Azure Global Infrastructure
Geography
Group of regions for data residency & compliance boundry https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/global-infrastructure/geographies/#overview
- typically containing at least one or more regions,
- preserves data residency and compliance boundaries.
- fault-tolerant to withstand complete region failure
Region
The Geographical area contains at least one but potentially multiple datacenters that are nearby and networked together with a low-latency network.
- 58 region over 140 countries
- Most number of region in all CSP
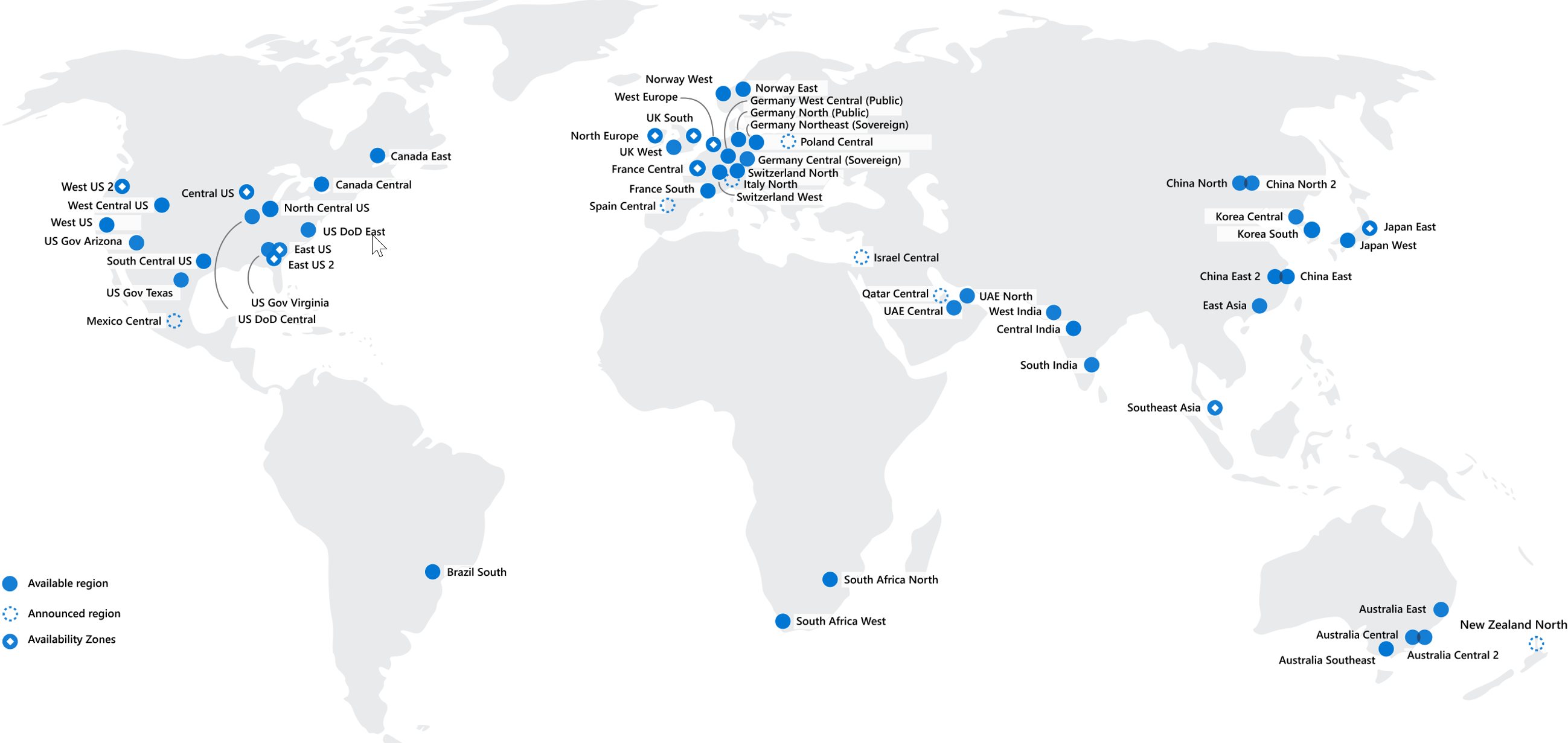
Recommended Regions:
Region with at least 3 AVZ
Alternate Region
Region which dost have support of AVZ
Special regions
- US DoD Central, US Gov Virginia, US Gov Iowa :: physical and logical network-isolated instances of Azure for U.S. government agencies and partners. These datacenters are operated by screened U.S. personnel and include additional compliance certifications.
- China East, China North: available through a unique partnership between Microsoft and 21Vianet, whereby Microsoft doesn't directly maintain the datacenters.
Region Pair
Each Azure region is always paired with another region within the same geography (such as US, Europe, or Asia) at least
300 miles away.
- Replication of resources (such as VM storage) across a geography for Disaster Planning.
- If a region in a pair was affected by a natural disaster, for instance, services would automatically failover to the other region in its region pair.
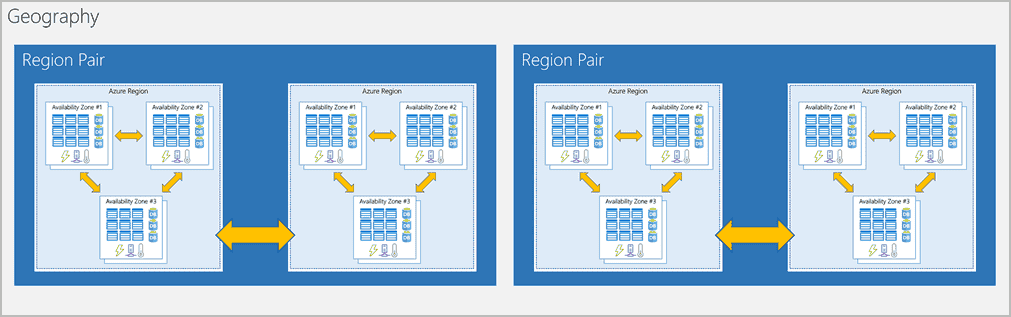
Advantage:
- If an extensive Azure outage occurs, one region out of every pair is prioritized to make sure at least one is restored as quickly as possible for applications hosted in that region pair.
- Planned Azure updates are rolled out to paired regions one region at a time to minimize downtime and risk of application outage.
- Data continues to reside within the same geography as its pair (except for Brazil South) for tax- and law-enforcement jurisdiction purposes.
Availability Zone(AVZ)
Physically separate datacenters within an Azure region.
- Oone or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
- An availability zone is set up to be an isolation boundary. If one zone goes down, the other continues working.
- Connected through high-speed, private fiber-optic networks.
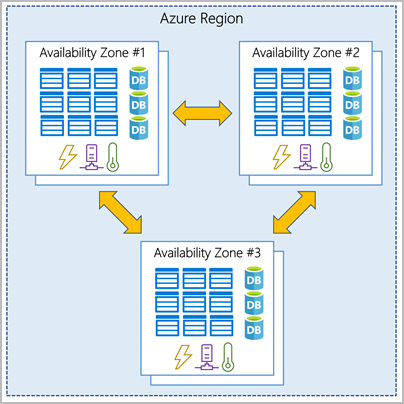
Azure services support availability zones:
Zonal services
You pin the resource to a specific zone (for example, VMs, managed disks, IP addresses).
Zone-redundant services
The platform replicates automatically across zones (for example, zone-redundant storage, SQL Database).
Non-regional services
Services are always available from Azure geographies and are resilient to zone-wide outages as well as region-wide outages.
Azure Content Delivery Network(CDN)
A distributed network of servers that delivers web content closer to users.
-
Store cached content on edge servers in
point-of-presence (POP)locations that are close to end users, to minimize latency. -
CDN endpoint:
awesomesite.azureedge.net -
Types of origin:
- Storage & Storage Static website
- Cloud service
- Web App
- Custom Origin(HTTP/S end point)
Limitations
Each Azure subscription has default limits:
- Max CDN profiles that can be created: 25
- Max Endpoints/CDN profile: 25
- Max Custom domains/ Endpoint: 25
set rules for different paths to allow or block content in selected countries/regions.
- CDN HTTP Cache-directive headers:
Cache-Control– caching behavior of a browser.Expires– a date based expiration time.
Time To Live(TTL)
Cache expiration duration in days, hours, minutes.
- Default TTL:
7 Days - Large file optimizations:
1 Day - Media streaming optimizations:
1 Year - Cache durations range : 0 seconds and 366 days.
- 0 seconds: CDN caches the content, but must revalidate each request with the origin server.
Caching Rules
CustomRule > Global Rule > Default Rule
1. Global caching rule
overrides any HTTP cache-directive headers.
- take precedence over the default CDN caching behavior
2. Custom caching rule
Rule to match specific paths and file extensions.
- take precedence over global caching rules,
Path:- Max Path length
260character - eg: /myfile.html, /my/folder/, and /my/images/.jpg.
- Max Path length
Extension:- Max
50extensions - Max
16Character/Extension - eg: .jpg, .mp3, or .png.
- Max
Global & Custom Caching behavior
1. Bypass cache
Do not cache and ignore origin-provided cache-directive headers.
2. Override
Ignore origin-provided cache duration; use the provided cache duration instead. This will not override cache-control: no-cache.
3. Set if missing
Honor origin-provided cache-directive headers, if they exist; otherwise, use the provided cache duration.
Azure CDN HTTP cache validators:
ETag– A string that is unique for every file and version of a file.Last-Modified– the origin server compares the date with the last-modified resource header.- Status code 200 = Modified
- Status code 304 = Not Modified
Troubleshooting
- Export basic usage metrics from your CDN by using diagnostic logs.
