Cloud Integration
Application Communicate Pattern
- Synchronous Communication: Bad pattern make it hard to decouple Application
- Tightly Couple System: If one component fails it can failed Other component or other system Eg: Monolith Application
- Asynchronous Communication: Use Event Base Queue to decouple Applications
- Loosely Coupled System: Components talk to each other over message & Queue Eg Microservice
Services helping with communicating Loosely Coupled Components
Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS)
Producer Store messages in Queue, Consumer Process the Message
- This allows us to scale Producer Layer & Consumer layer independent of each other based on Messages in Queue
1. Standard queues
- No Limit: Send, Store, Receive b/n component in any volume and any rate
- SQS SDK is used to send message using
SendMessageAPI - Fully Manged & Serverless
- Unlimited Throughput
- Low Latency
< 10 mS - TTL:
4 days to 14 days - Size
256kB/Messageencrypted in transit & rest using KMS - Consumer can poll upto
10 message at a time. - Consumer must delete message after processing.
Limitation;
- Duplicate Messages
- Out of order Messages
Security
- In flight encryption using HTTPS
- At rest encryption using KMS
- IAM Policy to regulate Access to SQS API
API
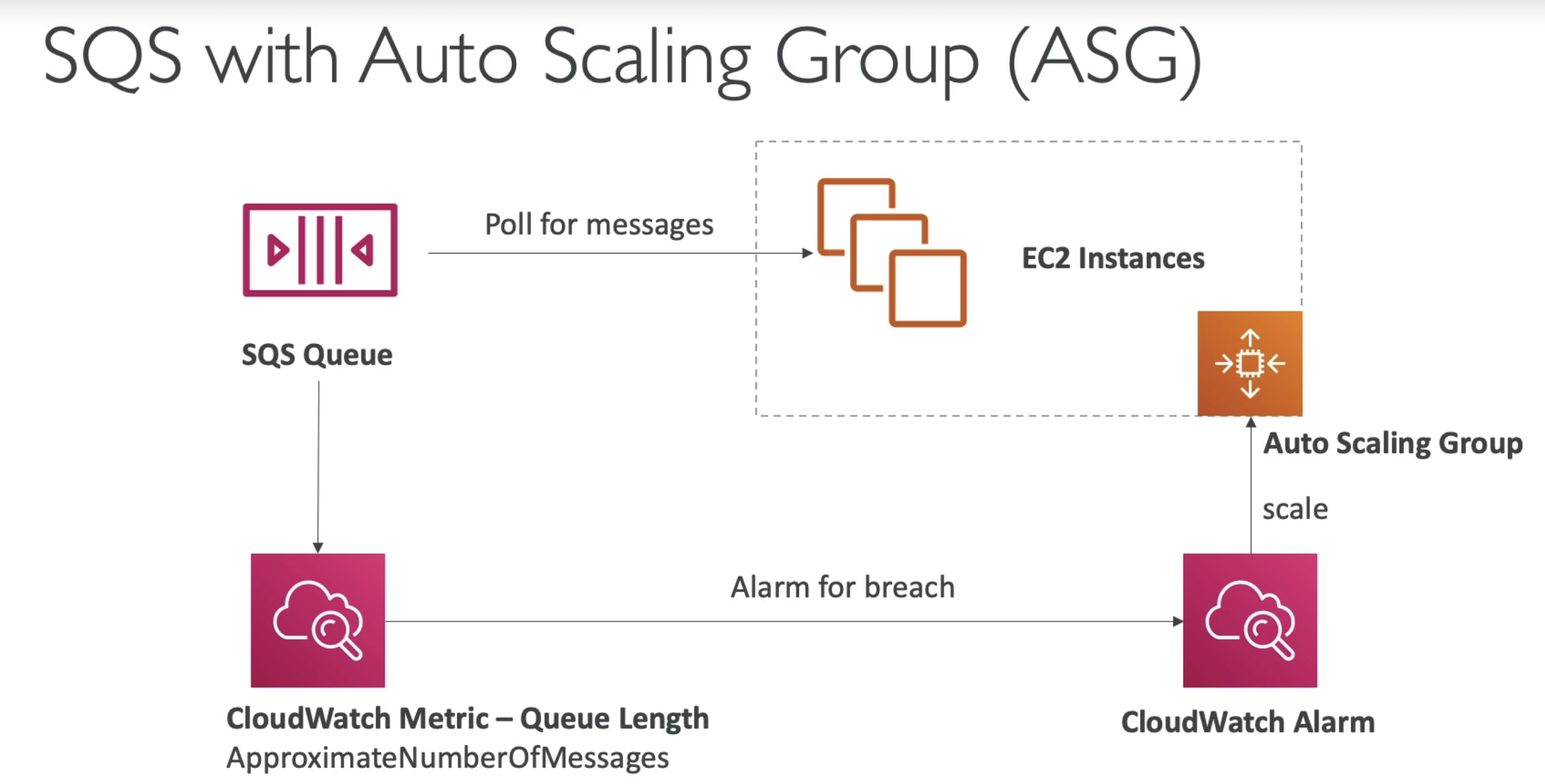
SQS & ASG
- Cloud watch alarm can be used to scale Consumer based on number of messages in Queue
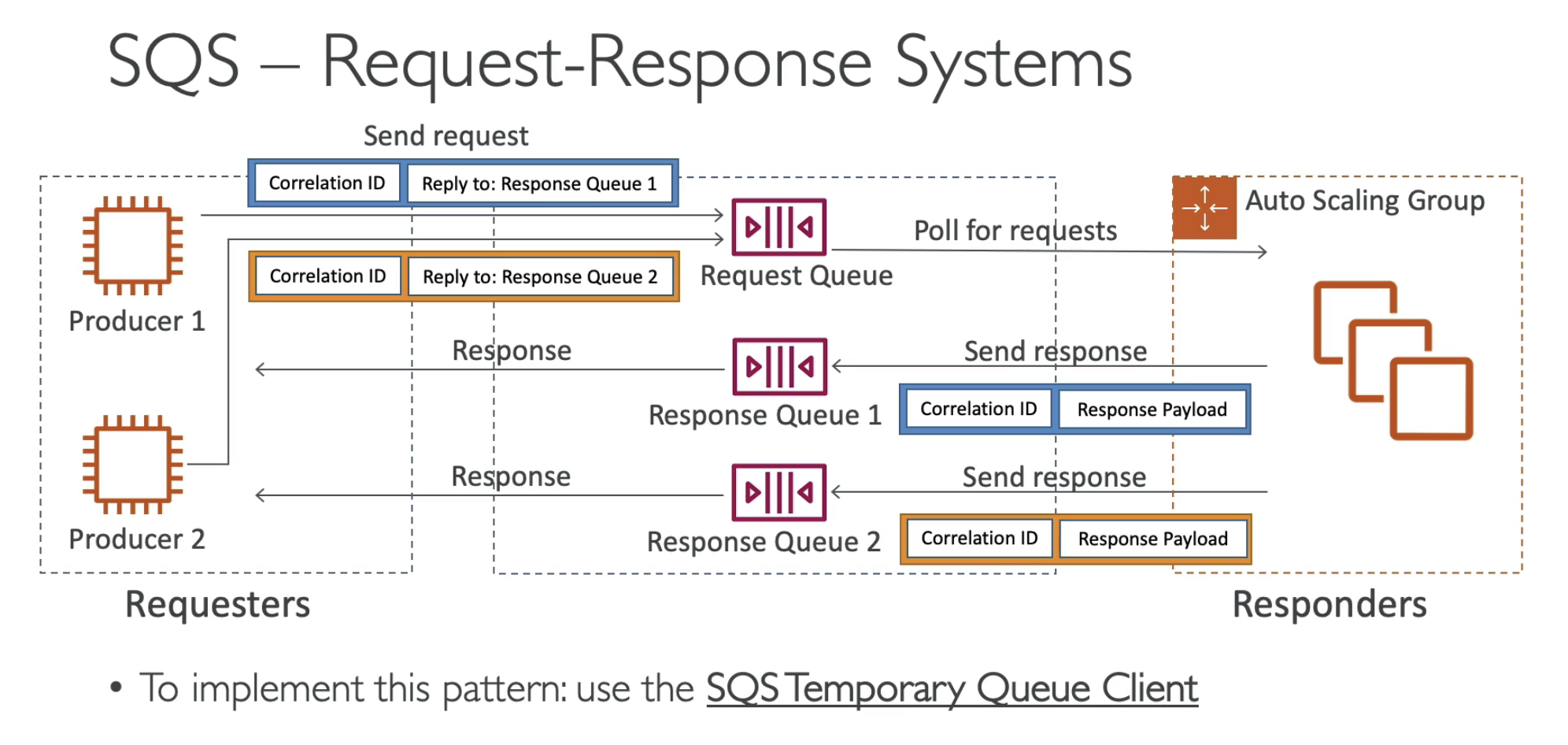
SQS Request Response System
Use 1 request queue & many response queue to scale Consumer & producer.
- Make use of ID to publish consumer result to a different queue.
SQS Temporary Queue Client: Can be used to simplify the process of creating & deleting queues
SQS ACCESS Policy
JSON based document to control who can write/read Queue
- Use Case: cross account access to poll messages or S3 Event Notification
SQS Message Visibility Timeout
When Message is polled by consumer it become invisible to other consumer within a timeout window.
- Default:
30 Seconds - If message is not consumed within 30 Sec it will be visible to other consumer
ChangeMessageVisibility- API to request more time for message
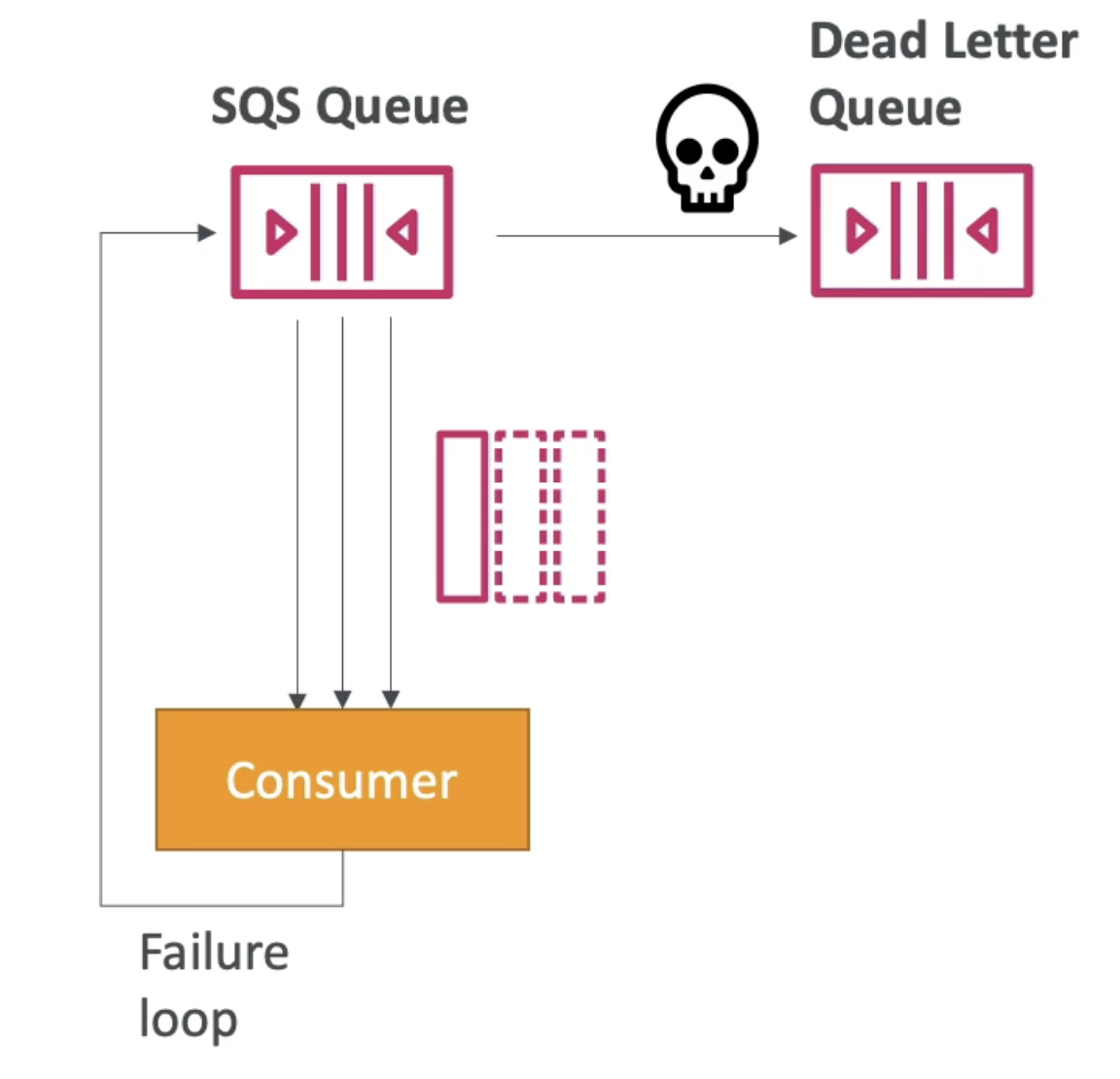
DEAD LETTER QUEUE(DLQ)
Threshold for max read time for consumer failed to read message within Visibility Timeout
- Retain in DLQ for
14 daysto debug message
DELAY QUEUE
Set delay for message visible in SQS.
- Delay can be upto
0-15Minute in Delivery Delay

SQL Long Poling
Consumer Wait for Message to Arrive to reduce latency
- Reduce number of time API call to SQS.
- Time can be set from
1Sec -20Sec - Reduce Latency
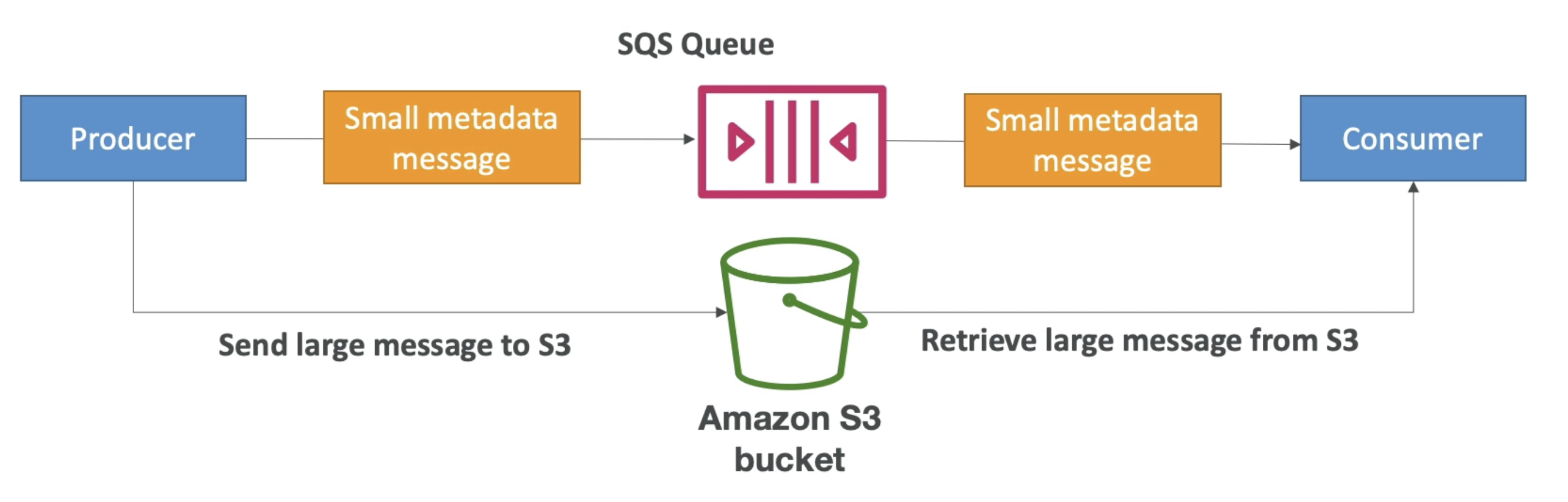
SQS Extended Client
Send Data beyond 256 kB message Limit
- Use SQS Extended Library(Java Lib)
| Feature | Amazon SQS | Apache Kafka |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Message Queuing | Distributed Event Streaming |
| Throughput | High, but limited (especially FIFO queues) | Extremely high throughput |
| Scalability | Scales automatically, but limited by throughput in FIFO | Horizontal scaling for large data streams |
| Message Retention | Configurable (1 minute to 14 days) | Configurable, long retention (months to years) |
| Ordering | FIFO queues (guaranteed) or unordered (standard) | Ordered within partitions, but not across partitions |
| Latency | Higher compared to Kafka | Low latency, suitable for real-time use |
| Complexity | Simple to use, fully managed | More complex, requires management |
| Cost | Pay per request and message volume | Higher operational costs for clusters, depending on scale |
| Use Cases | Simple queuing, decoupling services | Real-time streaming, event sourcing, log aggregation, analytics |
2. SQS FIFO Queue
First in first out, Order is maintained & no duplicates
- Limited Throughput
300/Msgwith Batching3000/Msg(send, receive, or delete operations per second) - The name of a FIFO queue must end with the
.fifosuffix. - The suffix counts towards the 80-character queue name limit.
To Convert Standard Queue to FIFO: Delete existing Queue & Recreate it as FIFO Queue
Deduplication Interval
Time within which next duplicate message will be ignored
Methods to remove duplicate
- Content Based Deduplication: SHA256 Hash of message Body is compared
- Deduplication ID: Provide Explicit ID to compare duplicate
MessageGroupID
Create Order of messages within Group
- 1 MessageGroupID = 1 Consumer
- Order of message with GroupID is maintained
- Order of group is not guaranteed
Standard vs FIFO Queue
| Feature | Standard Queues | FIFO Queues |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Nearly unlimited API calls per second | Up to 3,000 messages/sec with batching (or 300 API calls/sec) |
| Ordering | Best-effort ordering (may arrive out of order) | First-in-first-out (FIFO) ordering within message groups |
| Delivery Guarantee | At-least-once delivery (messages may be duplicated) | Exactly-once processing (deduplication supported) |
| Use Case: High Volume | Ideal for real-time data streaming, background jobs, large-scale apps | Suitable for sequential processing when message order matters |
| Use Case: Task Allocation | Distribute tasks to multiple worker nodes efficiently | Ensure commands execute in order (e.g., financial transactions) |
| Use Case: Data Processing | Batch messages for database processing | Process product price updates in correct order |
| Durability | Stored across multiple AWS Availability Zones | Stored across multiple AWS Availability Zones |
| Scalability | Highly scalable (scales automatically) | Can be scaled with high throughput mode (up to 30,000 TPS) |
| Deduplication | Not supported (handle duplicates at the application level) | Supported via MessageDeduplicationId or content-based deduplication |
| Latency | Low latency | Slightly higher latency due to ordering guarantees |
Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS)
One to many relationship. Send message to many Consumers on
SNS Topic.
- Send Notification along with messages over Pub/Sub Model in a topic
- End user can subscribe to different Channel to get message for relevant topics
- No Limit:
10 Million sub/topic, 100k topics
Producer:
- S3 Bucket Events
- ASG
- CloudWatch Alarm
- Cloudformation Template State Change
Subscriber :
- SQS Queue
- Lambda Function
- HTTP/HTTPS End Point
- Push Notification SMS, email
Security
- HTTPS: In flight encryption
- KMS: At rest encryption
- IAM Policy to regulate Access to SQS API
- SNS Access Policy: Limit who can write to SNS & cross account access
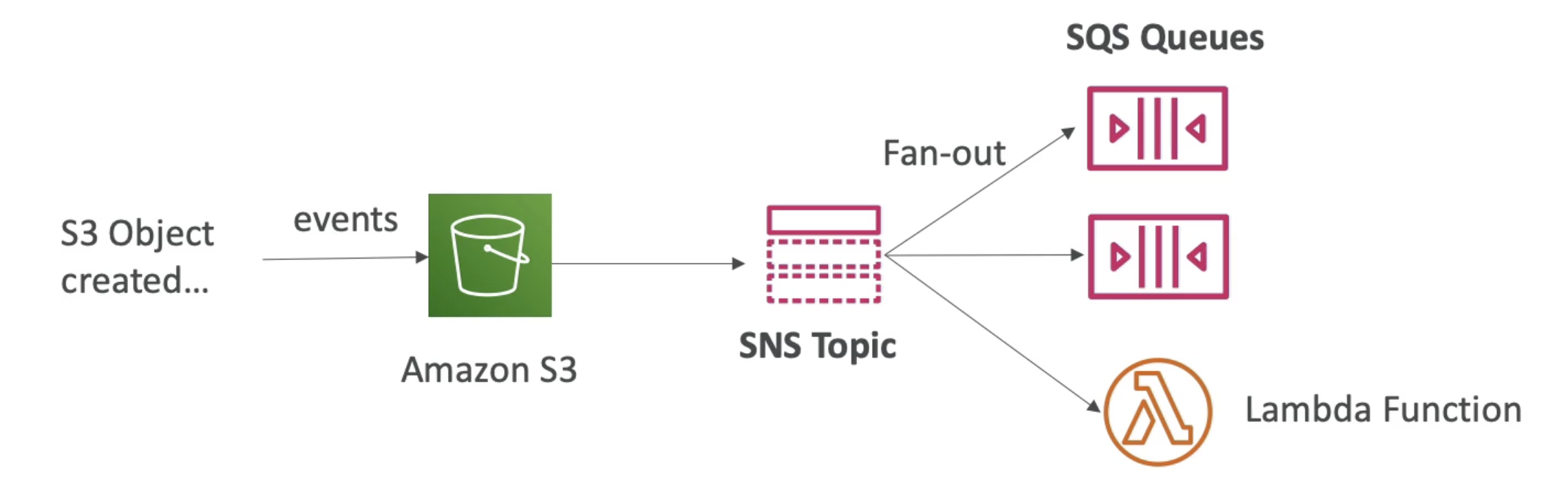
FAN OUT PATTERN
Push Once in SNS+ Subscribe to many SQS
- Fully decoupled and avoid data loss in SNS
- SQS Access Policy must allow to write from SNS
- SQS allow no data loss, retries, delay processing
- Use case: S3 Event to distribute to many SQS queue
SNS FIFO
Same as SQS Fifo to allow Fan out +Ordering+ de duplication.
- Ordering by Message Group ID
- Deduplicate using deduplicate ID
- Can Only have SQS FIFO Queue as subscribers

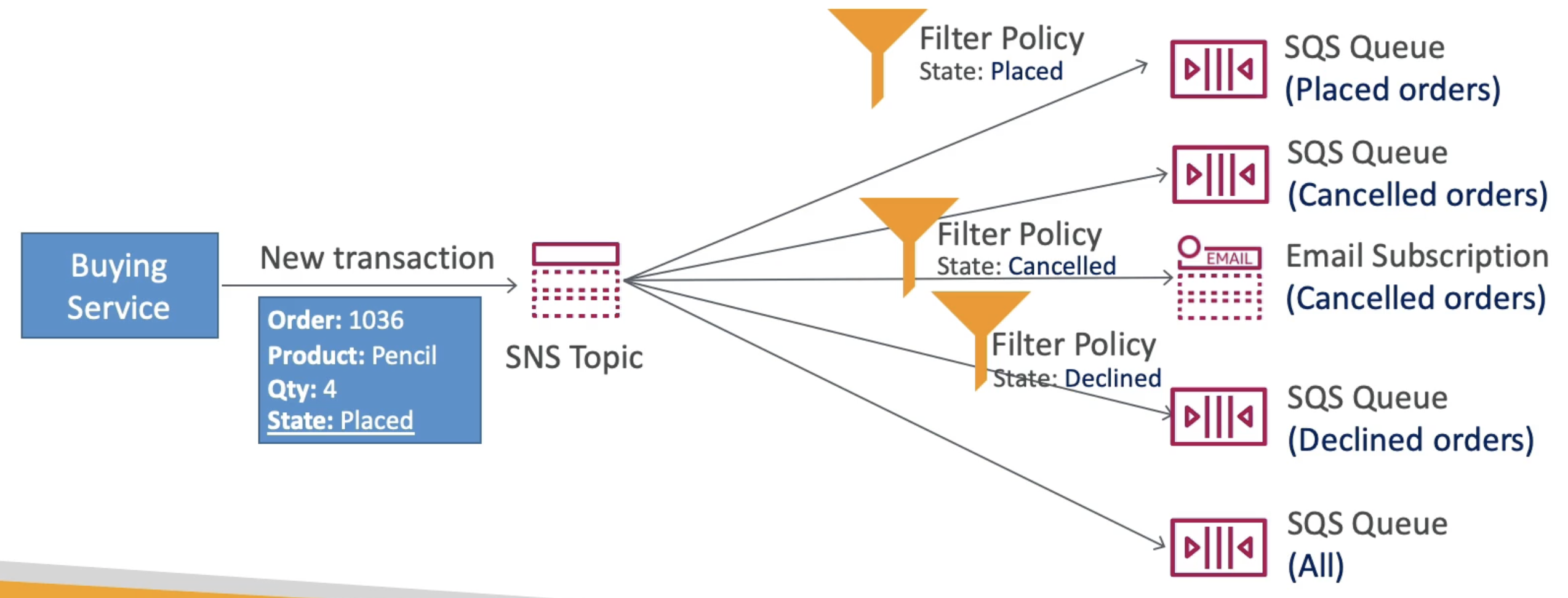
SNS FILTER POLICY
JSON Policy to Filter out SNS messages to different SQS in Fan out pattern
- Without FIlter Policy Subscriber will receive all messages
SQS vs SNS vs MQ
| Feature | Amazon SQS | Amazon SNS | Amazon MQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Message Queue | Pub/Sub (Publish-Subscribe) | Managed Message Broker |
| Use Case | Decoupling microservices, job processing | Event notifications, broadcasting messages | Legacy system integration (ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ, IBM MQ, etc.) |
| Message Delivery | Messages are pulled by consumers | Messages are pushed to subscribers | Supports both queues and topics (Pub/Sub) |
| Ordering | FIFO (Guaranteed) or Standard (Unordered) | No guaranteed ordering (FIFO via SNS+SQS) | Supports message ordering (depends on broker) |
| Durability | Stores messages for up to 14 days | No message persistence | Message persistence based on broker configuration |
| Latency | Low to moderate | Low | Low |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Highly scalable | Moderate scalability |
| Protocol Support | REST API, SDKs | HTTP, Email, SMS, SQS, Lambda | AMQP, MQTT, STOMP, OpenWire, JMS |
Amazon MQ (Managed Apache ActiveMQ)
Manged Queue system to use existing queue structure instead of SQS
- Run open protocol :MQTT, AMQP, STOMP,Open Wire, WSS
- Does not scale like SQS
- Not serverless: runs on dedicated Machine
- Have both SQS & SNS
Kafka vs. RabbitMQ: Key Differences
Architectural Differences
| Feature | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Partition-based design for high-throughput stream processing | Message broker designed for complex message routing |
| Message Model | Pull-based: Consumers fetch messages from topics | Push-based: Brokers send messages to consumers |
| Persistence | Messages are retained based on retention policy | Messages are deleted once consumed |
| Ordering | Maintains order within a partition | Ensures FIFO unless priority queue is used |
| Scalability | Horizontal scaling via partitions | Scales with multiple brokers but can slow down under heavy load |
| Message Routing | Uses topics and partitions to distribute messages | Supports complex routing with exchanges and queues |
Message Handling Differences
| Feature | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Message Consumption | Consumers track messages using an offset tracker | Brokers ensure message delivery to consumers |
| Message Prioritization | No message priority | Supports priority queues |
| Message Deletion | Messages retained until retention period expires | Messages are deleted after consumption |
| Throughput | Millions of messages per second | Thousands of messages per second (scales with more brokers) |
Security and Protocol Support
| Feature | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Uses TLS and JAAS authentication | Provides admin tools for user and broker security |
| Protocol Support | Uses binary protocol over TCP | Supports AMQP, MQTT, STOMP, and other legacy protocols |
| Programming Languages | Java, Python, Node.js | Java, JavaScript, Go, C, Swift, PHP, .NET, and more |
Use Cases
| Use Case | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Event Stream Replay | Ideal for log aggregation and data re-analysis | Not suitable as messages are deleted after consumption |
| Real-time Data Processing | High-throughput event streaming | Supports real-time messaging but lower throughput |
| Complex Message Routing | Less flexible, topic-based | More flexible with exchanges and queues |
| Guaranteed Delivery | Consumer-driven, does not guarantee immediate delivery | Ensures message delivery with push model |
| Backward Compatibility | Best for modern applications | Supports older protocols and legacy applications |
Scalability & Fault Tolerance
| Feature | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Adds partitions to distribute load | Can scale horizontally with multiple brokers |
| Fault Tolerance | Replicates log files across multiple nodes | Supports clustering with message replication |
AWS Kinesis (Kafka alternative)
Collect, Process & Analyse Data Data Stream in Real Time on Large Scale
Component of Kinesis
1. Data Stream:
Capture, Process & Store Data Stream
- Need to provisioned Data capacity ahead of time
- Data Input from many sources eg IOT Device, Logs, Video.
- Billing is per shard
- Data is immutable: once inserted & cant be deleted once injected
- Near real time
~200mS - Store data between
1Day -1year - Can reprocess/ replay data
Limitations
- Need to mange scaling manually by splitting Shard or merging them back
Data Record: Consist of Key Value pair
Partition Key: help to direct data to specificshardand allow ordering of data.Sequence no: Unique per/ partition Key in a Shard. Help location of data inshardData Blobof1MB
Shard: Stream can be split into Shards.
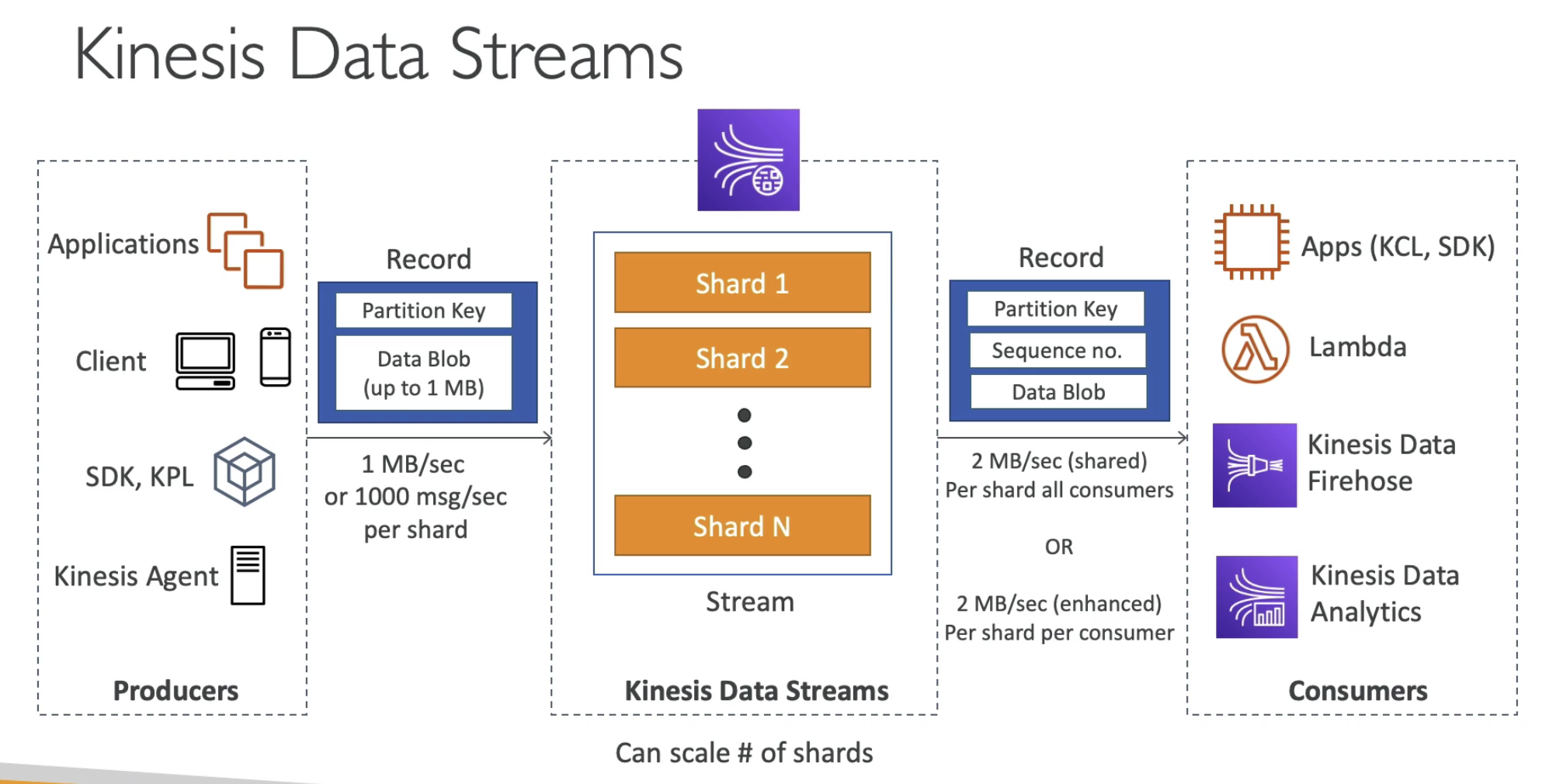
Producer
Client/ Agent Producing Data as record in real time:
- Input:
1MB/Sec/shardor1000 Msg/Sec/shard - API:
PutRecordAPI to put dataPutRecordsAPI to put data as batch to increase throughput & save cost
- Supports
- AWS SDK
- Kinesis producer Library (KPL): C++, JAVA, batch, compression, retries
- Kinesis Agent: built on top of KPL allow monitor logs
- IOT
- Application,App Clients
Hot partition: Chatty device can overload a shard partition
Cold partition: Shard partition with not enough data
ProvisionedThroughputException: When a shard receive data more than provisioned input capacity
- Use Highly Distributed Partition Key to avoid hot partition.
- Retry with Exponential back off
Shard Splitting-> increase capacity by increasing shard- Increase capacity by 1MB/Sec but also increase cost
- Data in old shard will be expired and Old Shard wil be deleted.
- 1 shard can spilt in Only 2 shard at a time
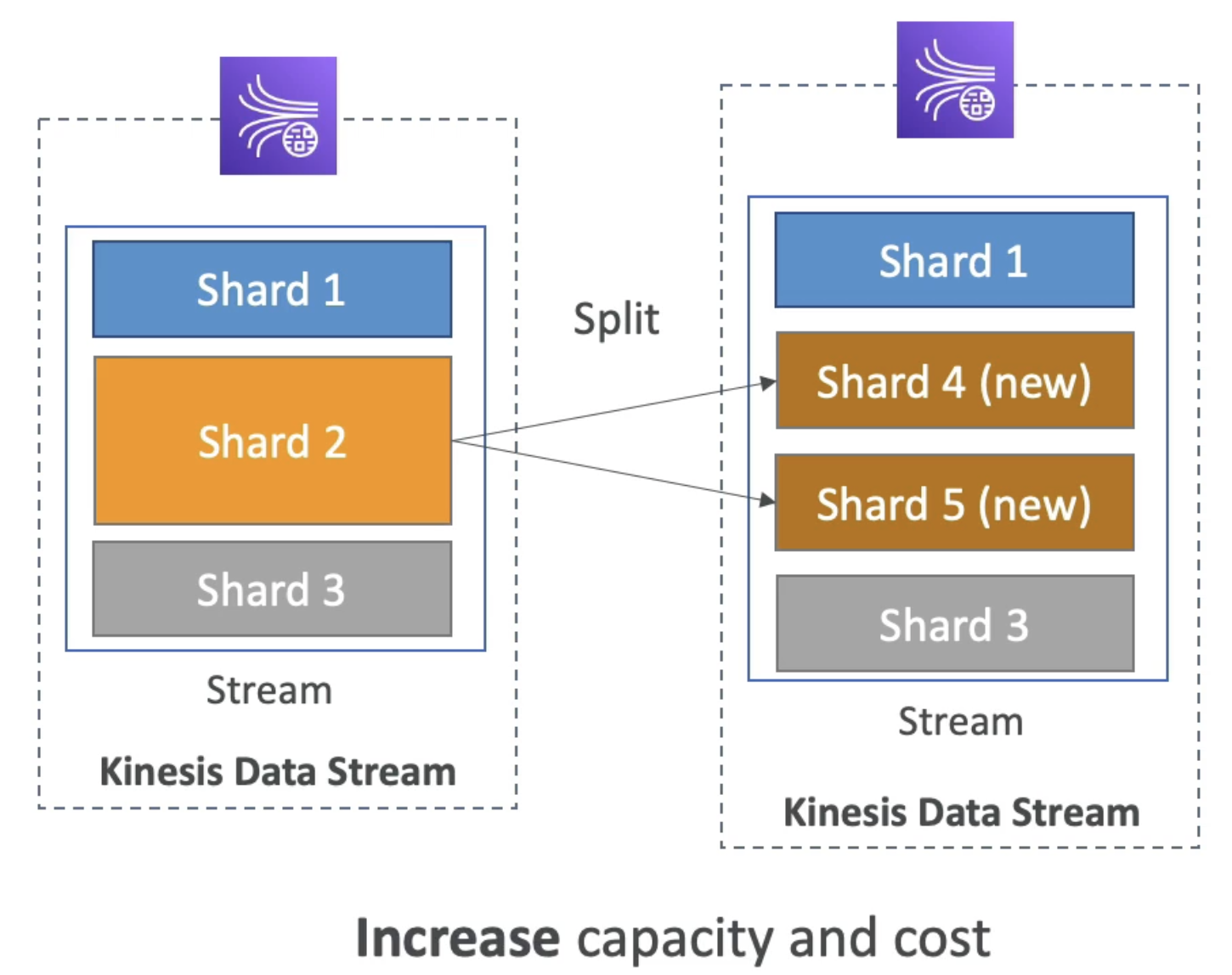
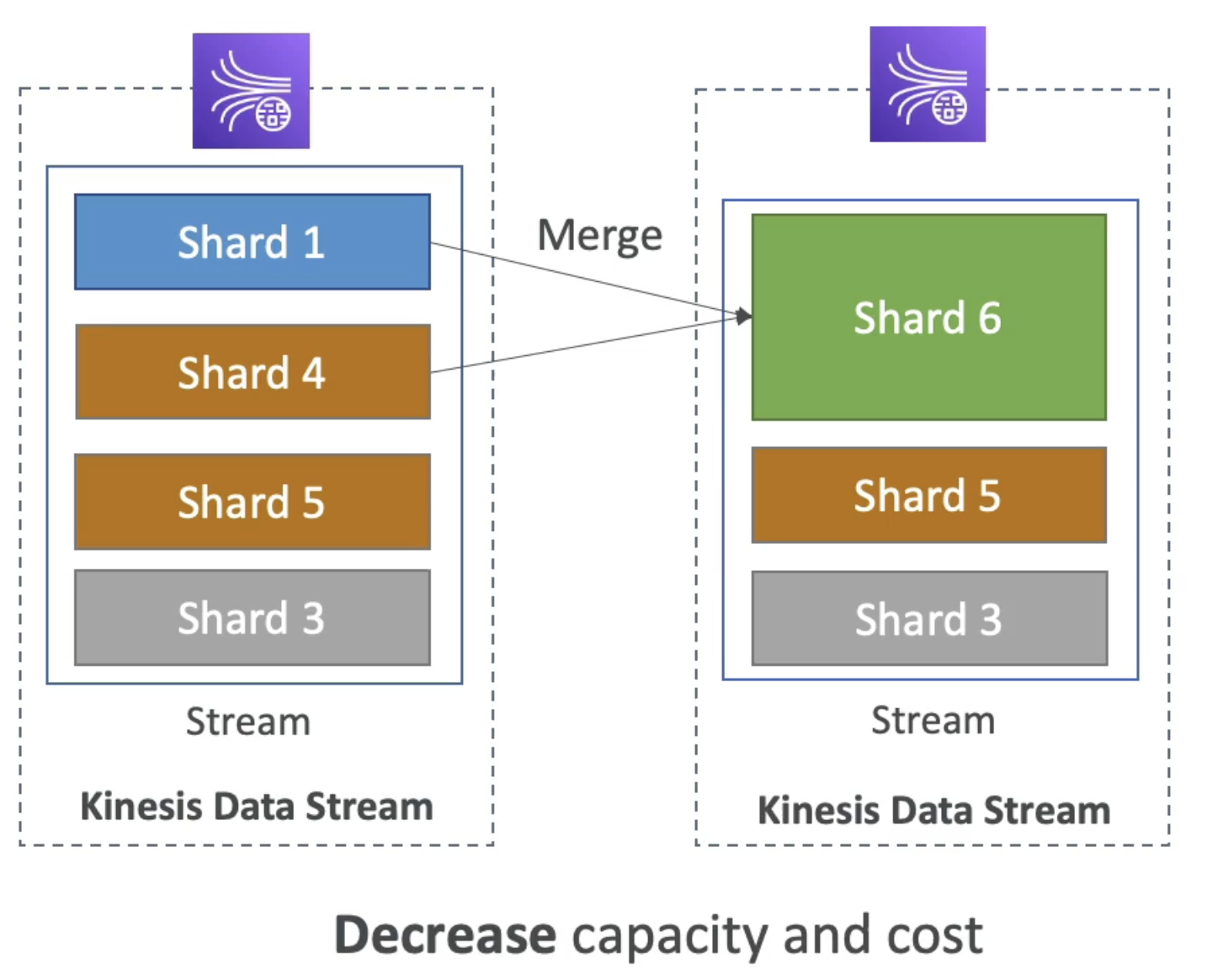
Shard Merging -> decrease capacity by decreasing shard
- Decrease capacity by 1MB/Sec to reduce cost
- Data in old shards will be expired and Old Shards wil be deleted.
- Only 2 shard can merge in 1 at a time
Consumer
Consume Data from data stream
- API:
GetRecordsAPI to get data at 2MB/s/all consumer rateSubscribeToShard: Enhanced FanOut Pattern 2MB/s/consumer rate
- Output:
2 MB/Sec/shardall consumer2 MB/Sec/shardper consumer
- Support:
- Apps
- Lambda
- Support Classic & Enhanced Data stream
- Batching: can set batch Size & Window
- Process 10 Batch/Shard
- Support retries till data expire/succeed
- Kinesis Data Hose
- Kinesis Analytics,
- Kinesis Client Library(KCL):
Consumer Pattern
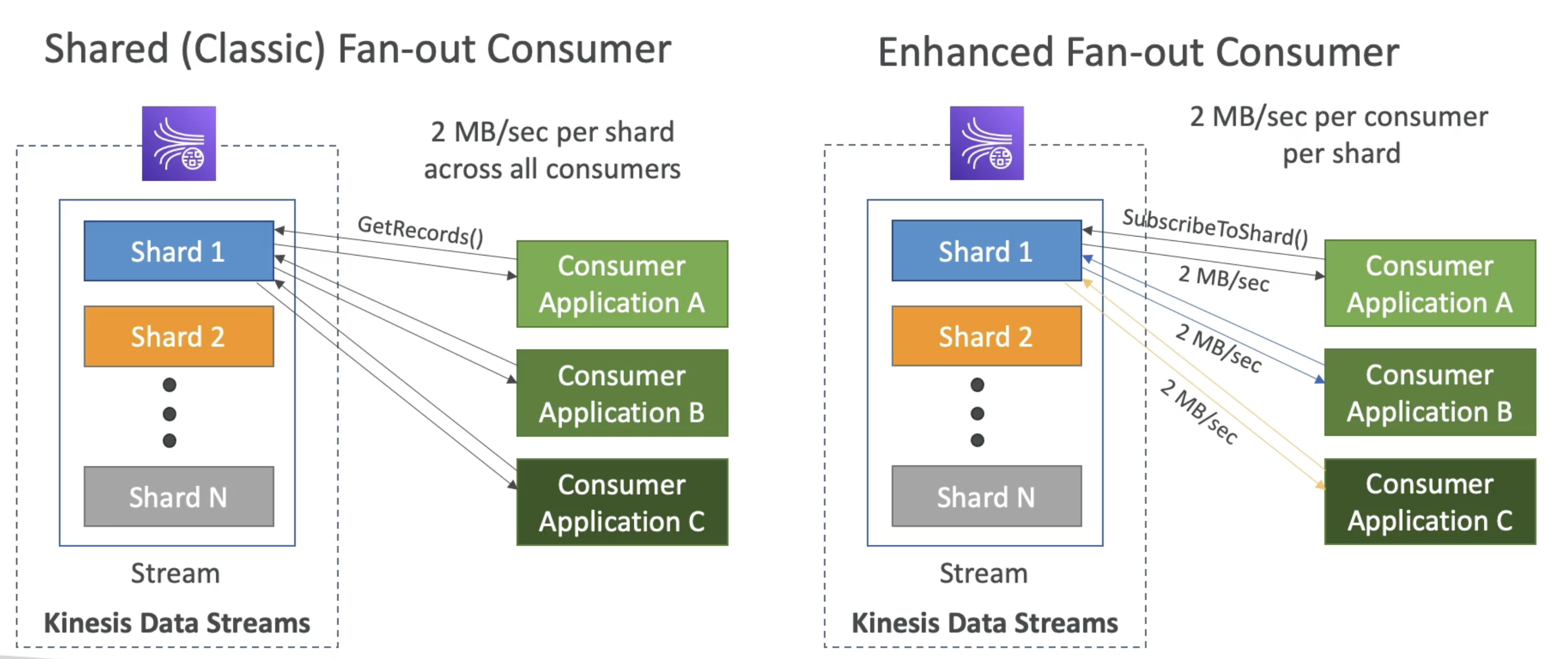
1. Standard(Classic) Fan Out pattern
- Read Throughput: 2MB/s/shard shared across all consumer
- Use
GetRecordsAPI - Pull Model
- Max 5 API Call/Sec = 2MBps*5 = 10MB/Sec (10K Record)
- Latency ~200mS
- Low Cost
2. Enhanced FanOut Pattern
- 2MB/s/shard/consumer for all consumer
- Use
SubscribeToShardAPI to get update from shard - Push Model
- Max 5 consumer/Data stream(default)
- Latency: ~70mS
- High Cost
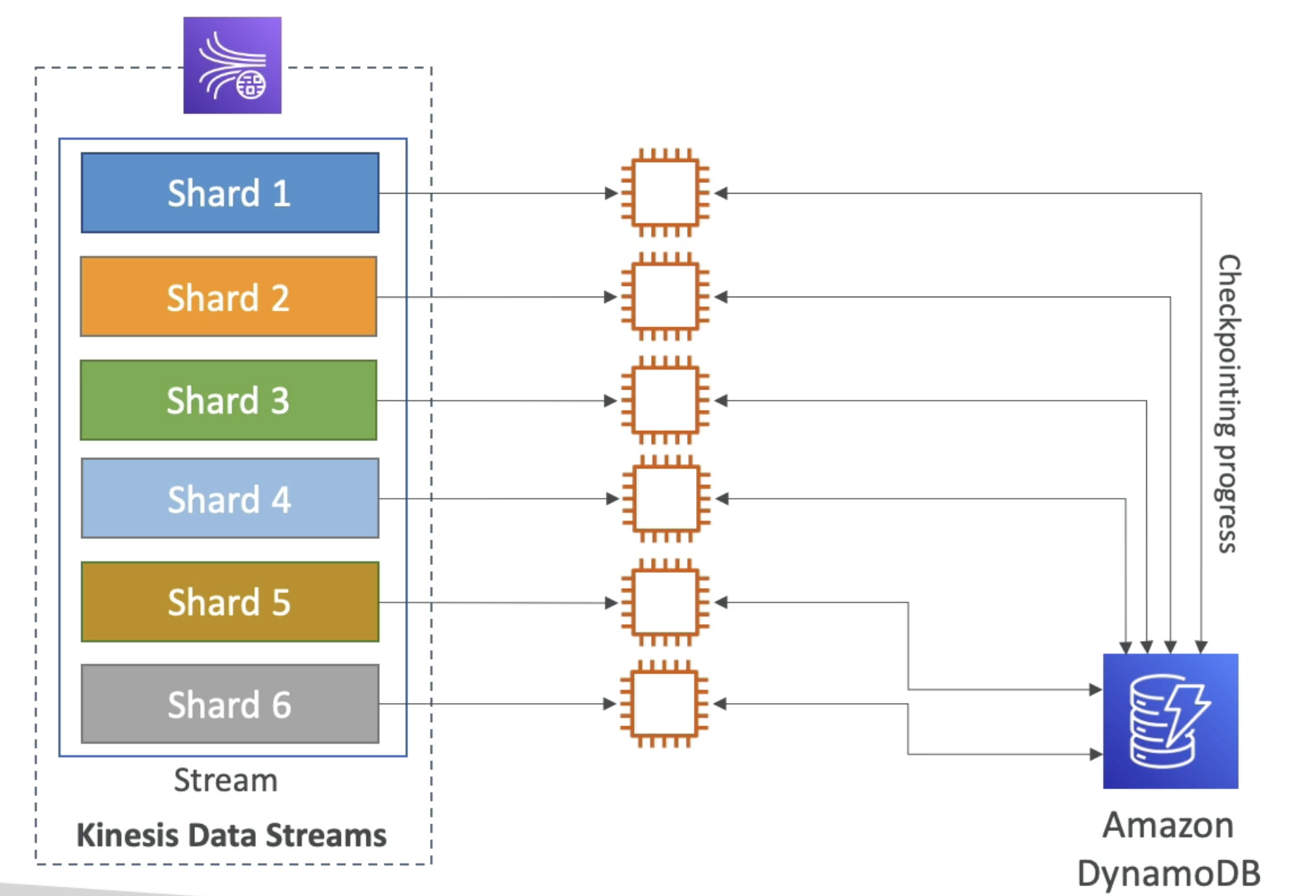
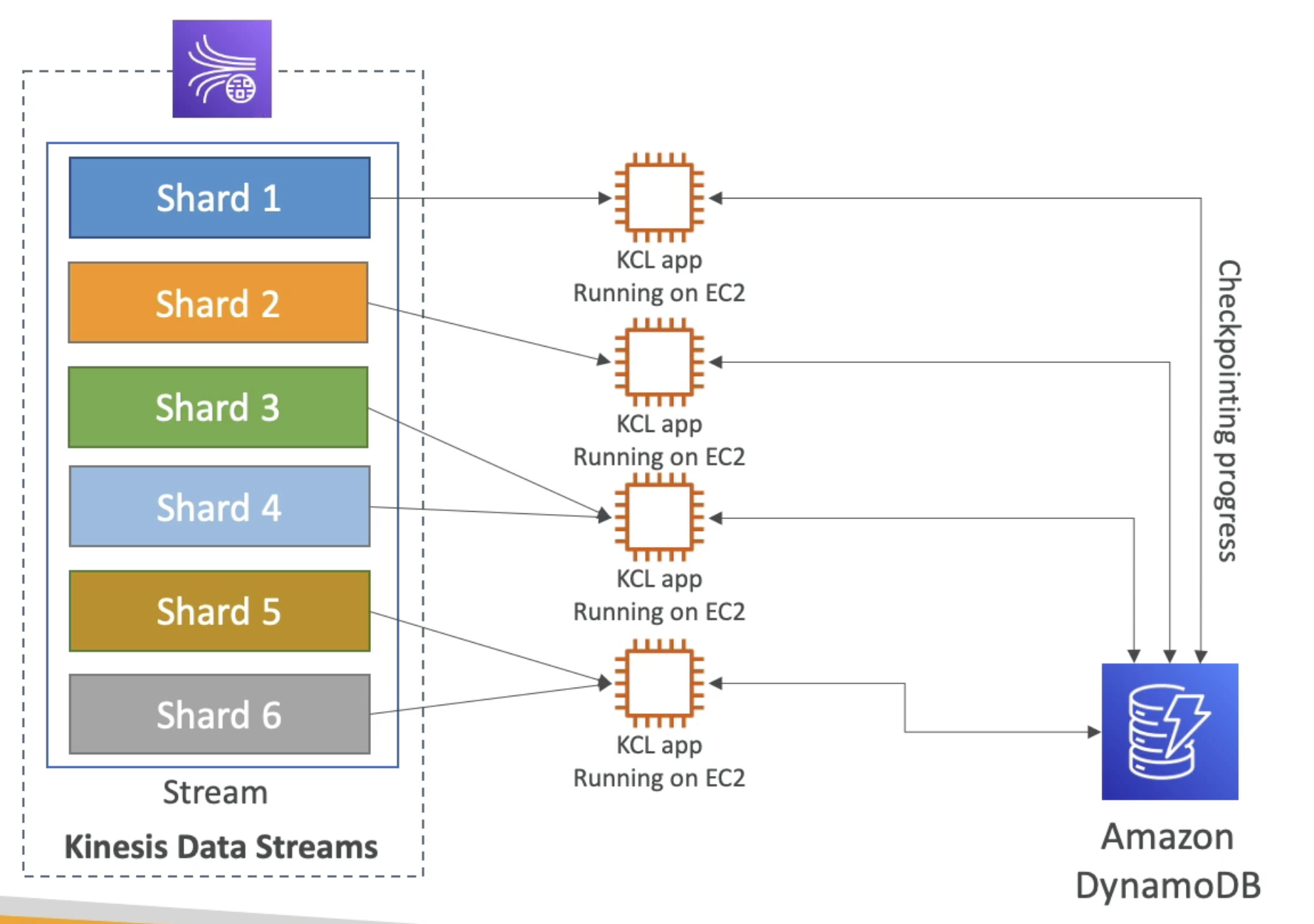
Kinesis Client Library(KCL)
Java Library which help read data from Kinesis Data Stream
- Runs on: EC2, Elastic Bean Stalk, on-premises
- 1-1 Relationship: Each shard can be read by only one KCL instance
- Checkpoints: Progress is check pointed into
DynamoDB. - Share Workload: Use check points to Track the work among other workers and share the work among other Shard
- Versions:
- KCL 1.X Only Shared consumer
- KCL 2.X Shared & Enhanced FanOut Consumer
KCL Auto load balancing
 Security:
Security:
- KMS: Data at rest
- HTTPS: data in transit
- IAM: Access policy
- VPC Endpoint: Access Kinesis within AWS network
- Cloudtrail: Monitor APi calls
2. Data FireHose:
Read Data from Producers, Optional process them using
Lambda& Batch write them into AWS target:S3, Elastic Search, Red Shift
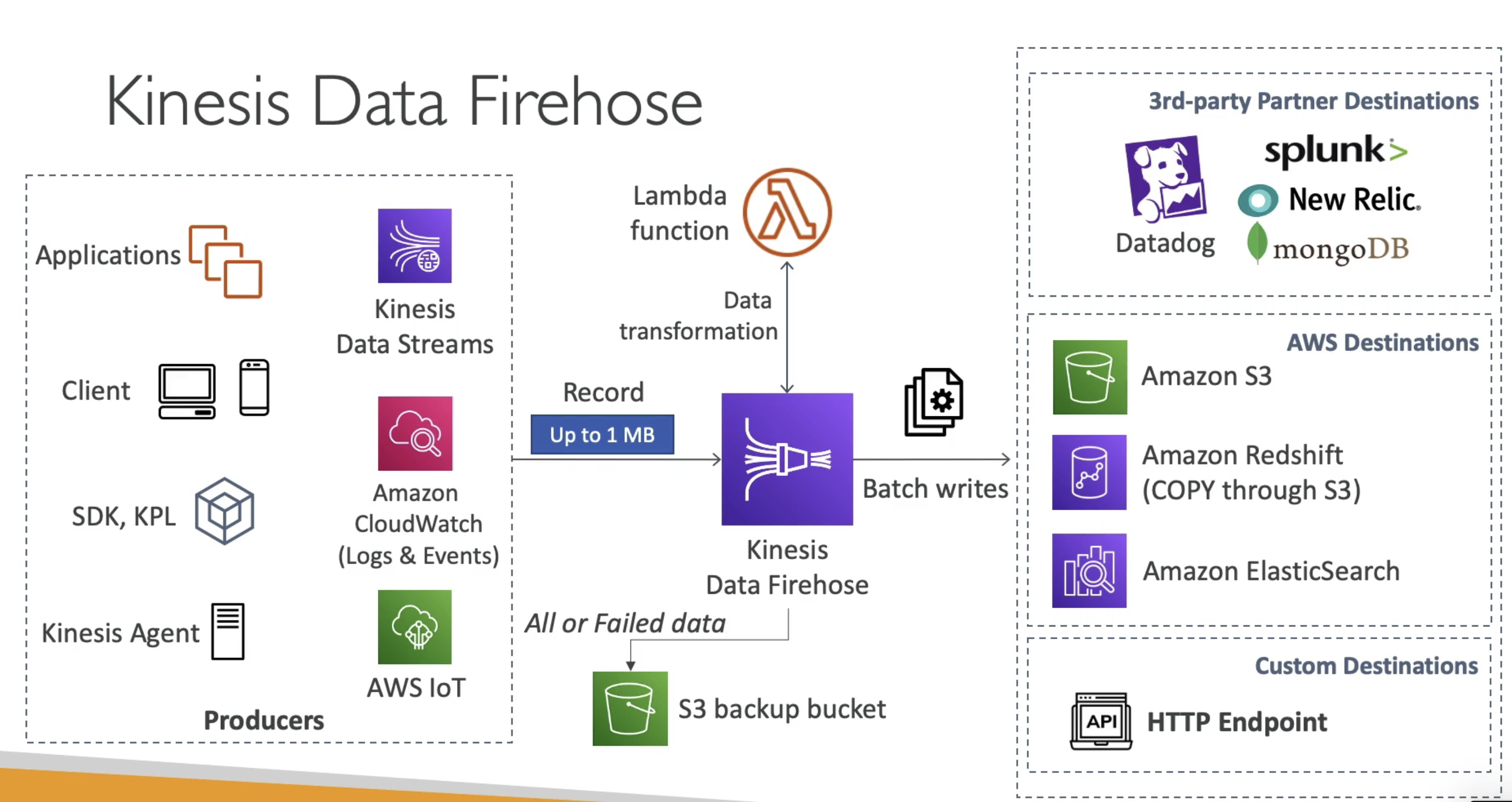
- Fully Manged service with automatic scaling
- Source:
- App, Clients
- Kinesis Data Stream, Kineis Agent
- Cloudwatch Logs, AWS IOT
- Destination:
- AWS target:
S3, Elastic Search, Red Shift - custom HTTP end points
- Third Party Destinations: MongoDB, Splunk, DataDog
- AWS target:
- Support many data format, conversion & transformations, compression
- Optional
Lambdacan be used to transform data - Auto backup failed data to
S3Bucket - Min Batch Limit:
60 Sec or 32 MB: Near Real time
Limitations:
- Does not support replay
| Kinesis Data Stream | Kinesis Firehose |
|---|---|
| Ingest Data at Scale | Ingest Data to S3, Redshift, ES, HTTP/ 3rd Party |
| Need to write own Producer/Consumer | Fully Manged Service |
Real Time (~200mS) | Near Real Time (60 Sec or 32 MB) |
Store Data between 1Day -1year | No Data Store |
| Mange Scaling | Auto Scaling |
| Pay per Capacity | Pay for Data goes through firehose |
| Replay Capacity | Cant replay Data |
3. Data Analytics:
Real time analytics on stream of Kinetics Data Stream or Kinesis FireHose
- Analyze Data using
SQLorApache Flunk - Run SQL Queries on Data STream in Real Time.
- Fully managed, auto scaling
- Pay for data pass
- Source/ Destinations:
- Kinetics Data Stream
- Kinesis FireHose
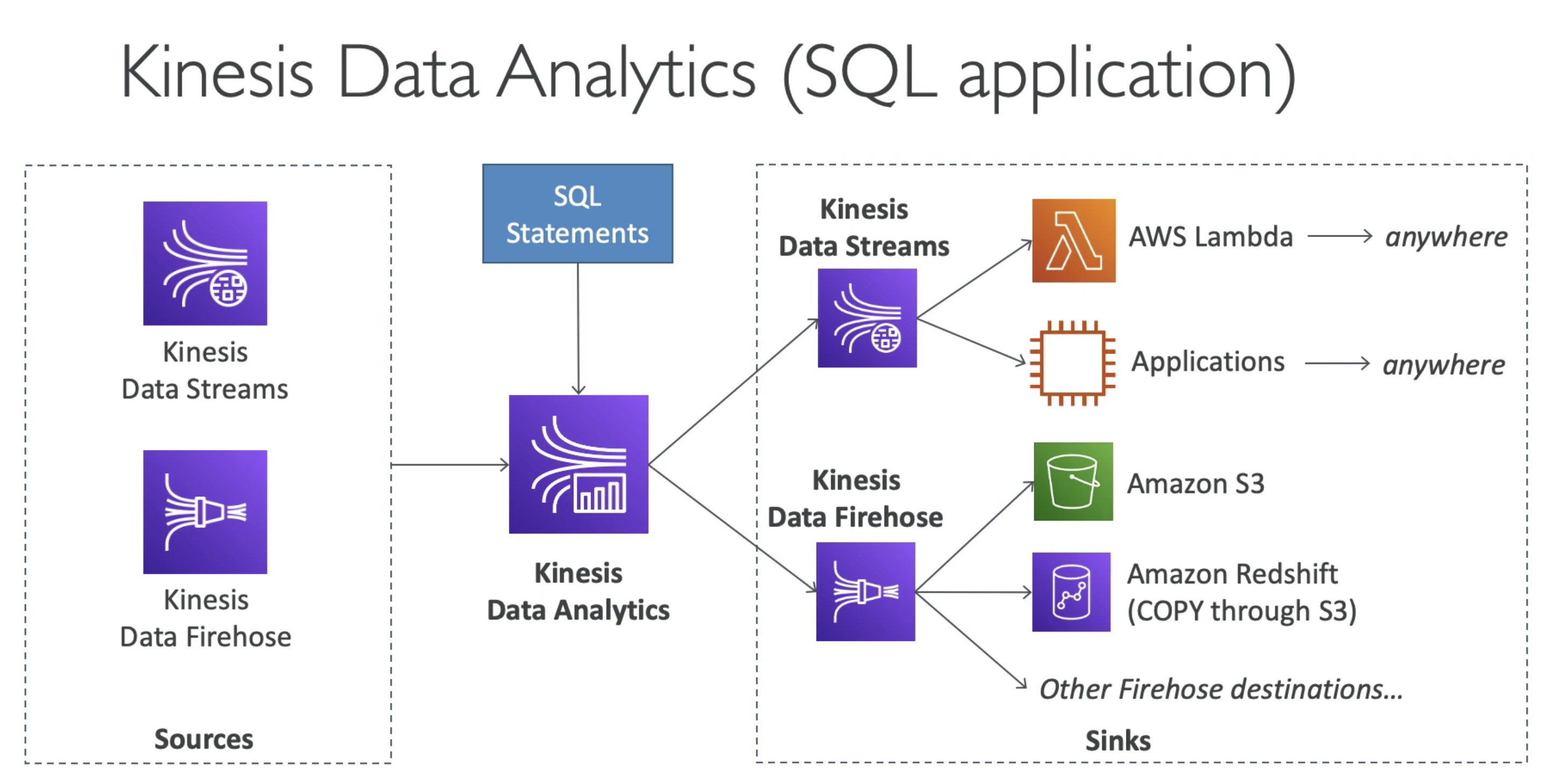
4. Video Stream:
Capture process & store Video Stream
- Usage: ML, Analytics on real time video stream
