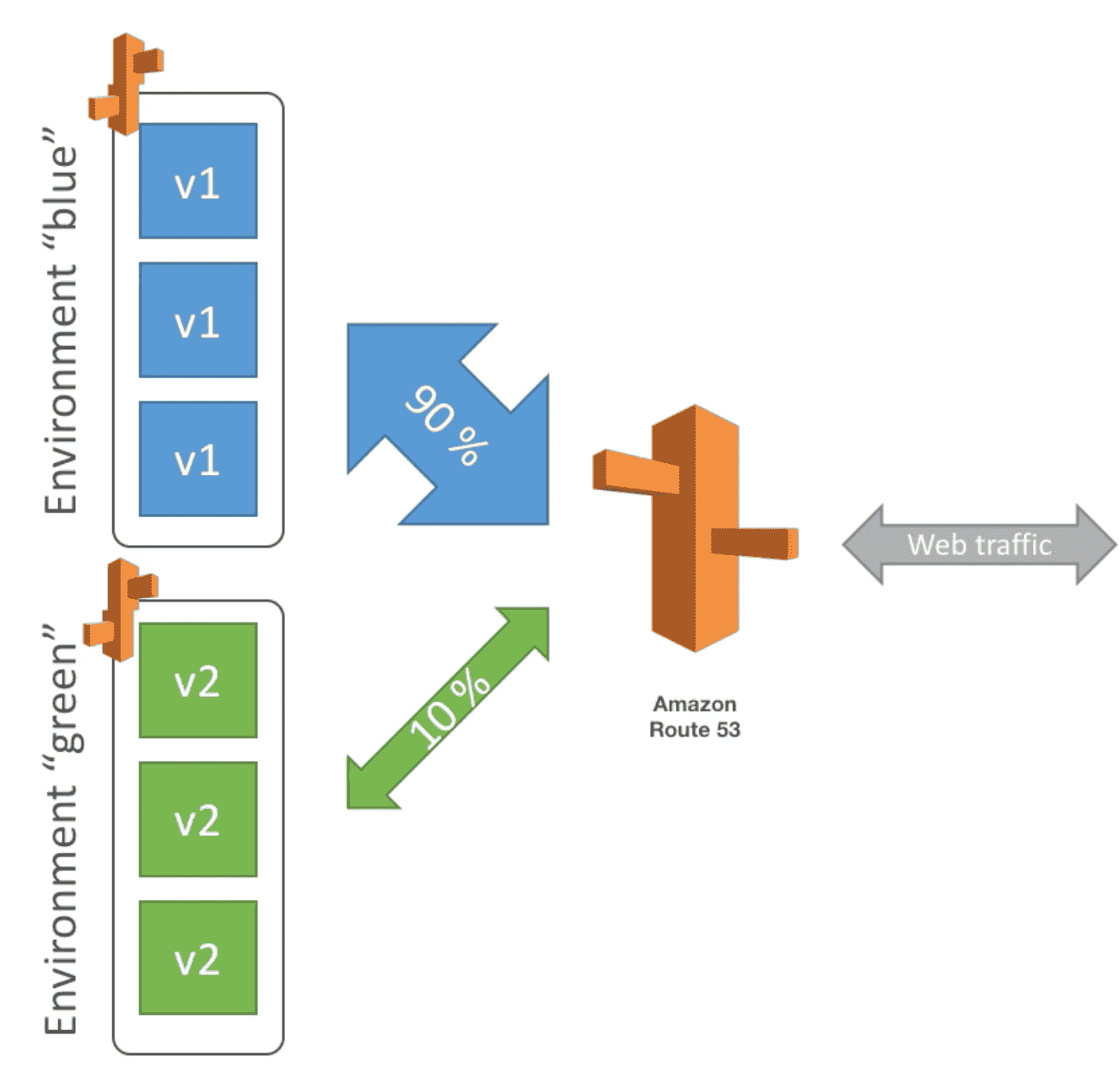
5. Blue Green Deployment
Route a part of traffic to new deployment to test A/B environment
- URL need to swap once testing is done
- USe Route 53 to route traffic
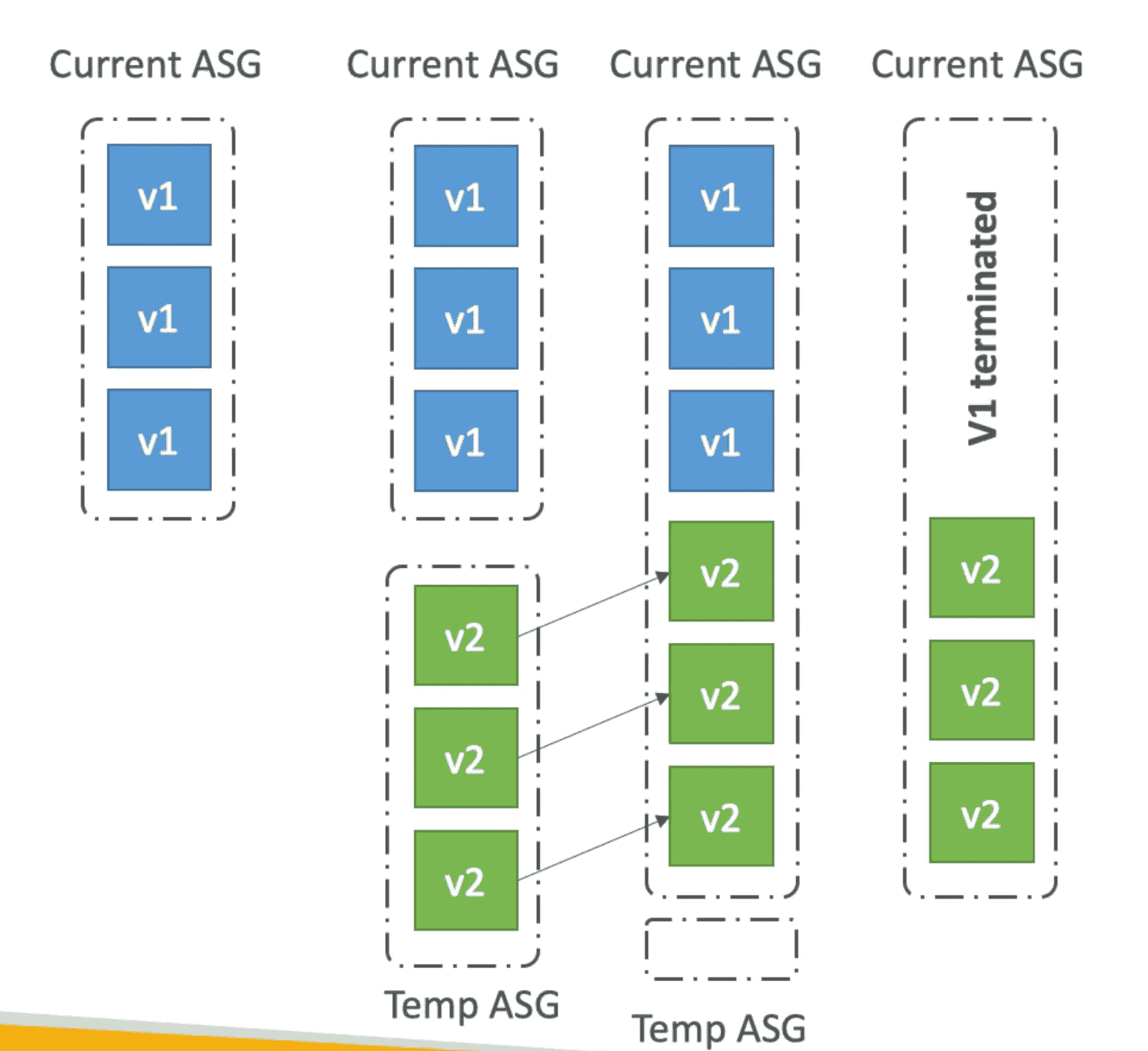
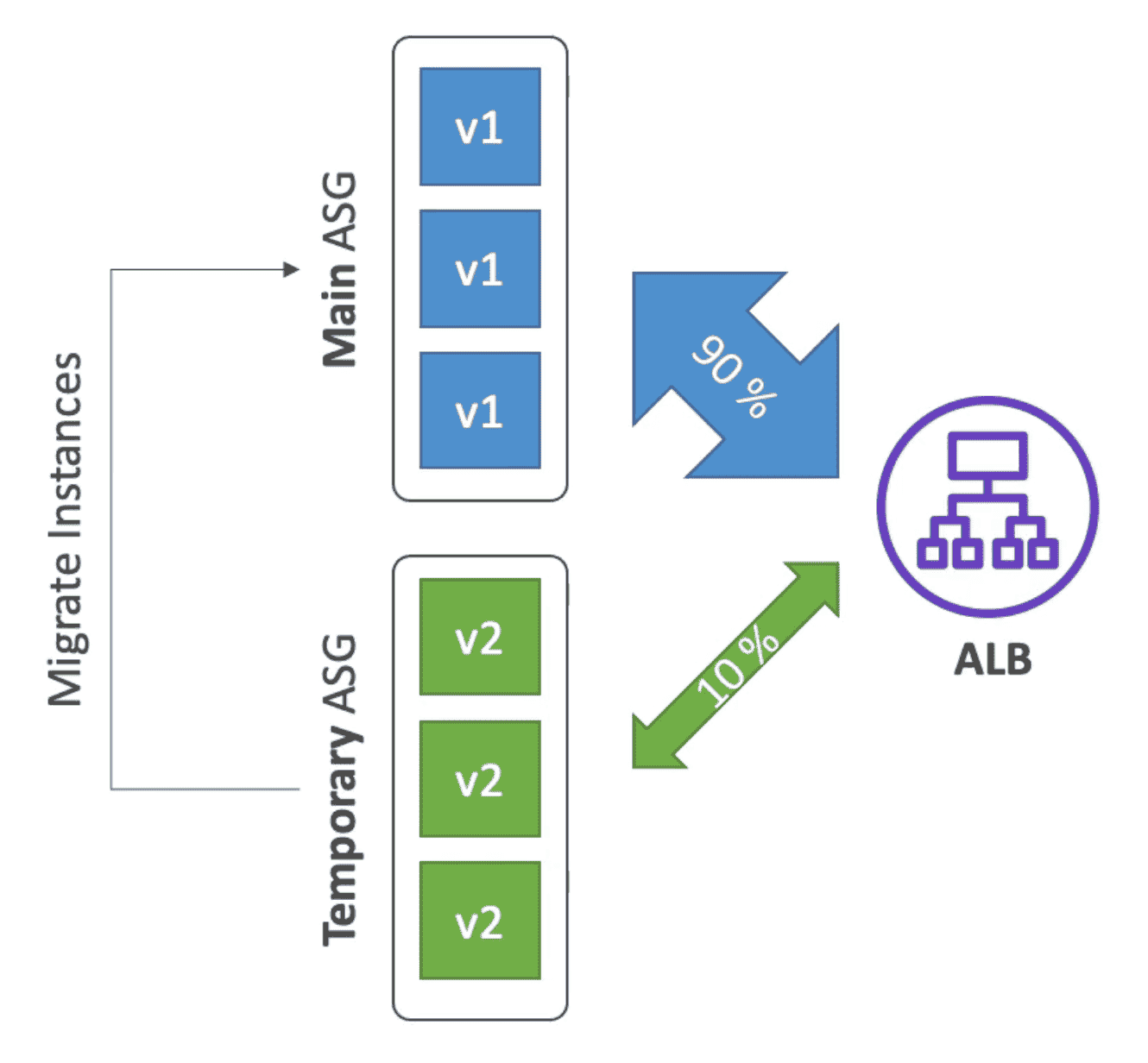
6. Traffic Splitting
used for
Canary Testing.
- New Version deployed to temporary ASG
- A small part of traffic is routed to new ASG using ALB
- Deployment health is monitored
- In case of failure quick rollback can be initiated
- No Application downtime
2. AWS CLOUDFORMATION
Declarative way of defining AWS Infrastructure as Code
- CloudFormation Template Use
JSONorYAMLtemplate to define process - Template is uploaded to
S3& version maintained on S3
Advantages:
- Save cost by deleting Infrastructure in night.
- Estimate cost using resource used in Template.
- Increase productivity : Automate provision of resources automatically based on Template
- Version controlled: Change in infrastructure is reviewed through code.
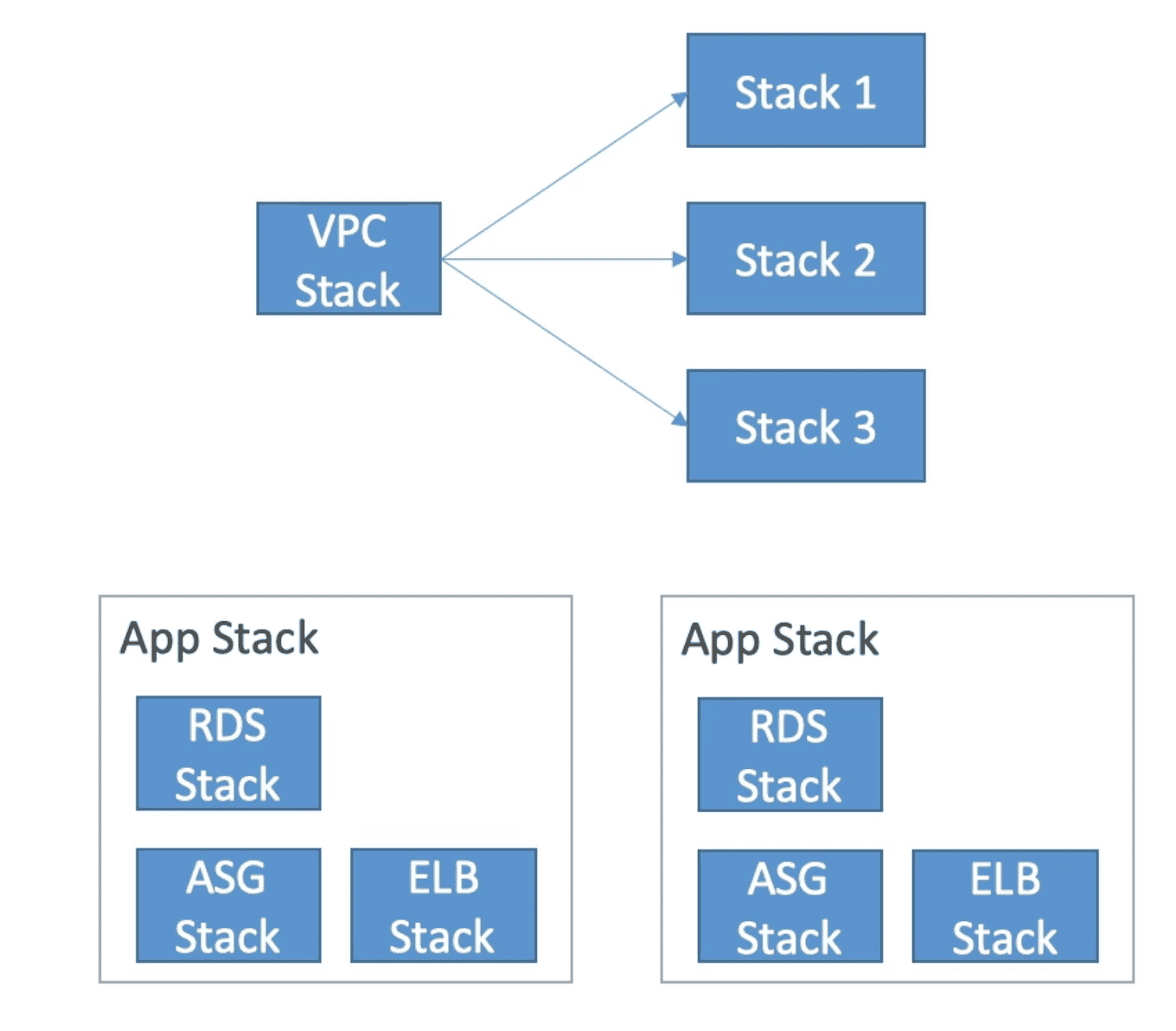
- Separation of Concern : Create Stack for different apps/layer
- Don't reinvent the wheel: use existing template & documentation for best practices
Cloudformation Drift
Detect manual changes to infrastructure created by Cloudformation
- Used to detect changes made stack resources outside CloudFormation
StackSet
Create Delete or update stack across multiple Account & Regions
- One account to edit, delete, create stack in multiple region
- Create Stack for different apps/layer
- Deleting a Stack also delete all resources created from Stack
Cross Stack
!Outputof a Stack is!Importto multiple Stacks
Nested Stack
Used when Stack is reused & recreated
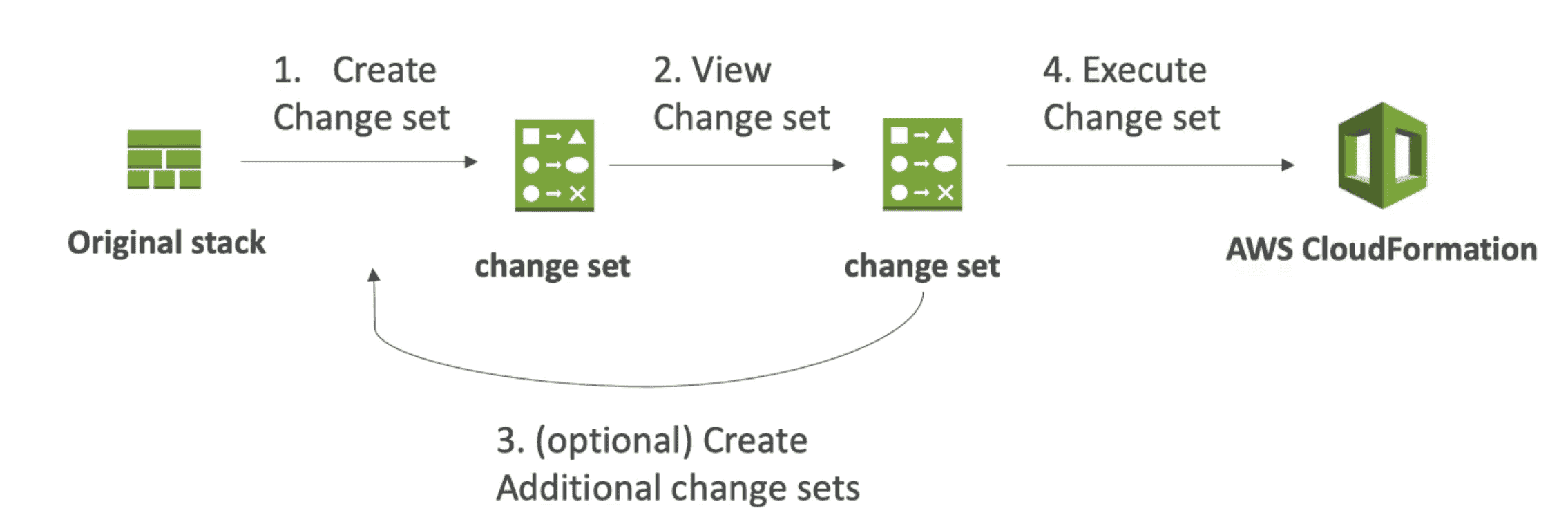
ChangeSet
Set of changes to update Cloudformation stack
Rollback
- If Stack creation failed everything roll back(deleted)
- Rollback Can be disabled for troubleshooting
- If Update failed everything rollback to previous known state
Template Component
Resources:(Mendatory)
Actual AWS Resources (MANDATORY) eg EC2, ALB etc
AWS:: aws-product-name::data-type-name- Resources can reference each other
- Dynamic resources are not supported
- Over 224 resources in AWS: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-template-resource-type-ref.html
Parameter: (Optional)
dynamic variables act as input to reuse template
fn::!Ref,!fn(YAML) function is used to reference parameters and resources
Pseudo parameter
- AWS internal parameter
- Example:
AWS::AccountIdAWS::StackIdAWS::StackName
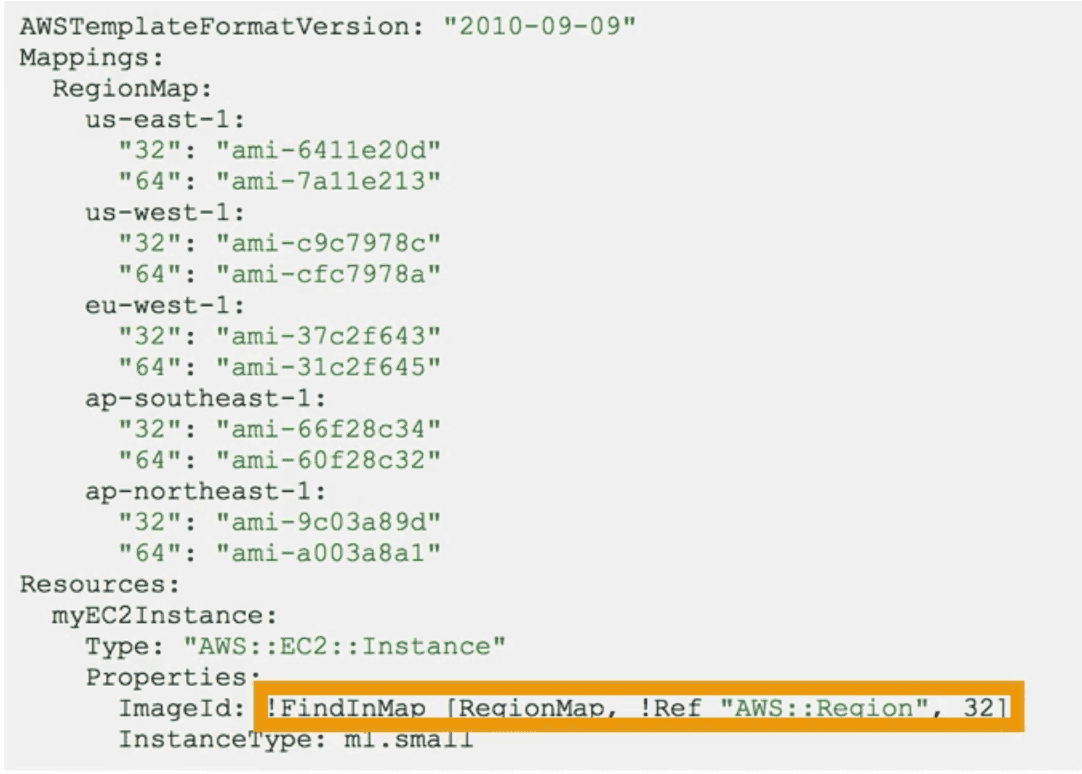
Mapping:(Optional)
static hardcoded variables
- Used to assign different value for different environments dev, prod, qa
!FinInMap[MapName, FirstLevelKey, SecondLevelKey]: find value in Map for a Key
Output: (Optional)
Output Reference to what has been created to use in other cloudformation template
- value contain reference to AWS resource
fn::ImportValue/!ImportValueused by other template to use Output- You cant delete resource if Output is referenced
Conditions:
conditions to create resource or output
!And, !Or, !Not, !Equal, !If
Intrinsic Functions:
!Ref:Return value of Parameter or Physical ID of resourceGetAtt: List of attributes attached to a resource!FinInMap[MapName, FirstLevelKey, SecondLevelKey]: find value in Map for a Key!ImportValueImport resources create from Output- !join[delimiter [comm separated values]]
!Subsubstitute variable from text!And, !Or, !Not, !Equal, !If: Conditions
Cloud Development Kit(CDK)
Use Programming Language code to convert into Cloudformation template