Core AWS Storage Service
Cloud storage is a reliable, scalable, and secure place for your data. Store, access, govern, and analyze data to reduce costs, increase agility, and accelerate innovation.
AWS uses two models for storage capacity:
- Consumed storage : Pay only for capacity used eg Simple Storage Service(S3)
- Allocated capacity: pay for allocated space eg Elastic Block Store(EBS)
AWS Storage Gateway
allow on-premises servers to seamlessly use the AWS Cloud at the storage layer.
- Data transferred between the gateway and AWS storage is
Encryptedusing SSL POSIXCompliance: permission, timestamp, ownership stored in S3 as metadata- Use Virtualized Gateway to send data
- Use case: Backup Recovery, DR,
Storage Gateway Activation
- Use Gateway VM CLI
- Make Web request to Gateway VM on Port 80
- Old Way of doing it
- Make sure VM Gateway running on
Port 80 - Make sure VM Gateway has time synchronized with Server with
NTP(Network Time Protocol)
Storage Gateway Types:
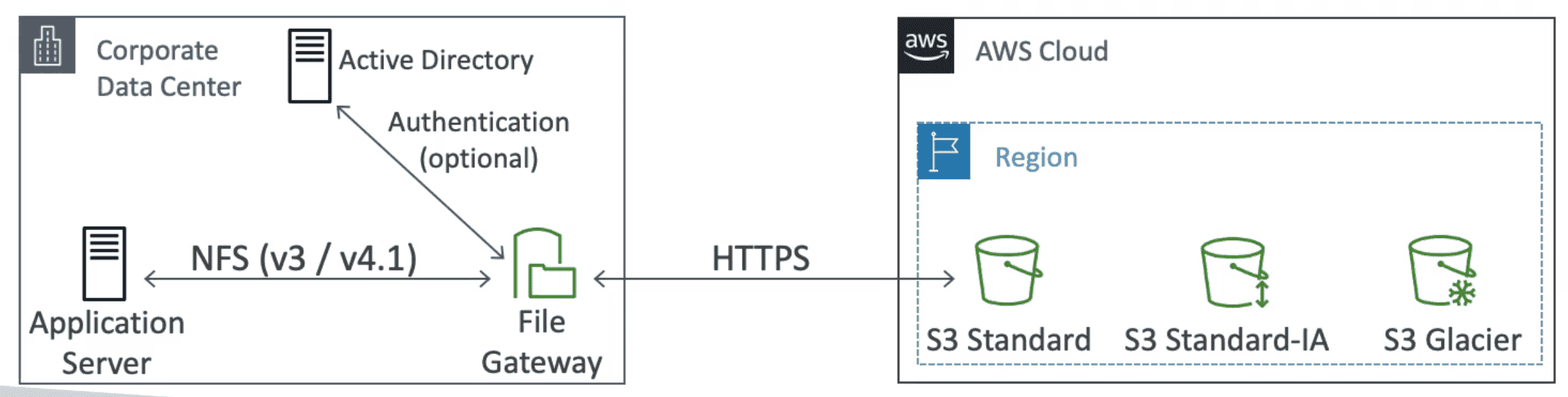
1. File gateway
S3 Connected with On Premises Data Center using
NFS&SMBProtocols
- Backed by S3 Standard, S3 IA, S3OneZone IA
- Cache recent file for low latency
- Can be mounted to multiple servers on premises
- Authentication done using Active Directory(AD)
- Reboot Storage Gateway: reboot VM
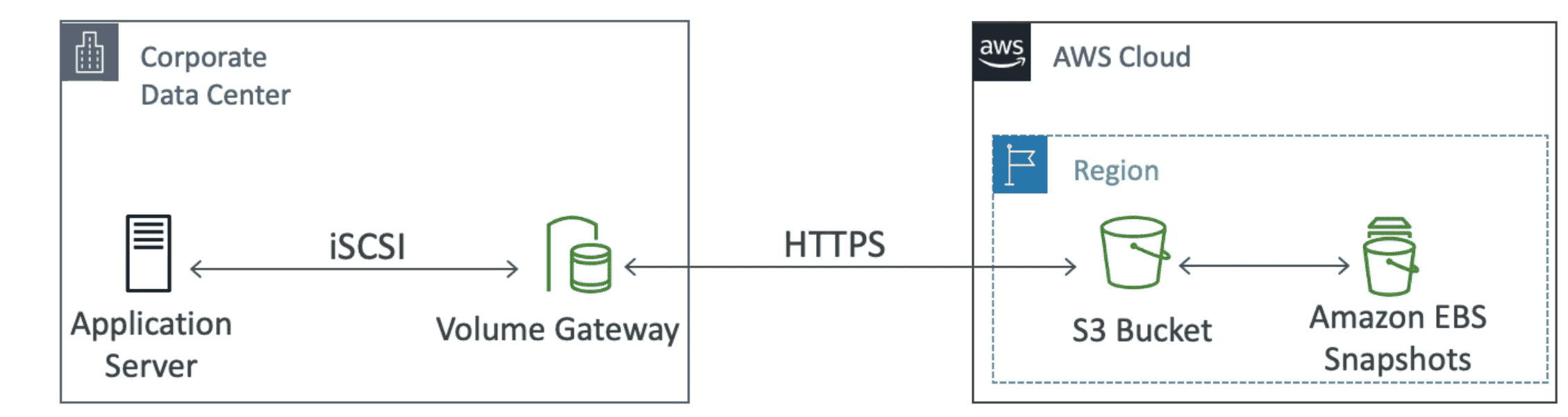
2. Volume Gateway
Block storage using
iSCIProtocol
- backed by S3 with EBS Snapshot
- Types
- 1. Cached Volume: Store recent volume data for low latency
- Make sure
CacheHitPercentagein CW Metric is High - Make sure
CachePercentageis Low. -> assign a new cache with large volume on high cache usage
- Make sure
- 2. Storage Volume: entire dataset is on premises scheduled backed up
- 1. Cached Volume: Store recent volume data for low latency
- Reboot Storage Gateway: Stop Gateway Service-> reboot VM -> restart Gateway Service
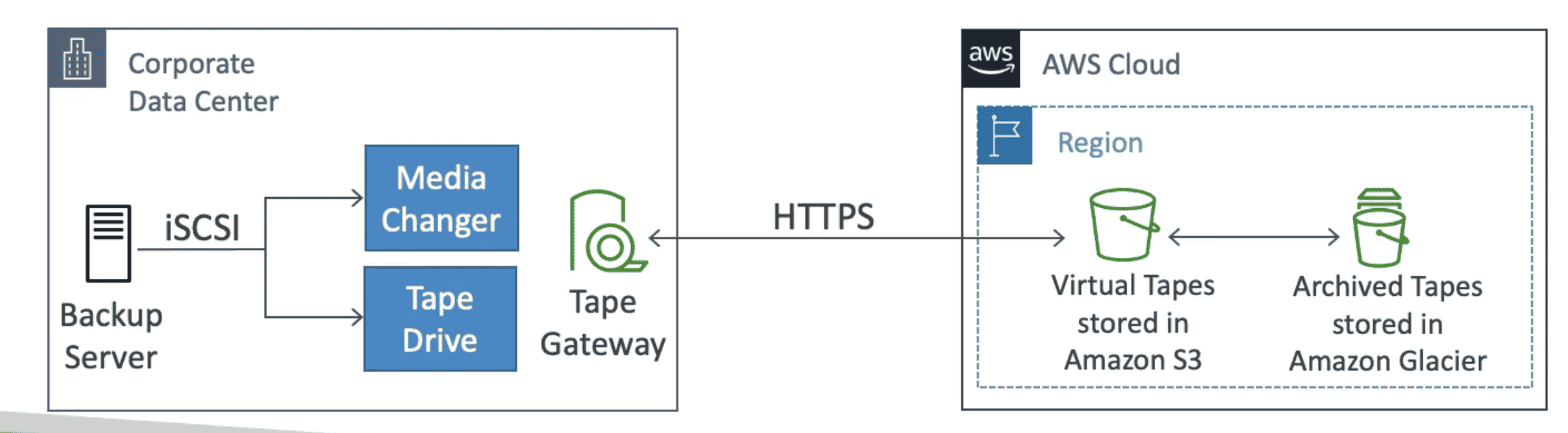
3. Tape Gateways
Physical Tapes Backed up to Cloud using
iSCIProtocol
- VTL: Virtual Tape Library created in S3 & Glacier
- Reboot Storage Gateway: Stop Gateway Service-> reboot VM -> restart Gateway Service
4. Storage Gateway Hardware Appliance
Physical hardware to back up data in server when Virtualization of gateways is not supported.
- provide virtualization hardware to host any of the above gateway

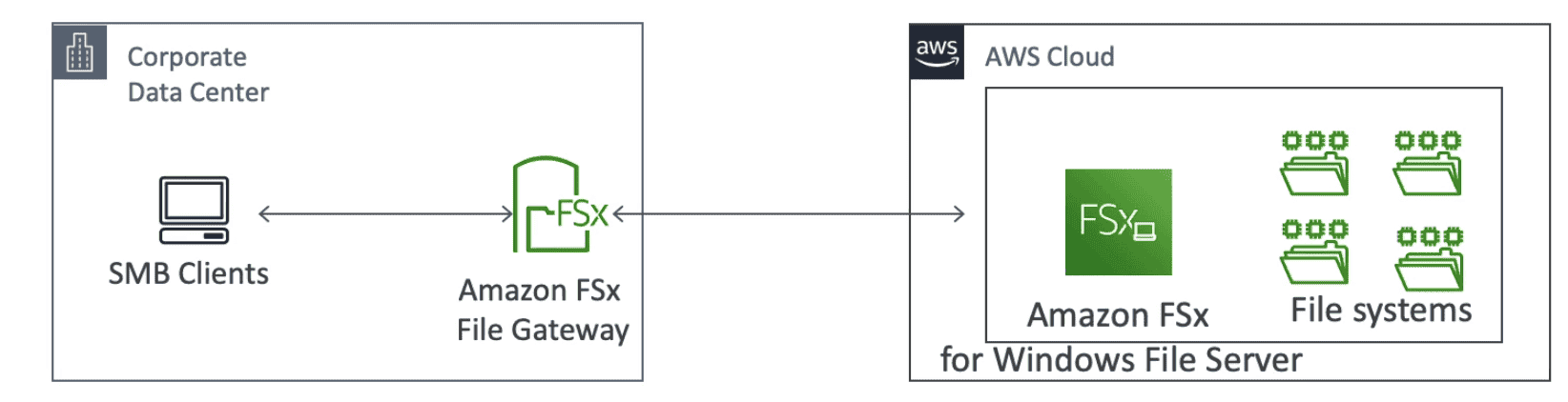
5. FSX Gateway
Link FSx to Windows File Server
- Support
SMB,NTFS, AD - Low latency using Caching of frequent access data -> main advantage of FSX Gateway
Core Storage Services
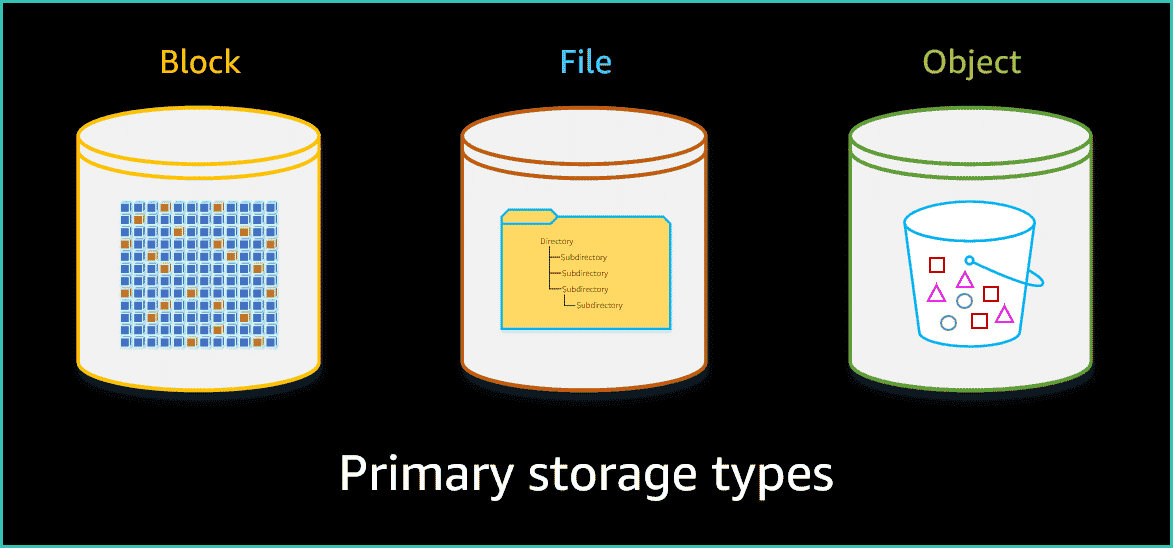

1. Block Storage
Low Latency Raw Storage connected to compute system by direct-attached storage (DAS) or storage area network (SAN)
- Provisioned with each Virtual Server
- Storage is consist of fixed storage unit Blocks.
- Work close to OS
- Storage: SSD, HDD, Non-Volatile Memory Express(NVMe)
- Example: Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
- Use Case: databases or ERP systems.
Types
1.1 EC2 INSTANCE STORAGE
Give Low Latency high performance Temporary Storage for Computation on EC2
- Data is
Nonpersistentand Lost when the associated EC2 instance is terminated. - Temporary Storage : Do not rely on an instance store for valuable, long-term data.
- Very High IOPS: Millions of IOPS
- Dev is responsible for Backup as Data is not replicated in other AVZ
- Use Cases: Buffer, Cache, scratch data, Data that is replicated across a fleet of instances, such as a load-balanced pool of web servers
1.2. ELASTIC BLOCK STORAGE (EBS)
High Latency, Easy-to-use, high performance, Persistent, Network Block storage Volumes.
-
Durable and
persistent databy default. -
Network Drive; Can be attached/detached to a EC2 Instance on the go
-
Latency: EBS are network drive so latency can be high.
-
Locked to a AVZ like EC2:: Must connect with EC2 instance in same AVZ
-
Capacity need to define in advance (GBs+IOPS)
-
Elastic Volume: Volume size can be extended or adapt to high performance on run time
-
Highly Available & Durable:Data is replicated over AVZ. Snapshot can be stored to recover data with 99.999 % durability.
-
Encryption:
not encrypted, by default. Can be enabled to encrypt in rest & transit. -
Monitoring: Cloud watch can give insight about performance of EBS
-
Use Case: Data that must be quickly accessible and requires long-term persistence.
-
Multi Attach not Possible: EBS cant be attached to multiple EC2 instance at a time but can be reattached and shared with other EC2.
-
One EC2 Instance can have multiple EBS Volume
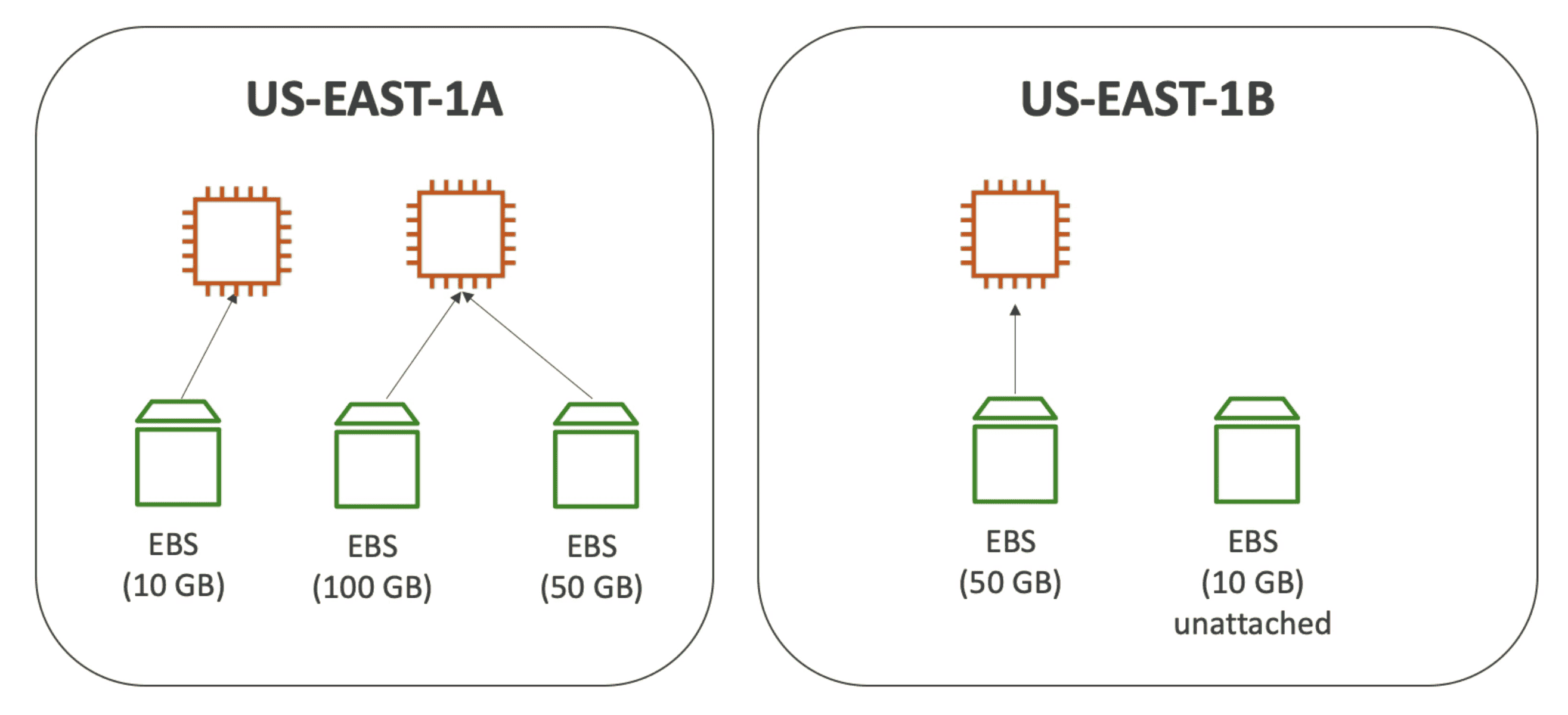
Delete on Termination:
- by default
root EBS Volumegets Deleted when EC2 instance gets terminated - by Default any other EBS Volume Not deleted when EC2 instance gets terminated
Pricing
You pay only for what you use.
- Pricing for EBS volumes is based on the volume type, provisioned volume size, and the provisioned IOPS and throughput performance.
- EBS volume pricing varies based on the Availability Zone where it resides.
- Price of EBS Snapshots is based on the actual amount of storage space that you use.
Volume Types
EBS Billed based on EBS Volume provisioned
1. SSD
Can Only be used for Boot Volume
1.1. General Purpose SSD volumes (gp2/gp3):
Balanced price performance Volume
- Size:
1GB-16TB - IOPS:
3k-16k IOPS - Throughput:
125 MiB/s - Usage: Boot Volume, VD, Environment
- GP2 IOPS & Throughput are Linked (+3 IOPS/GB)
- GP3 IOPS & Throughput are Independent (IOPS up to 10k MiB/s)
1.2. Provisioned IOPS SSD(io1/io2)
High Performance Volume for low latency & high throughput workload
- Size:
4GB-16TB - IOPS:
16k-64k IOPS(Much Higher than gp2/3) - Usage: High Performance Database
- IOPS & Throughput are Independent
- io2 have more IOPS & durability than io1.
- io2 Block Storage: Sub mS latency
256k IOPS
EBS Multi Attach
EBS volume can attach to multiple EC2 instance with full R/W in same AVZ
- Only Support by
io1/io2family only - Application must be able to manage concurrent write
- Must use file system which is cluster aware
2. HDD
- Size 125 MiB-16TB
- Cant be Boot Volume
2.1. Throughput Optimized HDD (st1)
for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads
- IOPS & Throughput: max
500iops @500 MiB/s - Usage: Big Data, Data Warehouse, Logs
2.2. Cold HDD (sc1):
lowest cost for less frequently accessed data.
- IOPS & Throughput: max
250iops @250 MiB/s - Lowest price Storage
- Usage: Archive Data
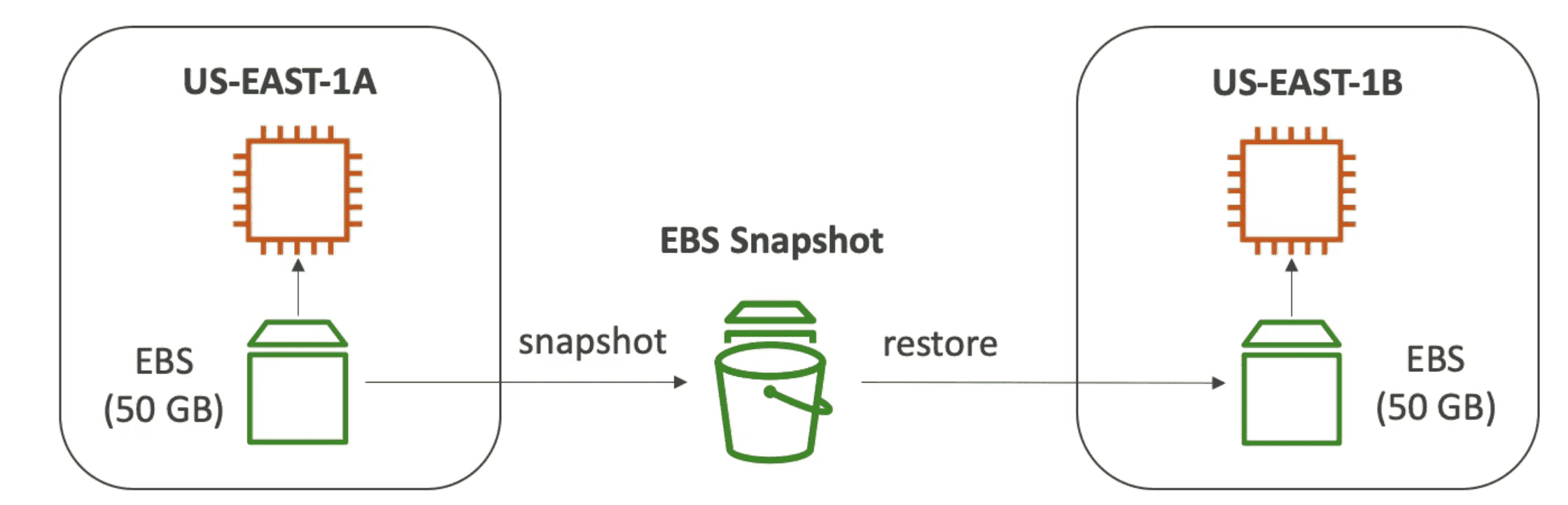
Backup using EBS snapshot:
EBS Snapshot:
incremental backup. First backup all the data & subsequent backups backup the blocks of data that have changed since last time.
EBS-> Create new Snapshot-> Create new Volume from Snapshot to new AVZ
- Snapshot can be used to copy & create EBS Volume to other AVZ or Region
Automatic Snapshots can be taken and stored across AVZ or regions.
2. ELASTIC FILE STORAGE (EFS)
Manged NFS for storing data as files typically in a directory tree hierarchy that can be mount to many EC2 in multi AVZ.
- Work only with LINUX based AMI: Not compatible with Windows
POSIXfile System: Work with Linux File System- Multi AVZ: EBS Locked to single AVZ , EFS can work across Multi AVZ
- 3X costly than EBS
not encrypted, by default- Protocol: Server Message Block (
SMB) and Network File System (NFS) - Built on top of EBS: Possibility to build custom File System Using EBS & EC2
- Operating system manages the storage protocol and the operation of the file system.
- File System could be Windows/Linux or Network Attached Storage(NAS)

SCALE:
- Support 1000s of concurrent NFS Clients
- Can Scale up to PetaByte scale
- 10GB/s Throughput
EFS Configuration Options
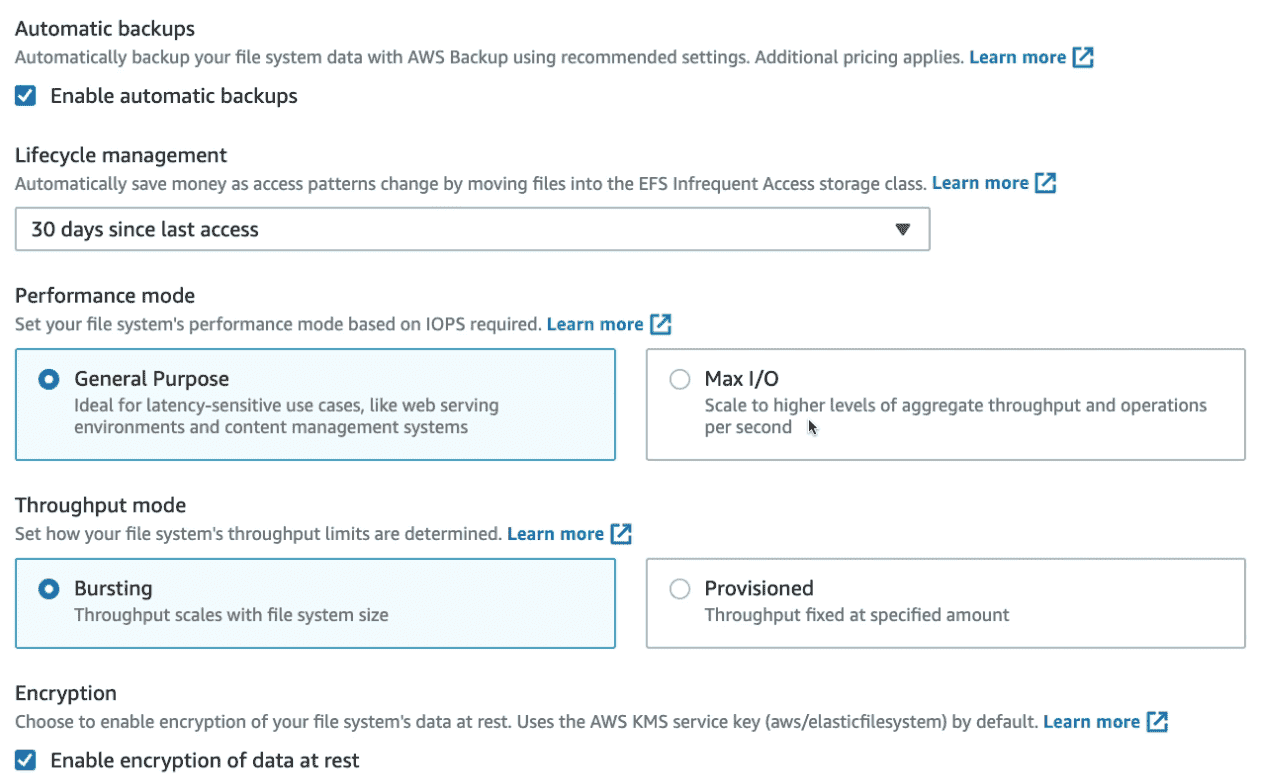
Performance Modes
- General purpose (Default): low latency eg CMS, Wordpress
- Max I/O: High Latency for parallel workload but higher Throughput eg. data processing, big Data, media Processing
Throughput Modes
- Burst Mode(Default): 1TB = 50MBps + Burst of 100MiB/s
- Provisioned Mode: Set Higher throughput for small file system
Storage Tier(Life Cycle Management)
- Standard: fast access
- Infrequent Access(EFS-IA): cost to retrieve file
Security
Security Group
EFS are placed behind Security Group.
IAM Policy
Control who can mount EFS Stsytem
EFS Access Points
Allow to access control such that only the permitted EC2 instances can read from the EFS file system.
Advantages
- Managed file system
- Can be scale & replicate Data
- Concurrent Access of Data
- Shared File System
- Region Level Availability
- Can be connected using AWS Direct Connect
- Use Case: large content repositories, development environments, media stores, or user home directories.
Types:
2.1. Amazon Cloud native file storage
- multi-Availability Zone file storage service
- Linux based File System
- Protocol: Network File System (NFS) protocol.
2.2 Amazon FSx file storage(File System X)
Allow to launch third party high performance File System on AWS
File System Types:
1. Lustre file system(Linux Cluster):
designed for high performance computing (
HPC) and machine learning (ML) workloads.
- Handle very high data volume at high IO
- built using the Lustre file system
- Protocol: Lustre client's Portable Operating System Interface (
POSIX)-compliant access protocol - Integration with S3 to read file & write back
- Scalable & Distributed: Scale up to 100Gbps,
- Seamless integration with
S3as backend - Support On Premise communication
FSX System Deployment Option
1. Scratch File System:
Temporary store and not replicated
- High Burst Throughput (10X Persistance File System)
- Use for short term processing of data
2. Persistance File System
Long term storage & processing
- Data replicated within same AVZ
- Use for long term processing, sensitive data.
2. Windows File Server:
Fully Manged FS designed for Microsoft applications and Windows workloads.
- built using Windows File Server.
- Protocol: Server Message Block (
SMB) &NTFS - Support Active Directory(AD)
- SIngle AZ replication:
- Single AZ1 : SSD
- Single AZ2 : SSD+HDD
- Can be configured to
Multi AVZfor high availability- Automatic
synchronousreplication across AVZ with automatic failover
- Automatic
- Scale up to 10Gbps,100s of PB
- Support File Backup daily to
S3 - Scalable & Distributed FS
- Support On Premise communication
3. NetApp ONTAP File System:
- designed to provide both NetApp block and file storage
- built using the NetApp ONTAP ´OS
- Protocol: iSCSI for block storage, NFS and SMB for file storage.
4. Open Zetta byte File System (OpenZFS)
- designed for OpenZFS storage
- built on the OpenZFS file system
- Protocol: OpenZFS storage
3. OBJECT STORAGE
Place to store file as Objects(Key, METADATA, DATA)
- built on top of EBS
- Storing data within a binary object
- Does not differentiate between types of data. The type of data or the file type becomes part of the data's metadata.
- Non-hierarchical structure. All data stored as Bucket(upto
5TB) - Durable: 99.999999999 percent (11 9s) of durability.
- Use Case: importing existing data stores for analytics, backup, or archive. Store snapshots and backups of data from EBS
Amazon Simple Storage Service(S3)
Store file in object as Buckets in various S3 Storage class
- Store Data as Object(
5TB/Bucket) - Regional Service: must select region for bucket while creating
- Store/ Retrieve Unlimited Data Common Usage:
- Software Delivery
- Site & Application Hosting
- Media Hosting
- Backup Recovery
- Disaster Recovery
- Big Data
- Archives
Amazon S3 delivers strong read-after-write consistency
A process replaces an existing object and immediately tries to read it. Amazon S3 always returns the latest version of the object
- No extra cost
S3 Bucket Name
- Globally Unique Name across AWS
- Can only contain lower case, numbers, dots (.), and hyphens (-)
- should not contain "." & IP
- name must start with alphanumeric (letter or number)
S3 Bucket Limitations
- Max Object size
5TB - Cant upload More than
5GBat a time uaw multipart upload - Buckets can't be nested.
- Default limit
100 Bucket per accountbut can be increase to 1000. - Bucket names are globally unique and once created, you cannot change a bucket name.
- Bucket name will be available only after after 24 hours of deleting a bucket & if not taken by another account.
- Owned by the account that creates them and cannot be transferred to other accounts.
- Buckets are permanent storage entities and only removable when they are empty.
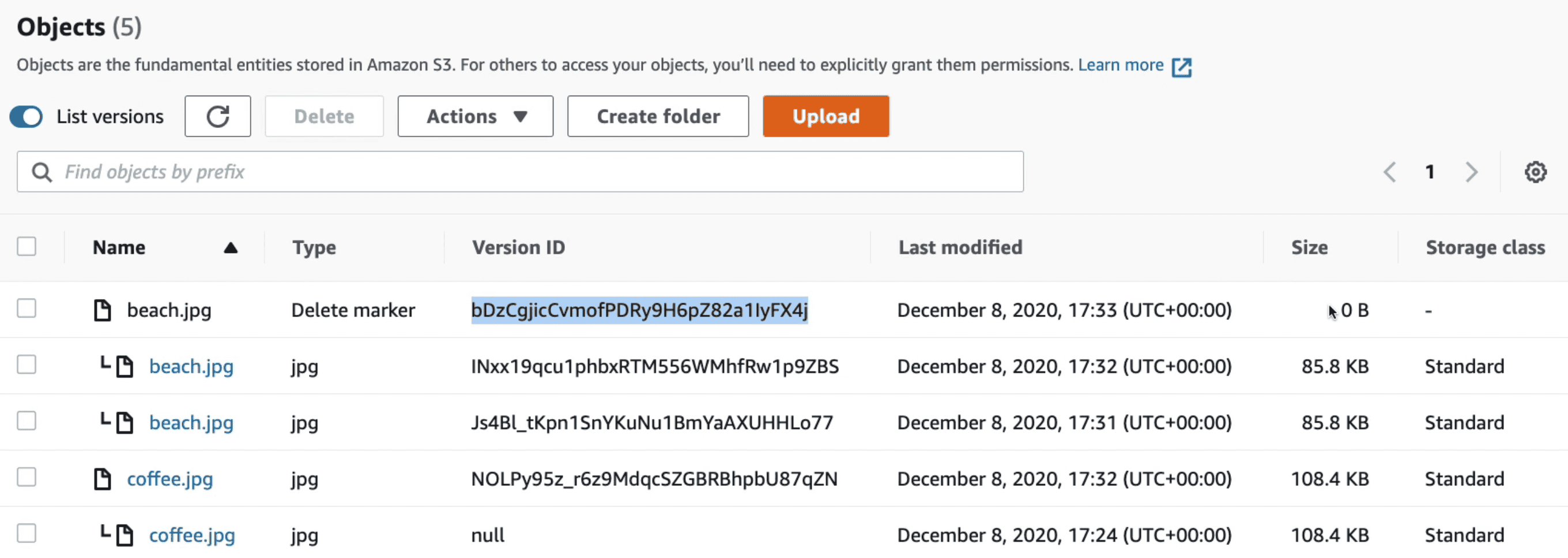
S3 Versioning
Allow Rollback to old version & Undo Deletion of files
- Files not versioned before versioning started will have version
null - If Disabled Versioning it do not delete old version instead stop adding Versions to new files
- Deleting a versioned file will not delete file but add a marker
Delete Marker - Deleting a file with delete marker called
permanently delete
S3 Bucket Object Anatomy
-
Object key:
uniques and consist of full path to the object
bucket name + prefix + delimiter + file name -
MetaData:
Key value pair associate with Object. Can't be changed once added. It can be modified only by making a copy & assigning new metadata.
-
Version ID:
auto generates a unique version ID to preserve, retrieve, and restore object.
-
Tag :
key and an optional value label that you assign to an AWS resource.
- upto 10 Key/Value pair
-
Value :
Actual file which is stored up to 5TB.
- File must be upload in multi part of 5GB
-
prefix:
We can give prefix to give a hierarchy structure in S3
photos/2006/January/sample.jpg
photos/2006/February/sample2.jpg
photos/2006/February/sample3.jpg
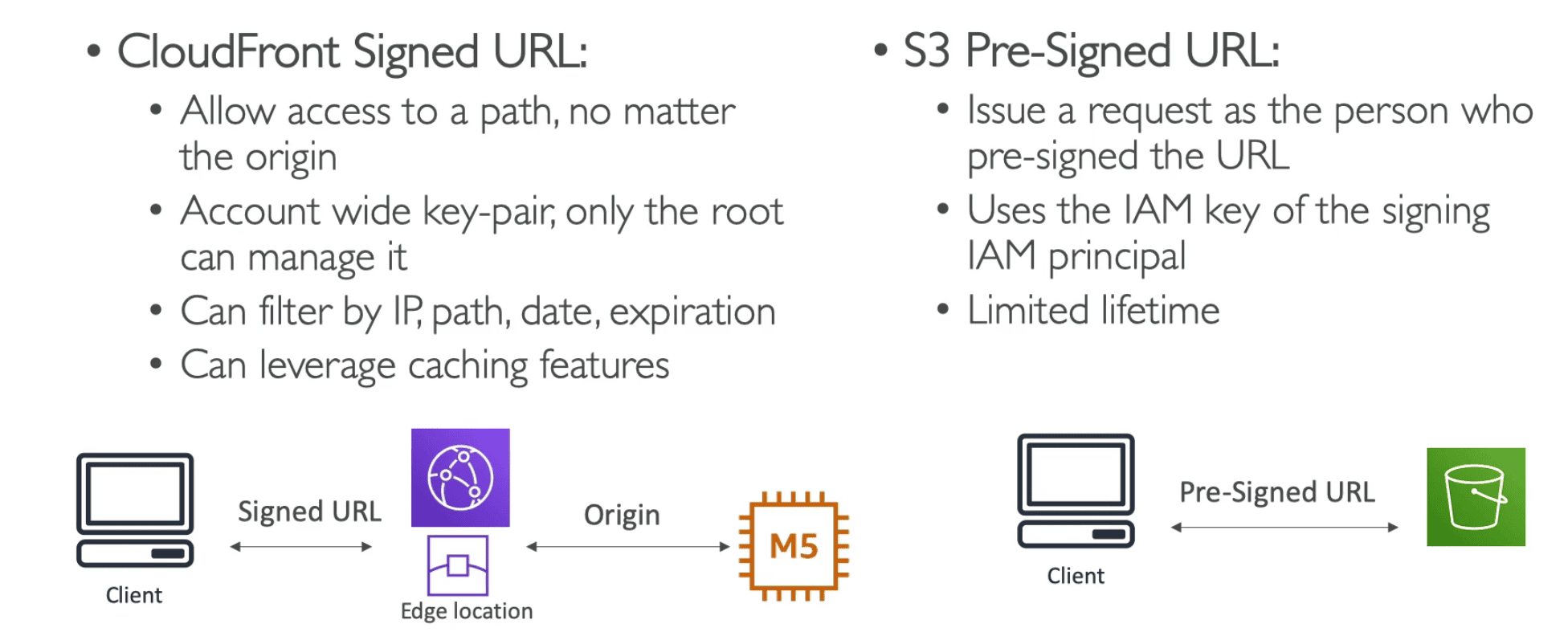
**Presign url **
Buckets are private by default and can be open by presign url
- Can be generated using SDK & CLI
- Default TTL =
3600 Sec(1 Hour) - TTL can be set by
--expire in TIME_IN_SEC - Permission of user creating presign url gets inherited gor GET/PUT Object
CLI:
aws s3 presign s3://bucketname//objectname --expire-in 300 --region eu-west-1
S3 Security
Block Public Access
Prevent any data leak on internet
- Can be set on account level to all Bucket

MFA Delete
Enable MFA on delete of objects
- Must Enable Versioning on Bucket to enable MFA
- Only root user of Bucket can enable/disable MFA
- Can only be enabled using CLI
- Need MFA to
- Suspend Versioning
- Permanently delete object
Policies
A Principal can access S3 Bucket if IAM Policy Allow it OR Bucket Policy Allow it
AND there is no explicit Deny
1. User Based:
IAM Policy to assign access to IAM users to access S3 Bucket
- IAM Policy : Allow/Deny User Access to S3 Bucket
- IAM Role : Allow/Deny EC2 Access to S3 Bucket
2. Resource Based Security
2.1 S3 Bucket Policy
JSON Based rule on bucket consist of Version & Statement
- User Level as well as Cross Account-level access permissions
- Use Case:
- Force Encryption: must send header with encryption header
- Make bucket Public on internet
- Add Cross Account Access to allow other accounts to access Bucket
Statement:
Define;Action/scan be performed byPrincipalonResourcesas anEffect
{ "Id": "Policy1642847767949",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{ "Sid": "Stmt1642847761635", <- Statement ID
"Action": [ <---Set of API to Allow/Deny
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow", <---Allow/Deny
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::hassium-s3-storage-21jan2022/*", <---Bucket & Object
"Principal": "*" <---Who
}
]
}
Force SSL
Bucket Policy can be used to force HTTPS for upload using aws:secureTransport:true condition

Force SSE-KMS

2. 2. Object Control List(ACL)
Fine Level control to block access to bucket objects
- Prevent data leak
2.3. Bucket Access Control List(ACL)
less common
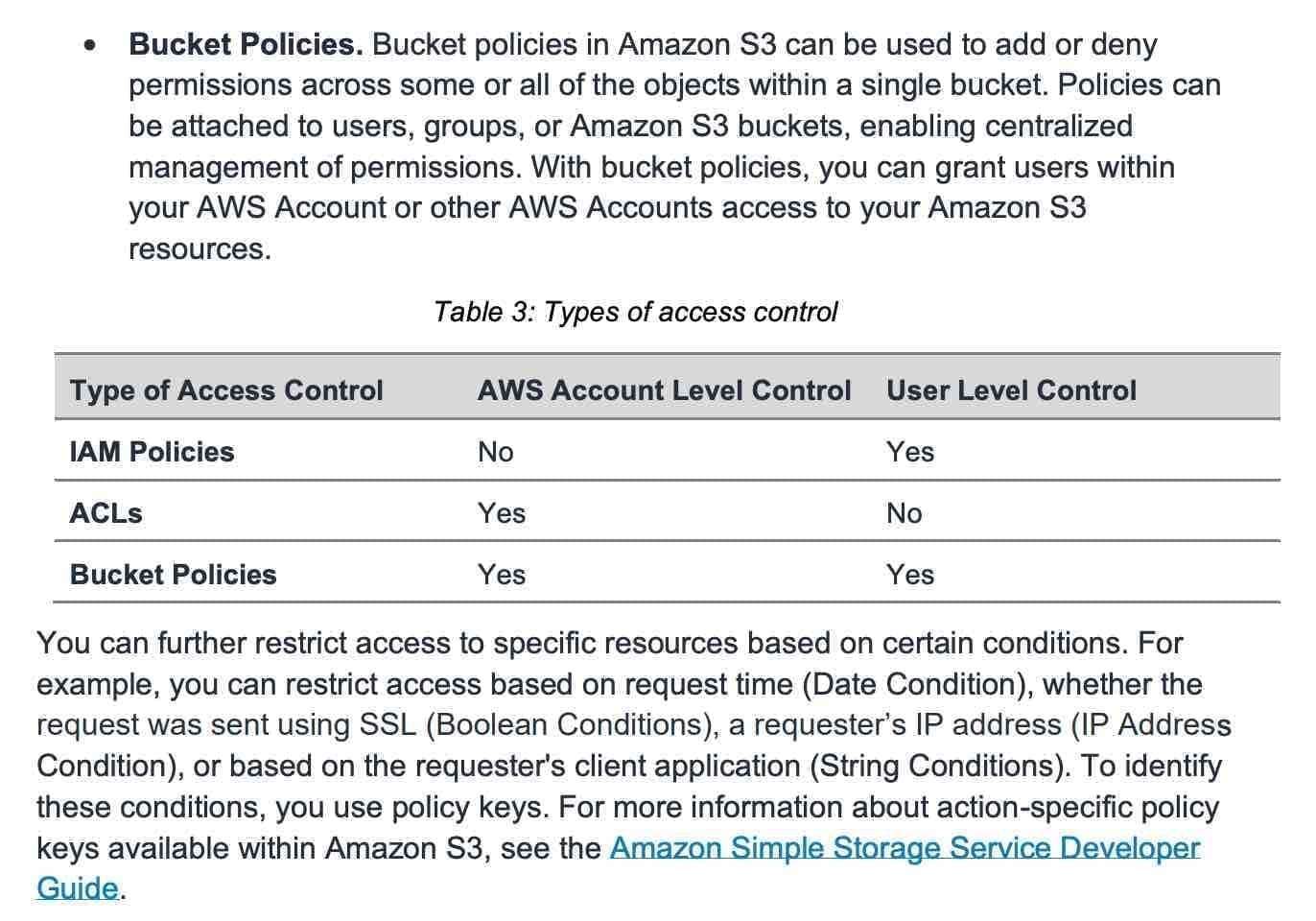
CORS(Cross Origin Resource Access)
We must allow cross origin header policy in S3 bucket to allow resources access by other S3 site
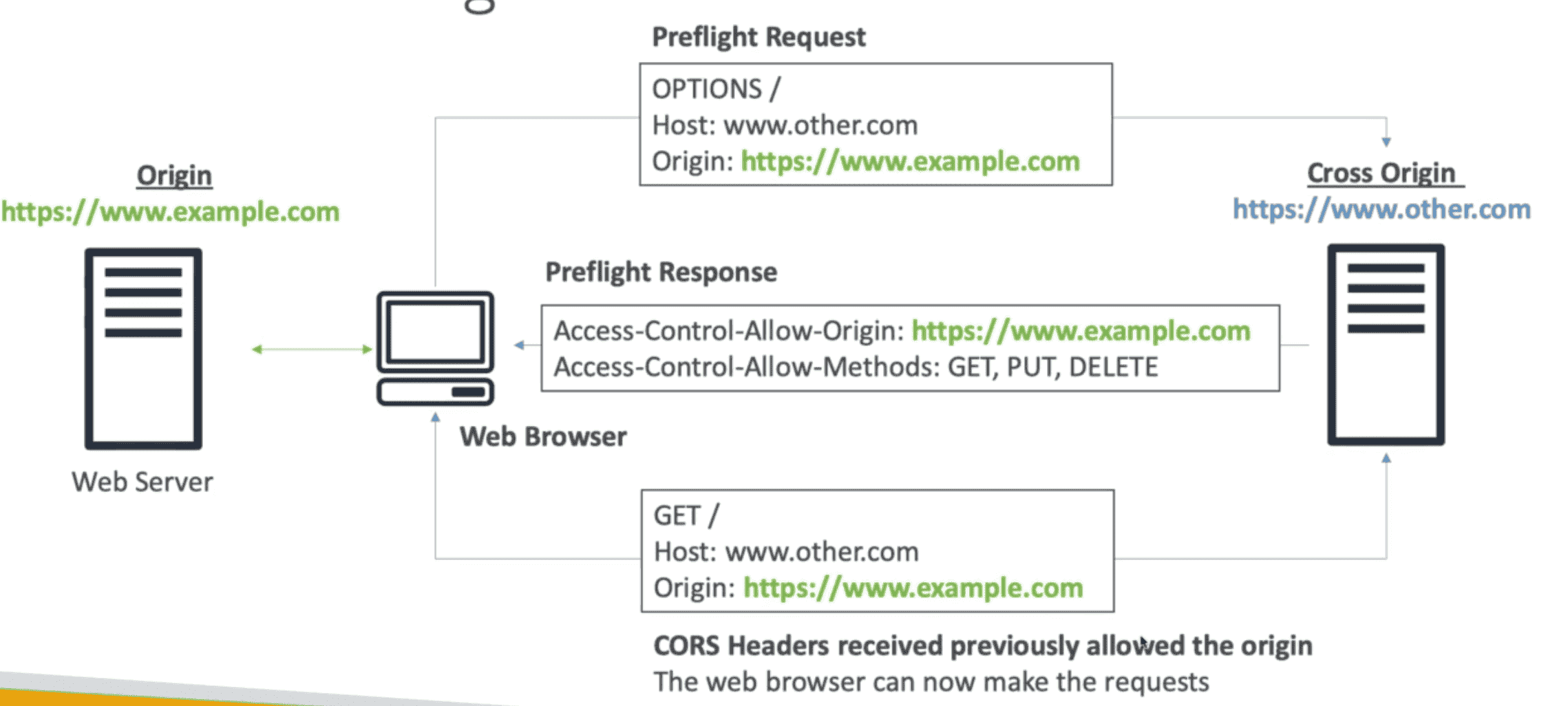
Need to add JSON in AWS Console of Bucket to allow request from second bucket
Amazon S3 Static Website Hosting:
Use bucket to host static website/ blogs
- Bucket must be public
- Disable block public access
- Add bucket policy to allow readObject form everyone
S3 Encryption Model
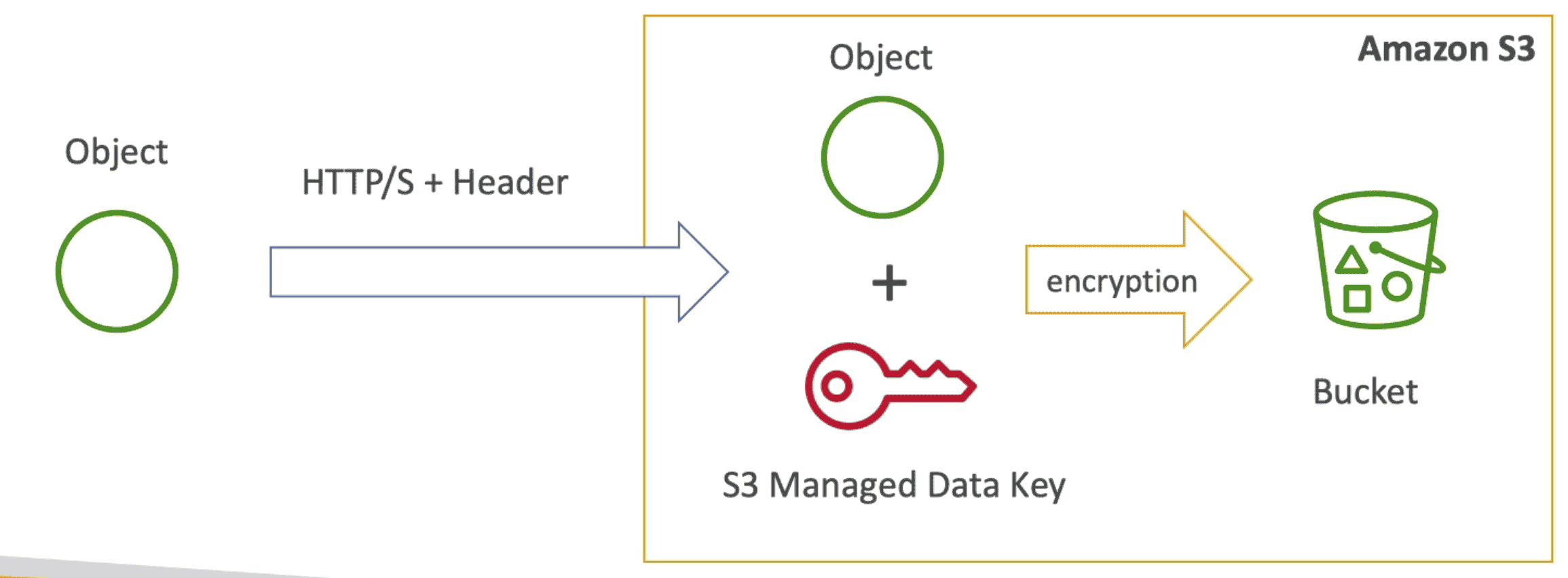
1. Server Side Encryption(SSE-S3)
AES 256 encryption with data key own & managed by AWS
- Set
"x-amz-server-side-encryption":"AES256"as header inHTTP/Scall for upload object
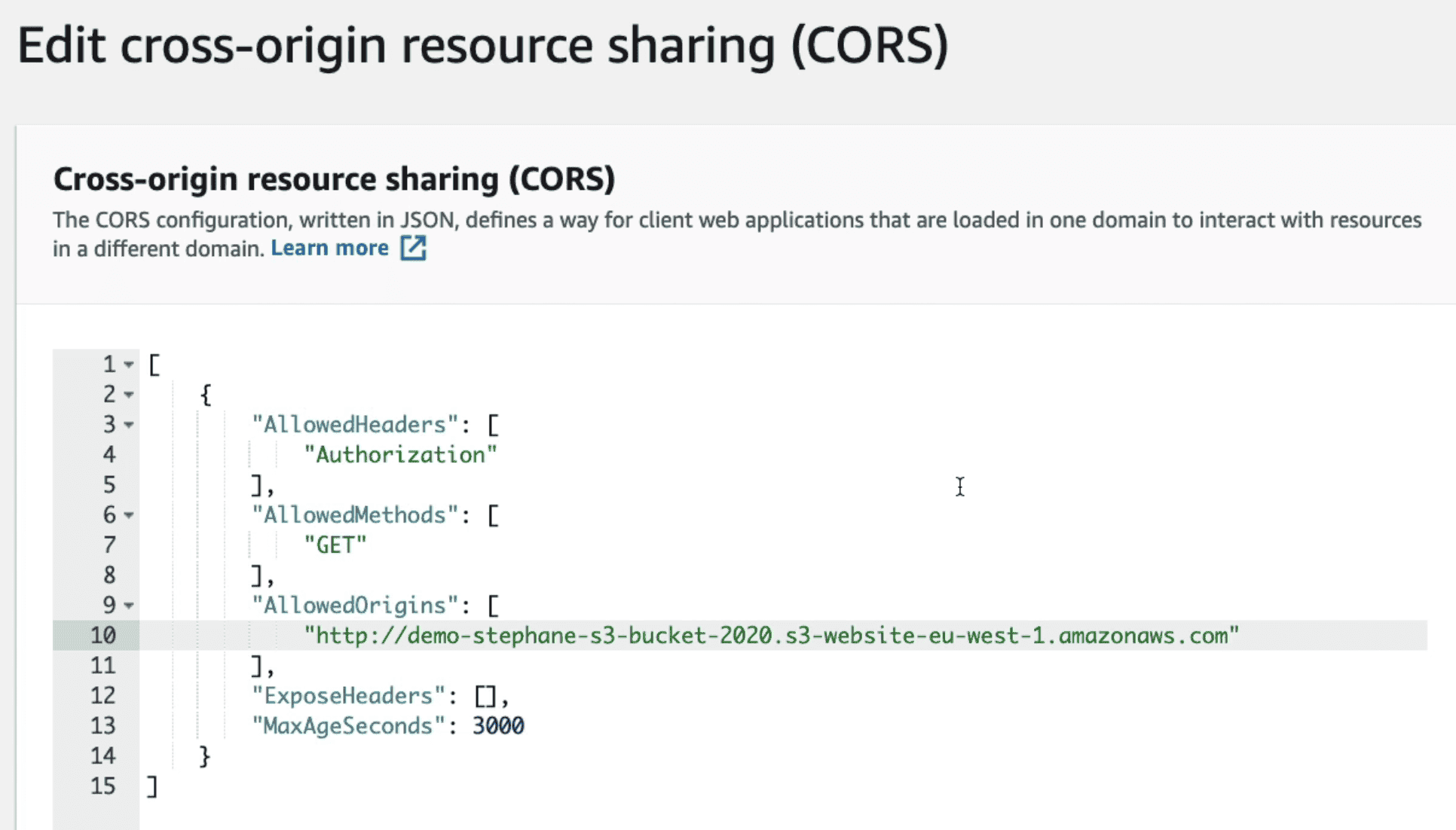
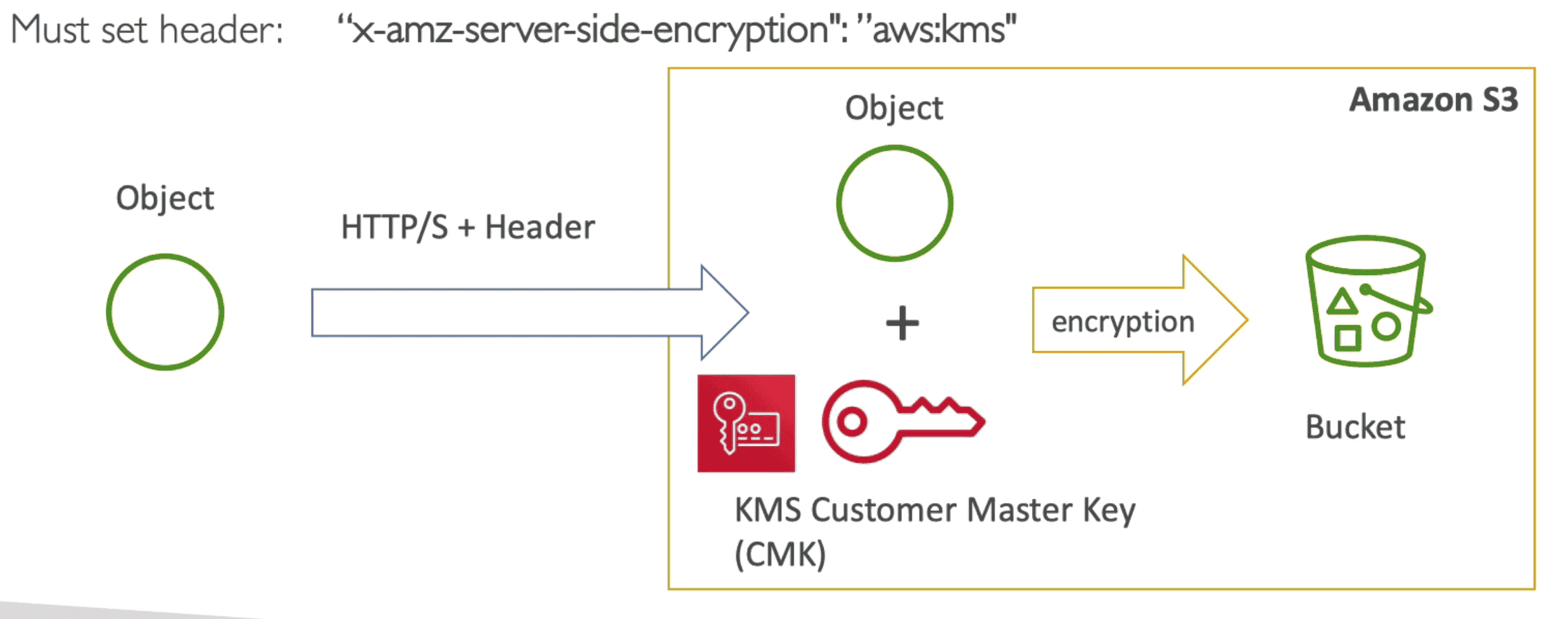
2. Server Side Encryption (SSE-KMS)
User controlled KMS Key used for SSE
- Set
"x-amz-server-side-encryption":"aws:kms"as header inHTTP/Scall for upload object - User Controlled + allow Audit trail: KMS Key usage logs show in
Cloudtraillogs - Make use of
GenerateDataKey&DecryptAPI - KMS Quota decrease with SSE-KMS
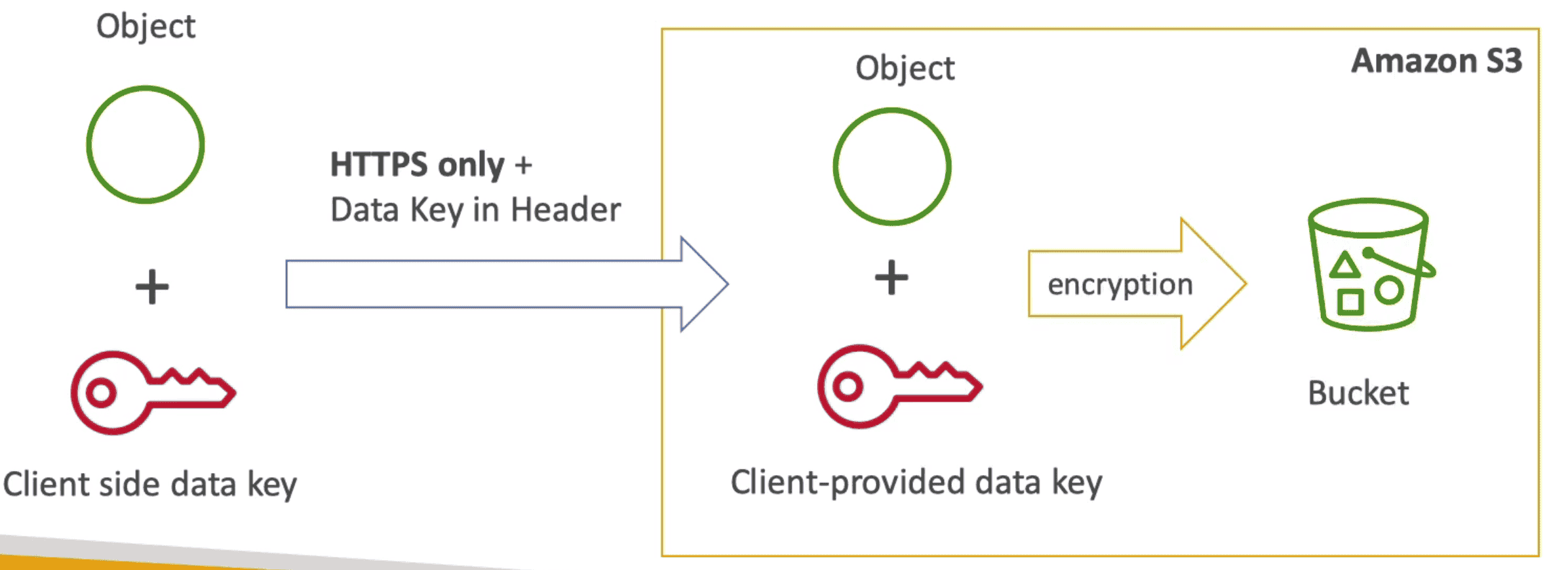
3. Server Side Encryption(SSE-C)
SSE using key provided by Customer.
- Send Key to S3 in Header of
HTTPScall for upload object - HTTPS is must
- Key must be provided in HTTP header with each request
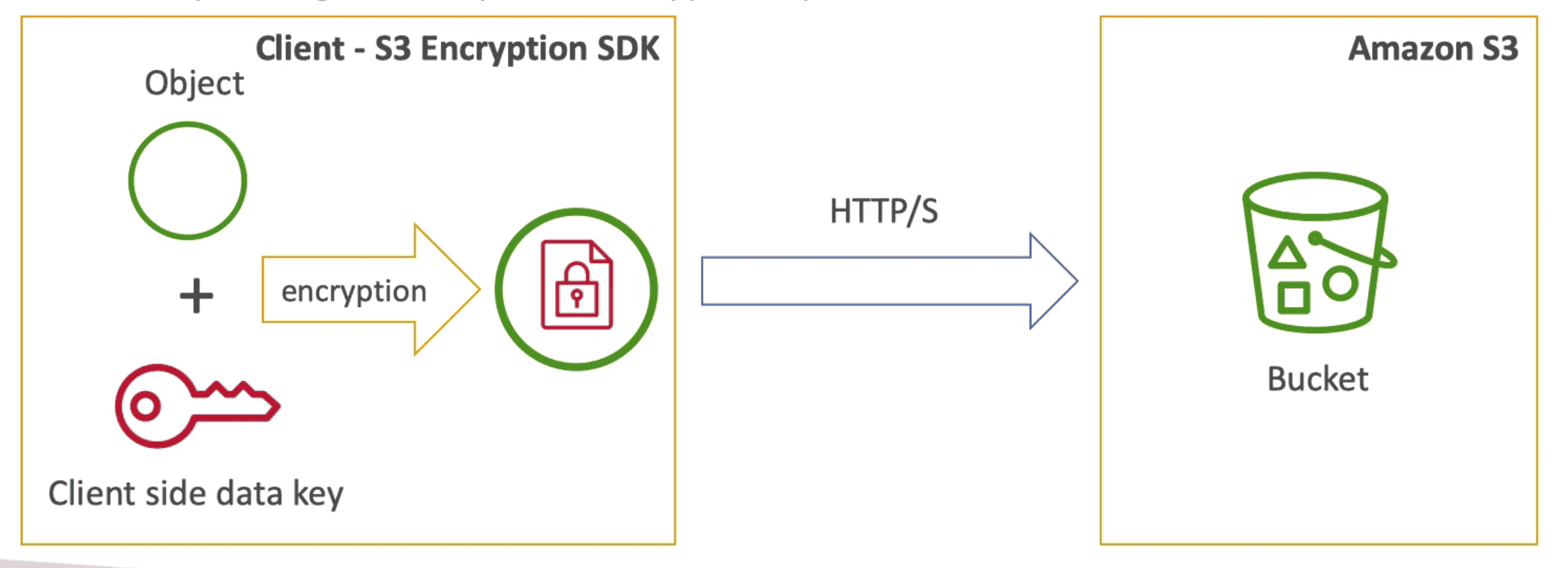
4. Client Side Encryption(CSE):
fully managed by Client, customer manage Key + Encryption/Decryption
- Customer Encrypt data before upload & Decrypt Data after download of data
- Client side library help with CSE eg AWS S3 Encryption Client
5. Encryption in Transit/Fly (SSL/TLS)
Use
HTTPSto encrypt data in transit
- S3 Support both HTTP & HTTPS end point
- HTTPS is recommended
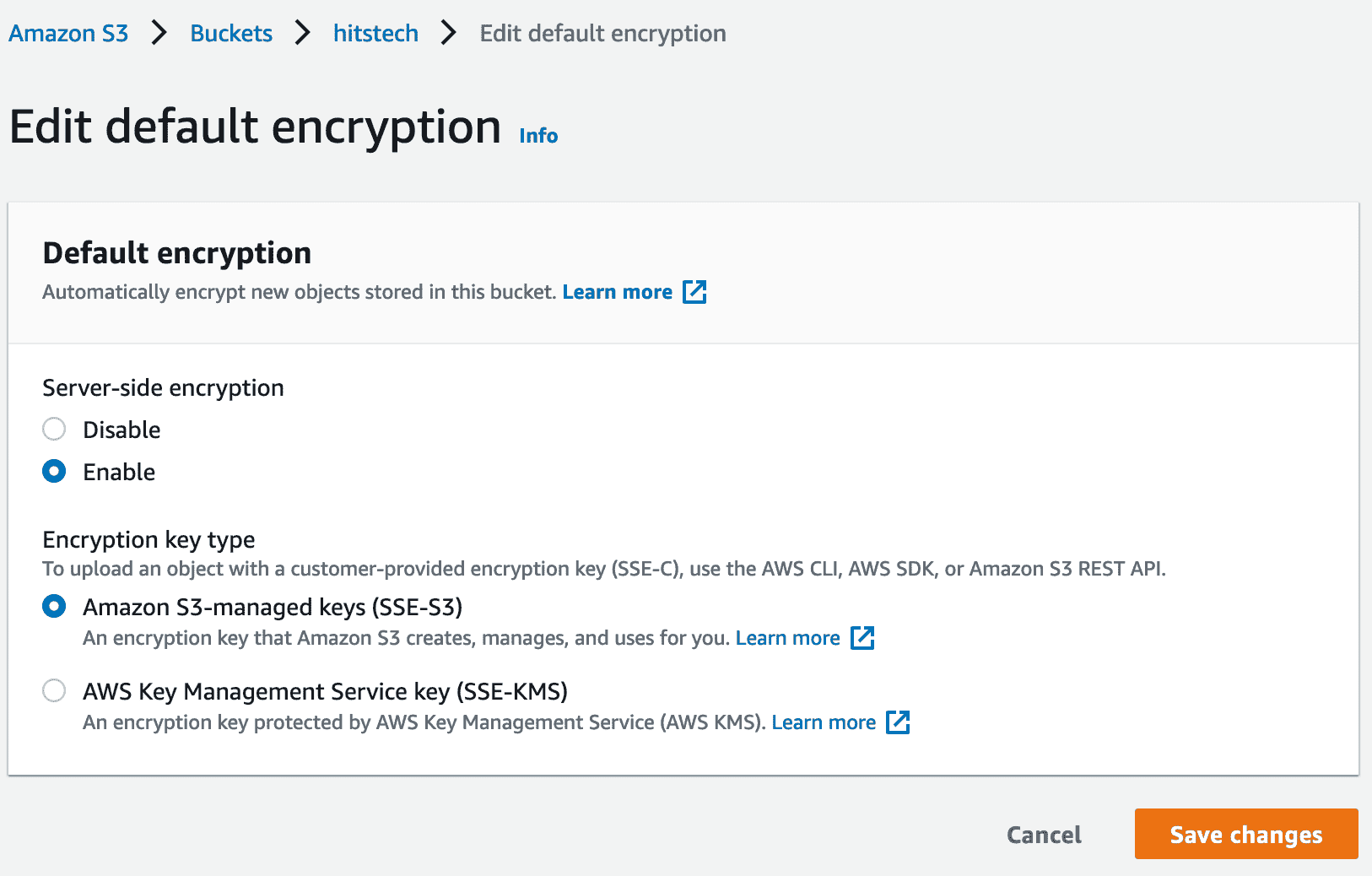
6. Default Encryption
Default Encryption can be enabled for all S3 Uploads
- Bucket Policy are evaluated before applying Default Encryption method
- Force encryption on S3 Bucket
- Bucket -> Properties
Replication
Behind the scene
asynchronous continuos replicationof data
- Support Cross Region Replication(CRR), Same Region Replication(SRR) & Cross Account replication
- Must Enable Versioning in both source & Target buckets
- Must give proper IAM permission to copy bucket

Notes:
- Only new objects are replicated
- Optional: Delete markers gets replicated
- Deletion with Version ID not replicated
- Replication is not chained 1->2->3
Update replication rule in Bucket-> Management to specify target
S3 Access Logs
Logs of All S3 Events to S3 Bucket for Audit, Troubleshooting or Monitoring purpose
Athenacan be used to read logs- It take some time to generate logs
- Never use same bucket to store access logs of a bucket it will be infinite loop
S3 Inventory
Log list of object & Metadata for Audit, Report of all objects
- Output: CSV, ORC, Apache Parquet
- Generated Daily , Weekly in defined target S3 bucket
- Athena, Redshift can be used to read logs
- Filter using S3 Select
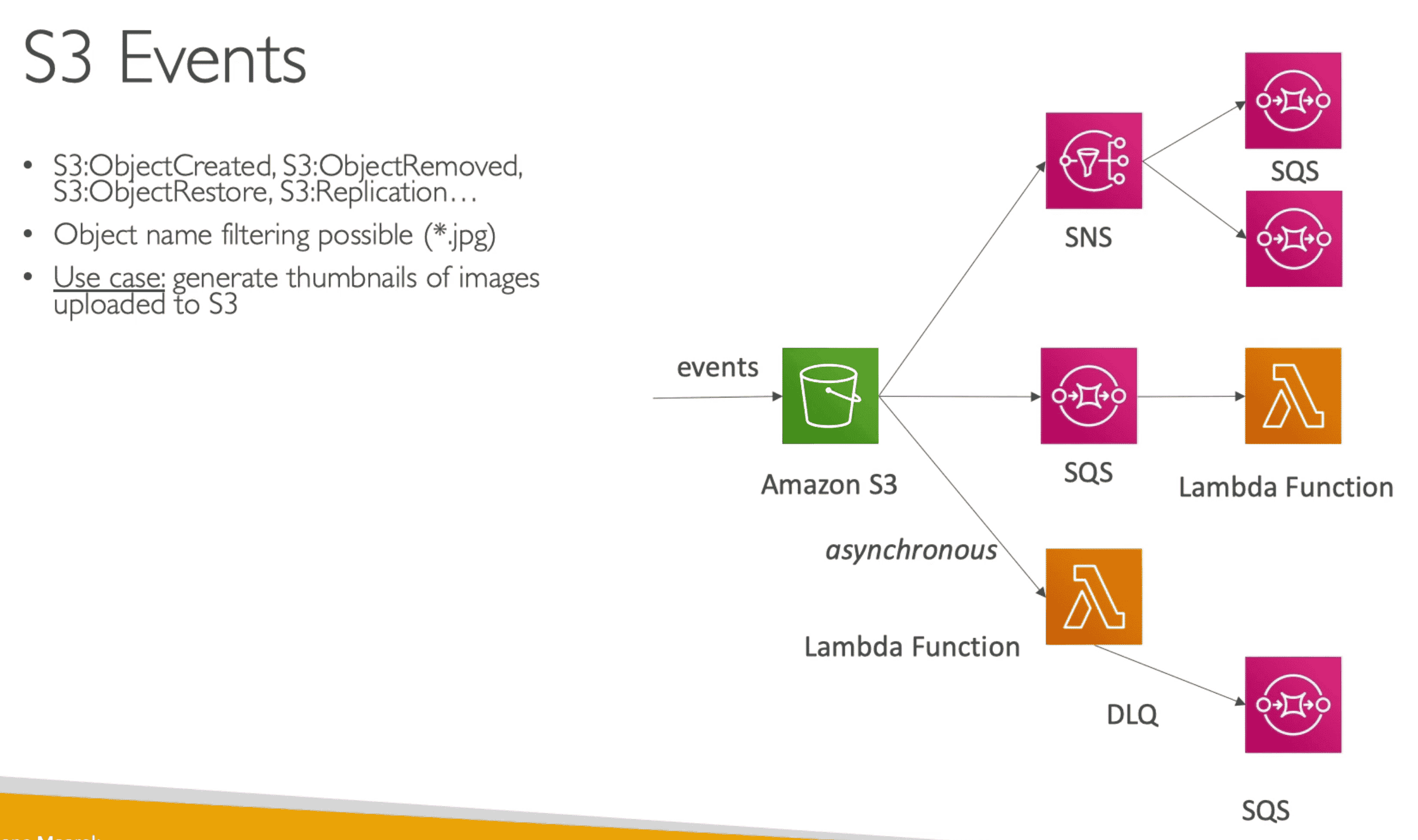
S3 Event Notification
Notified when there's an object event eg uploaded, removed, replicated etc on S3 bucket
- Destination could be
- SNS
- SQS
- Lambda Function
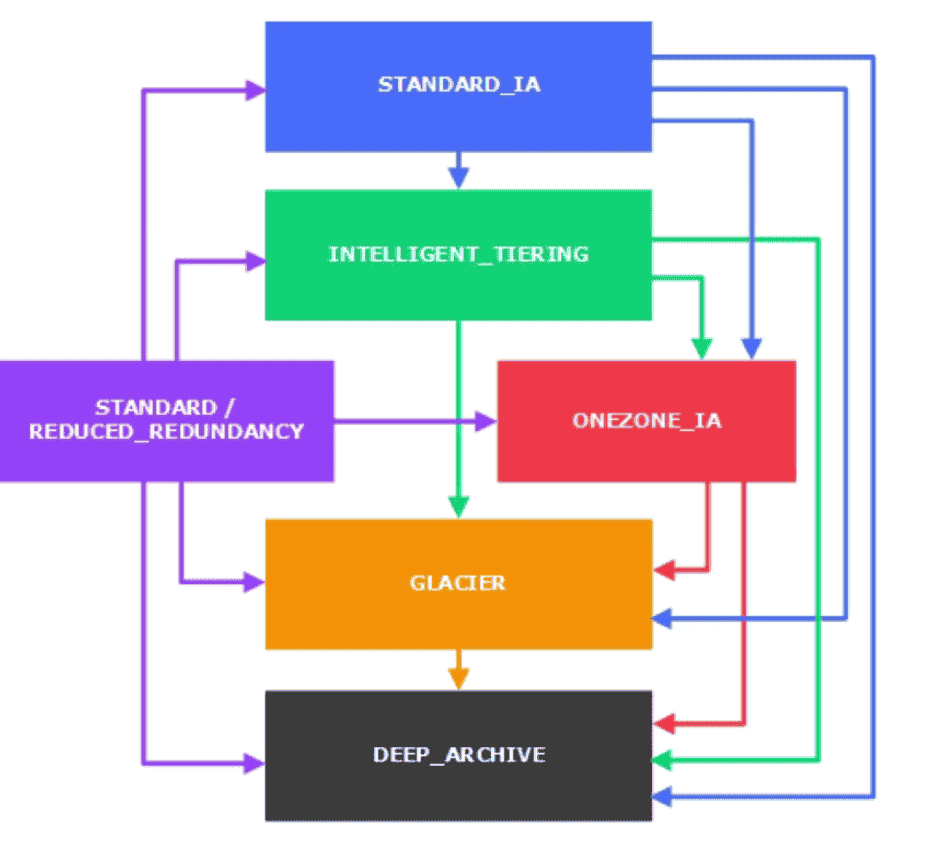
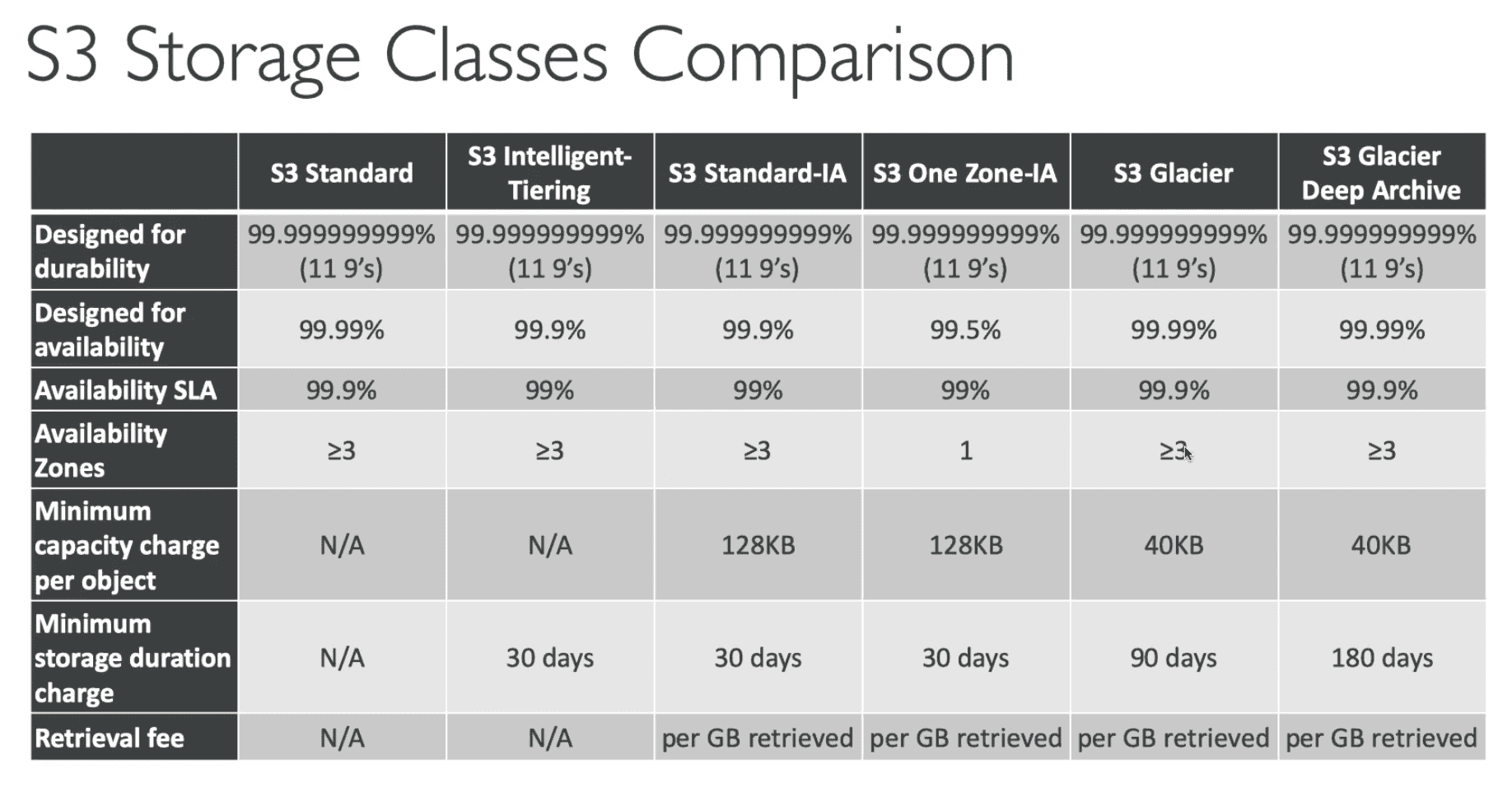
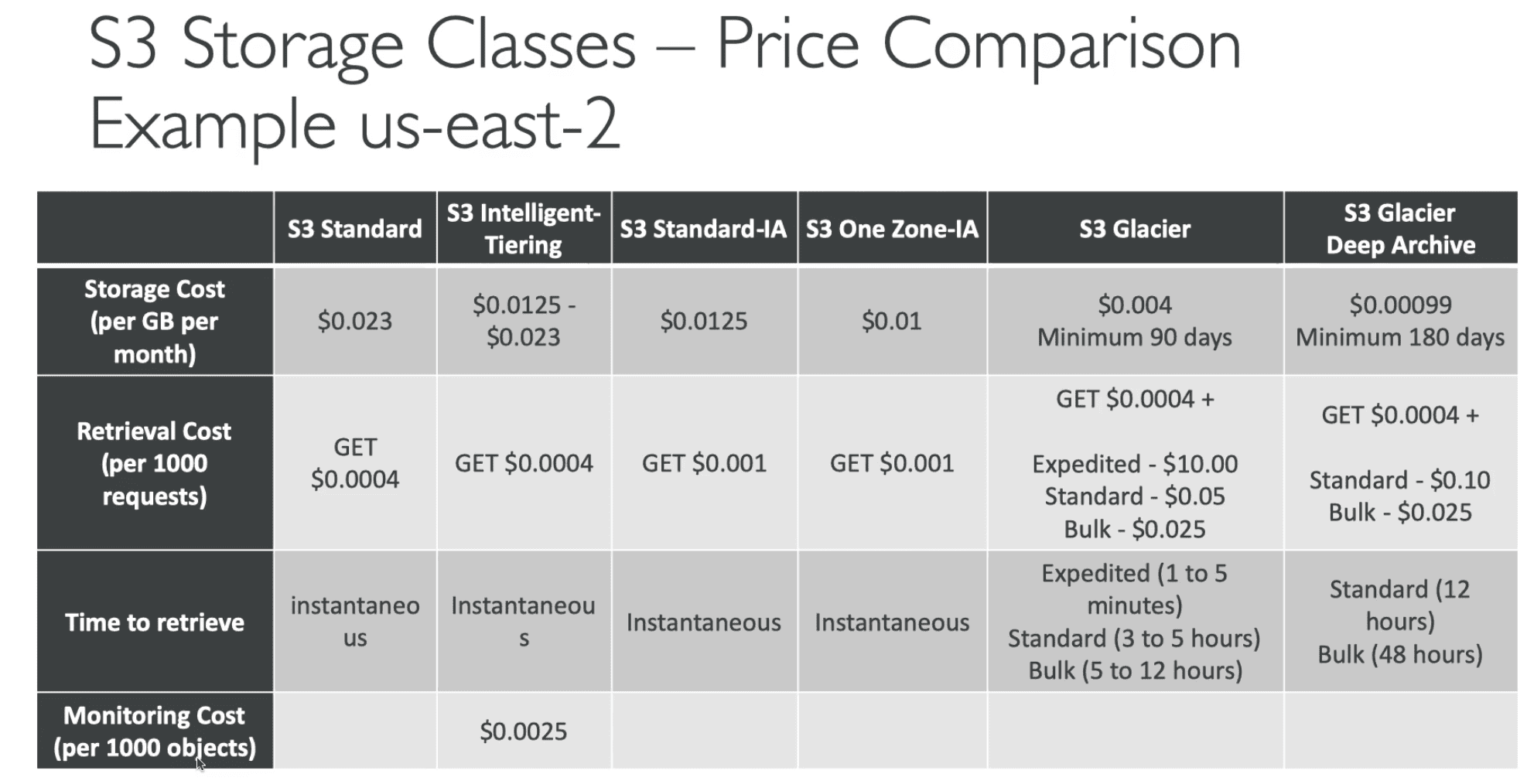
S3 Storage Classes
Lifecycle policies:
Automatically move data between 3 Tiers
- Can be apply for Object & Bucket or Prefix, Object Tags
Transition Actions: Move object to different classExpiration Action:- Delete objects after expiration
- Delete old version
- Delete incomplete multipart upload
S3 Analytics
Setup Analytics to determine object transition Rule
- Report is updated daily so it will take 24-18 Hour on first start
- Works with
Standard & StandardIA
Tier 1
Amazon S3 Standard General Purpose
- 99.99% Availability
- 99% Durability after 1 year
- High Availability: Concurrent loss of data in 2 location can be recover out of 3 (3 Location Backup)
- Frequent Used Data
- High Cost than other 2 Tier
- Min Storage Duration
30Days
Tier 2:
S3 Standard Infrequent Access (S3 IA)
- 99.9% Availability
- Used for less frequent Access Data
- Less frequent data but access fast
- Backup/ long term storage
- Same Level of Availability as S3 Standard (3 Location Backup)
- Lower storage price and higher retrieval price
- Backup, Disaster Recovery
- Min Storage Duration
30Days
S3 Intelligent-Tiering
- 99.9% Availability
- Ideal for data with unknown or changing access patterns
- Requires a small monthly monitoring and automation fee per object
- Automatically Assign Data to Tier based on usage.
- Min Storage Duration
30Days
S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (S3 One Zone-IA)
- Stores data in a single Availability Zone
- Has a lower storage price than S3 Standard-IA
- Use Case: Secondary Data, Reproducible data, eg thumbnail
- Min Storage Duration
30Days
Tier 3:
S3 Glacier Instant
- Retain data long time and faster retrieval
- Retrieve objects within few millisecond
- Great for data access within each quarter
S3 Glacier flexible Retrieval
- Before known as S3 Glacier
- Retain data long time but slow retrieval
- Retrieve objects within few Hours
- low-cost storage class
encrypted, by default: for both data at rest as well as in transit.- Encrypted using AWS manged
AES 256 key - Min Storage Duration
90 Days - Usage: Archive Data/ Audit Data, alternate to magnetic tapes
- Operations:
-
Download: Initiate retrieval job to prepare for download. Once archive is ready user get limited time to download.
- Vault can send SNS notification when archive is ready to download/restore
- S3 Event Notifications:
-
S3:ObjectRestore:Post: initiate restore -
S3:ObjectRestore:Completed: finish restore
-
- Upload: Single or multipart
- Delete: Delete Archive with Archive ID using AWS SDK or Glacier REST API
-
Retrieval Options
1. Expedited
1-5 Minute
2.Standard
3-5 Hour
3. Bulk
5-12 Hour
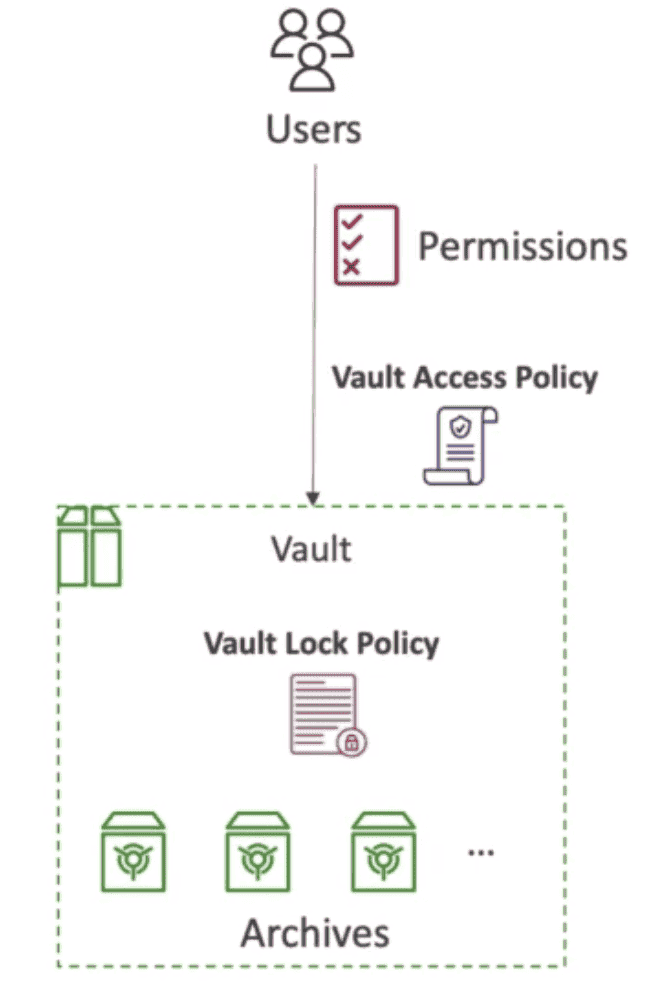
Archive: Each item in Glacier called Archive.
- Archive is like Objects in S3
- Max Size:
upto 40TB - Vault Lock: Write once Read Many(WORM)
Vault: Archives are stored in Vault
- Vault is like Bucket in S3
- Vault Operations:
- Create, Delete(if Vault is empty)
- Retrieve MetaData
- Download Inventory
S3 Object Lock & Glacier Vault Lock
WORM Model: Write on Read Many. No one can delete or modify a file for a period of time. Future edit is disabled.
- Useful for compliance data for Audit
Each Vault have
- Vault Access Policy:
Similar to S3 bucket policy
- restrict access to vault
- Vault Lock Policy:
immutable policy, cant be changed once LOCKED.
- forbid deleting archive before 1 year
S3 Glacier Deep Archive
- Lowest-cost object storage class ideal for archiving
- Min Storage Duration
180 Days - Data can be stored directly in Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive.
Retrieval Options
1.Standard
12 Hour
2. Bulk
48 Hour
S3 Performance Improvement
Base Line Performance
3500PUT/COPY/POST/DELETE &5500GET/HEAD per second per prefix in a bucket
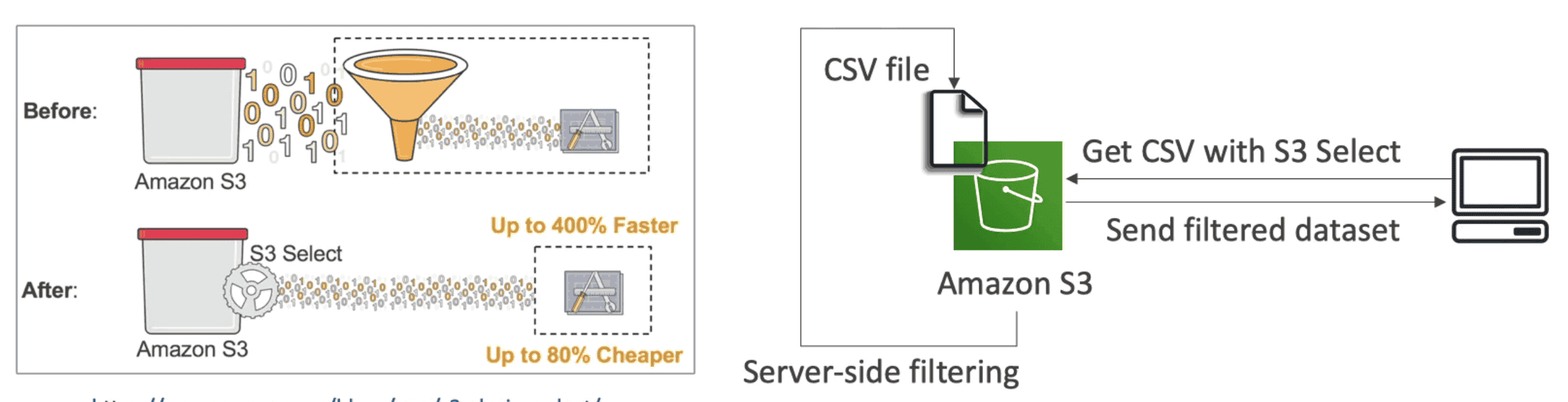
S3 Select/Glacier Select
Server Side SQL Filtering of data to reduce traffic and faster retrieve of objects
- 400X Faster & 80X Cheaper
- Less Network Traffic & CPU usage on Client side
KMS Limitation
KMS Quota Limit Slows down Server side Encryption/ Decryption
- KMS Quota need to increase if slow down
- Call GenerateDataKey API to Encrypt & Decrypt KMS call to decrypt object
S3 Bucket Key
Store KMS key in S3 Bucket to generate Data key for further SSE-KMS
- Eliminate need to call KMS by 99% for future uploads
- Reduce KMS logs from S3 on CLoudtrail
- Reduce Cost by increasing KMS Quota.
Multi Part Upload
Parallel Upload of
5 GBfile in parts.
S3 Transfer Acceleration
Use Edge Location to accelerate Upload of multipart Upload
Byte Range fetch
Fetch a part/range of Bytes of Object to Parallel Download
AWS SNOW FAMILY
Collection of physical devices that help to physically transport up to exabytes of data into and out of AWS.
- All Data is encrypted using 256 bit encryption handled by customer
- Life Cycle Policy can be used to migrate data to Glacier
AWS Ops Hub
Software to manage Snow family device
- Transfer files
- Launch & Manage Instance running in snow family
- Monitor device Matrices
- Launch AWS Services eg DataSync to sync data
Challenges with Network Transfer
If it takes more than a week to transfer data use Snow device
- Limited Bandwidth
- Limited Connectivity on some location
- High Network cost
- Shared Bandwidth
AWS Snowcone
8 TBData for S3- Use DataSync to sync data with AWS
- Edge Computing:
- 2CPU, 4GB Memory
- USB C power
- Usage: Analytics, Video, Backup, Tape Data
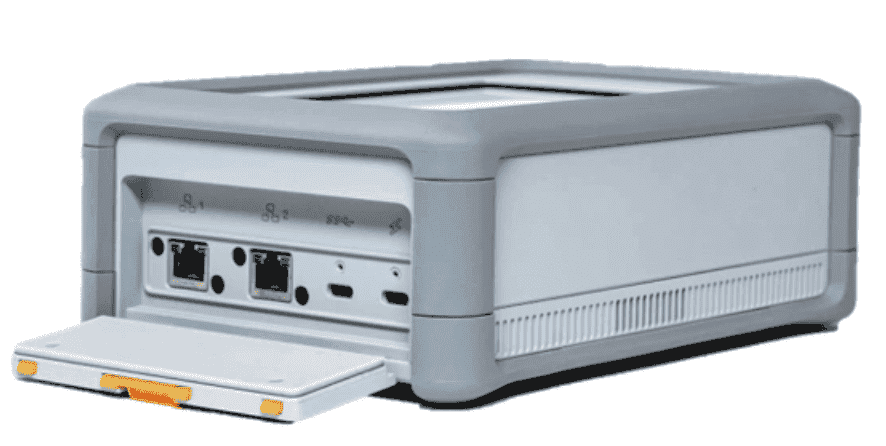

AWS Snowball Edge
TB-PB data Transfer
- Ship to remote location
- Block storage or S3 compatible storage
- usage: Image compression, IOT, Video Transcoding
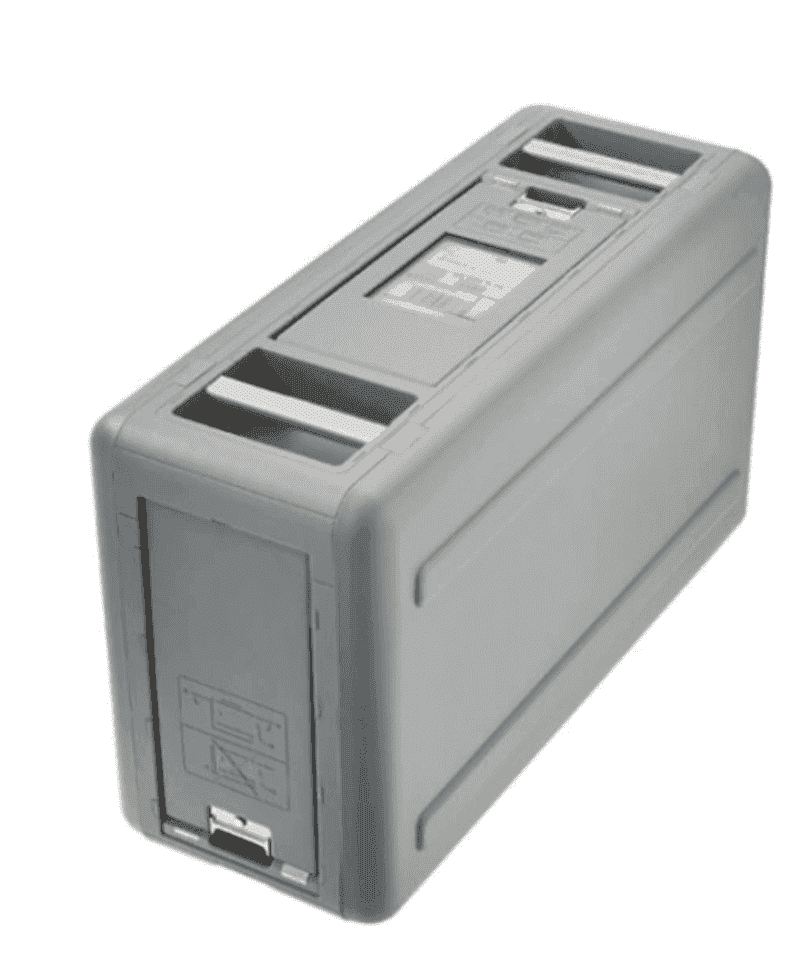

Types
-
Snowball Edge Compute Optimized
40 TB HDDfor S37.68 TB SSDfor EBS52 vCPUs, 208 GiB RAM- NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPU(Optional)
-
Snowball Edge Storage Optimized
80 TB HDDfor S31TB SSDfor EBS40 vCPUs, & 80 GiB RAM
AWS Snowmobile
Shipping Container on Truck with
- Use for more than
10 PBData - 100 petabytes per snowmobile
- Exabyte-scale data transfer service used to move large amounts of data to AWS.
- Video Surveillance, escort vehicle, water proof, fire proof
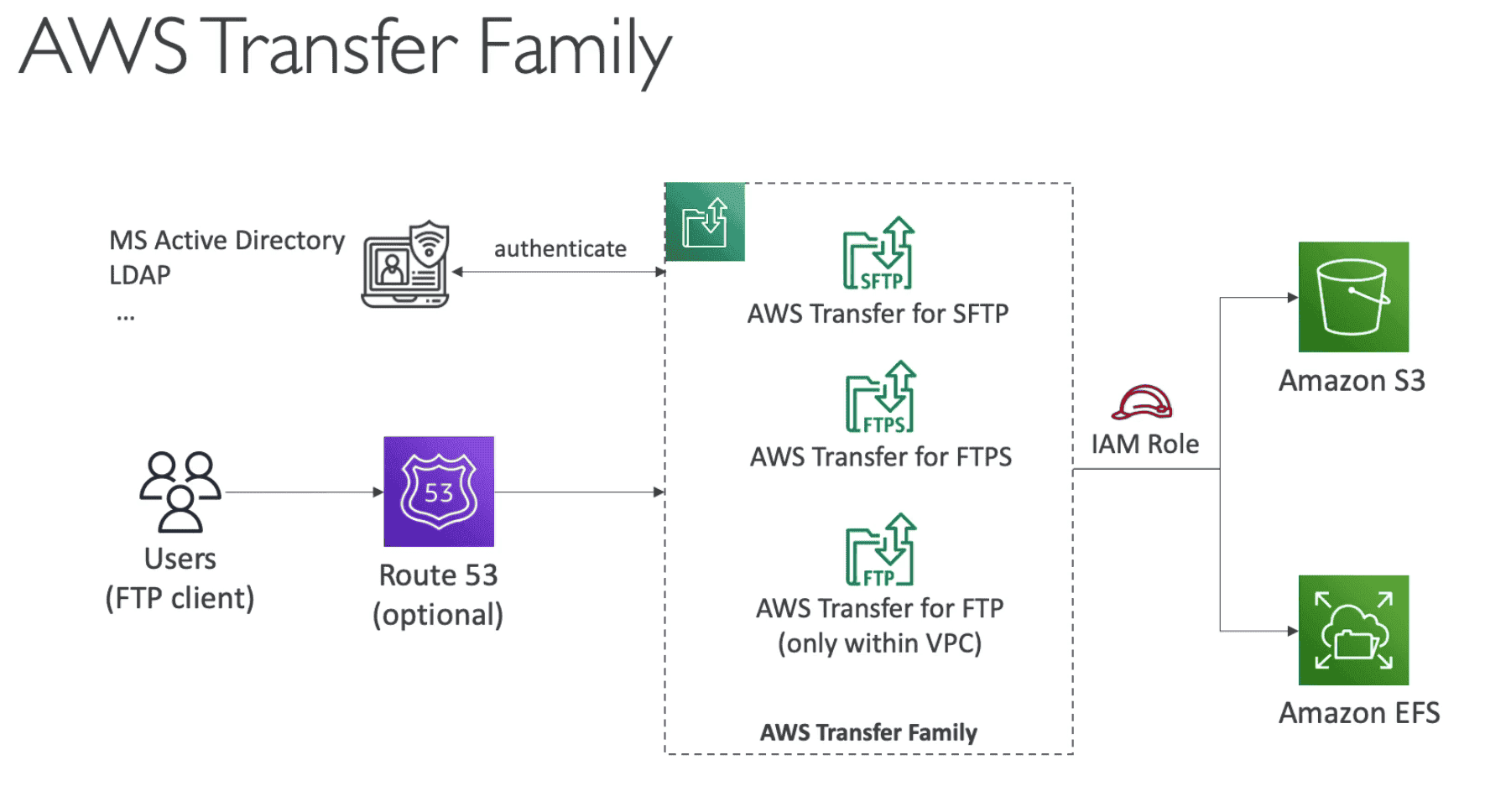
AWS Transfer Family
Fully Manged service to transfer file in/out of S3 or EFS using FTP protocol
- Scalable, Reliable, Highly Available (Multi AVZ)
- Auth using: Okta, AD, Cognito
Supported Protocol Family
- FTP :File Transfer Protocol
- FTPS: File Transfer Protocol over SSL
- SFTP: Secure File Transfer Protocol