COMPUTE
VIRTUAL MACHINE (VM) 
Provision Linux and Windows virtual machines in seconds with the configurations of your choice
- infrastructure as a service (IaaS) to provide VM on Azure
Limit
- Each subscription can deploy max
20 VMs/ Region. - Disk:
- A single storage account has a fixed-rate limit of
20k IOPS= max40 standard VHDsat full utilization. - Ultra Disk reservation charge even without attaching it.
- A single storage account has a fixed-rate limit of
SSH into VM
Download Key
chmod 400
.pem
Generate RSA key
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Copy RSA Key and add to Azure Portal
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Use SSh key to login
ssh -i /Users/hiteshsahu/.ssh/id_rsa hits@20.70.182.240
VM image
- Use own image, or use images from Azure Marketplace.
- List all images:
az vm image list
VM disks
Every virtual machine has one attached operating system disk
- Support: Standard HDD, Standard SSD, and Premium SSD
- Max capacity:
4TB. - Data on the temporary disk may be lost during a maintenance event or when you redeploy a VM
- Ultra disk : high throughput, high IOPS, and consistent low latency disk storage. Reservation charge even without attaching an Ultra Disk
1. Standard disks
- Backed by HDD
- Cost-effective storage
- Ideal for cheap dev and test workload.
2. Premium disks
- Backed by SSD
- high-performance, low-latency disk
- Ideal for production workload.
Storage Option
1. Managed disks:
Managed by Azure.
- Support up to
4 TB - Azure creates and manages disk, storage & storage account limits
- Easier to scale.
2. Unmanaged disks
you’re responsible for the storage accounts that hold the virtual hard disks (VHDs) that correspond to your VM disks.
- Pay the storage account rates for the amount of space used.
- Scaling is Hard: A single storage account has a fixed-rate limit of 20k IOPS = max
40 standard VHDsat full utilization.
VM Status
- Start – run VM and billing will start
- Stop – shutdown VM. VM billing stops but billing will continue for storage.
- Restart – reboot VM.
VM extensions
Post deployment configuration and automated tasks to install user data.
Windows VMs
Custom Script ExtensionRun custom scriptsPowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC): Setting up DSC on a VM to manage configurations and environments.Azure Diagnostics Extension: configure the VM to collect diagnostics data
For Linux VMs, Azure supports cloud-init across most Linux distributions & major automation tooling like Ansible,
Chef, SaltStack, and Puppet.
Availability Sets
logical grouping of VMs that allows Azure to understand how your application is built to provide for redundancy and availability
- Free of charge, billing is only for the VMs inside the Availability Sets.
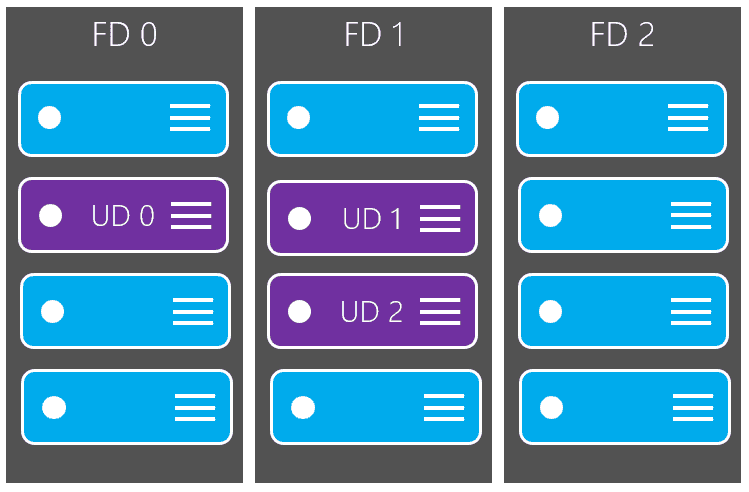
Update domains (planned maintenance)
A logical group of virtual machines that can undergo maintenance at the same time.
- By default, it has
5 non-user-configurable update domains. It can be increased up to20update domains. - Given
30 minutesto recover before maintenance is initiated on a different update domain.
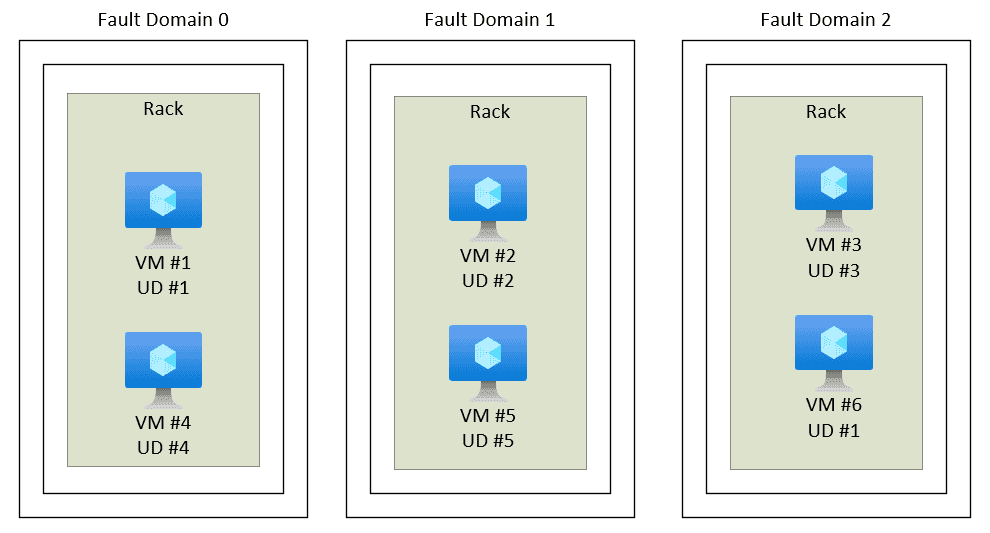
Fault domains (unplanned maintenance)
A logical group of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch.
- By default, VMs within an availability set are separated up to
3 fault domains. - If 2 Server column fails at least 1 will be running the App
Dedicated Host
Deploy VM on a physical server only used by your organisation
- capacity is not shared with other customers.
- As you provision the host, you gain visibility into and control over the placement of your Azure VMs and you determine the host's maintenance policies.
- Use case: host-level isolation helps address compliance requirements.
Azure Spot Virtual Machines
Get deep discounts when you provision unused compute capacity to run your workloads
- For workloads that can handle interruptions and don't need to be completed within a specific period of time.
- deep discounts of up to 90 %
- Use Case: big data, machine learning and AI, batch jobs, rendering and transcoding of videos, graphics and images at a very low cost.
Virtual Machine Scale Set(VMSS) 
Achieve high availability by autoscaling to create thousands of VMs in minutes
- Automatically scale application as demand changes.
- Deploy and manage a set of identical VMs.
Options for scaling VM instances up and down.
- Manually through the Azure portal
- Auto-scale based on metrics
- Auto-scale based on a defined schedule
VM Type based on Workload
| VM Type | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | Balanced CPU-to-memory ratio. | Testing and development, small to medium databases, and low to medium traffic web servers. |
Compute Optimized | High CPU-to-memory ratio. | Medium traffic web servers, network appliances, batch processes, and application servers. |
Memory Optimized | High memory-to-CPU ratio. | Relational database servers, medium to large caches, and in-memory analytics. |
Storage Optimized | High disk throughput and IO | Big Data, SQL, NoSQL databases, data warehousing and large transactional databases. |
GPU | Available with single or multiple GPUs. | Heavy graphic rendering and video editing, model training, deep learning. |
HPC (High Performance Compute) | Fastest and most powerful CPU virtual machines with optional high-throughput network interfaces (RDMA) |
az group create --name azhash-vm-rg --location westeurope
az vm create \
--resource-group zhash-vm-rg \
--name azhash-vm \
--image UbuntuLTS \
--generate-ssh-keys \
--admin-username azureuser
HPC
Azure Batch
Cloud-scale job scheduling and compute management with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds or thousands of virtual machines
- Large-scale parallel and high-performance computing (HPC) batch jobs with the ability to scale to tens, hundreds, or thousands of VMs.
- Run jobs in a group of Linux or Windows virtual machines.
Constrains on Job
-
Maximum wall clock time
tasks are terminated if the job runs longer than the specified time.
-
Maximum number of task retries
if the task fails, it will be requeued to run again.
Task:
A task represents a unit of computation and a
jobis a collection of tasks.
Job priority values
range from the lowest priority to the highest priority.
Job manager task: contains the information needed to create the tasks required for the job.
Scheduled jobs allow you to create recurring jobs.
multi-instance task: Simultaneously run on more than one compute node
Task dependencies, the task depends on the completion of other tasks before its execution.
Pricing
- No additional charge for using Azure Batch and you are only charged for the underlying resources consumed.
Cycle Cloud
Create, manage, operate, and optimize HPC and big compute clusters of any scale
-
Orchestrating and managing High Performance Computing (HPC) environments
-
Enables you to provision infrastructure for HPC systems, deploy familiar HPC schedulers, and scale the infrastructure automatically to run jobs efficiently at any scale.
Features
-
Scheduler Agnostic – use standard HPC schedulers or extend CycleCloud autoscaling plugins to work with your own scheduler.
-
Manage Compute Resources – manage VMs and scale sets to provide a set of compute resources to meet your workload requirements.
-
Autoscale Resources – adjust cluster size and components automatically based on workload, availability, and time requirements.
-
Monitor and Analyze – collect node-level metrics and analyze the performance data using a visualization tool.
-
Template Clusters – enables you to share your cluster topologies.
CycleCloud agent (called Jetpack)
Installed by Azure CycleCloud on each virtual machine to provide the following functions:
- Node Configuration
- Distributed Synchronization
- Health Check
Containers
There are two ways to manage both Docker and Microsoft-based containers in Azure:
Azure Container Instances(AKI) 
- PaaS: allows uploading a containers & run it
- Docker as Service
Feature
- Fast startup: start containers in seconds, without the need to provision and manage VMs
- Container access: expose container groups directly to the internet with an IP address and a fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- Hypervisor-level security: Isolate application as completely as it would be in a VM
- Customer data: Stores the minimum customer data required to ensure your container groups are running as expected
- Custom sizes: allowing exact specifications of CPU cores and memory
- Linux and Windows: Schedule both Windows and Linux containers using the same API.
Persistent State:
Mount Files shares directly to retrieve and persist state such as:
- Azure file share
- Secret
- Empty directory
- Cloned git repo
Mount Limitation
- Can only mount Azure Files shares to Linux containers.
- Requires the Linux container run as root.
- Limited to CIFS support.
Container group
Collection of containers started in the same host machine.
- The containers in a container group share a lifecycle, resources, local network, and storage volumes.
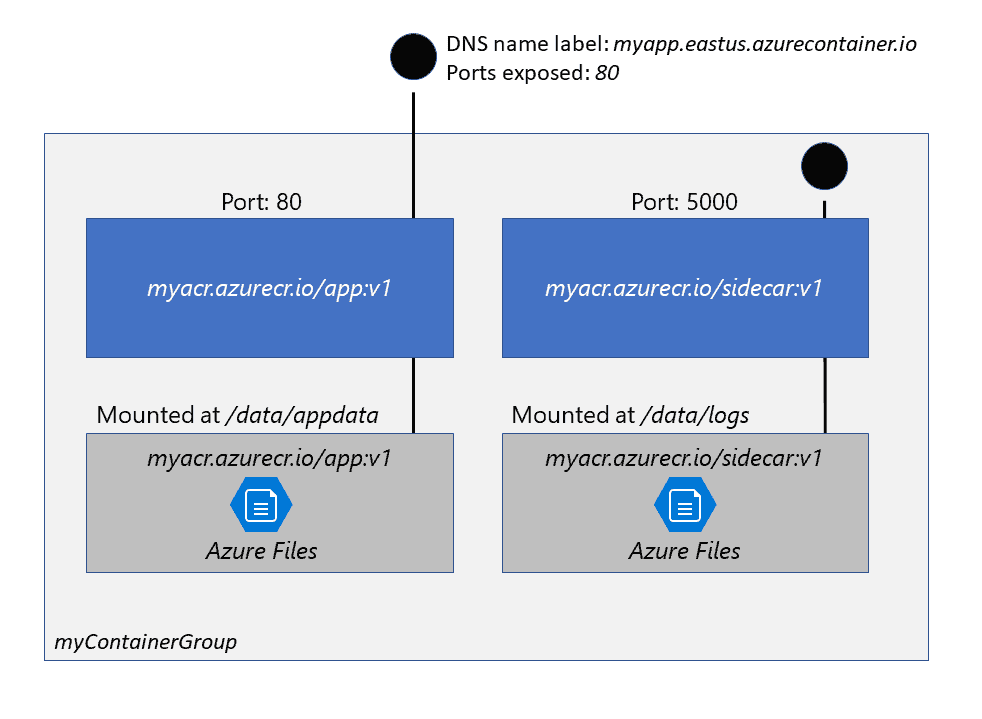
Deploy Mode
1. Resource Manager template
- recommended when need to deploy additional Azure service resources eg. Azure Files share)
2. YAML file
- recommended when deployment includes only container instances.
Restart Policy
Always: Containers are always restarted. Default.Never: Terminated on its application, or script, exits.OnFailure: restarted only when the process executed in the container fails (terminates with a nonzero exit code).
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Serverless Kubernetes & Container Service
- complete orchestration service for containers with distributed architectures and large volumes of containers.
- Kubernates as Service
Azure Container Registry (ACR) 
Managed, private Docker registry service based on the open-source Docker Registry 2.0.
- Create, store and manage private Docker images.
Service Tiers
1. Basic
- A cost-optimized
- Lowe Storage & image throughput
- Use case: Dev/Test
- Same programmatic capabilities as Standard and Premium
- such as Azure Active Directory authentication integration
- image deletion, and webhooks.
2. Standard
- Basic+ increased storage and image throughput.
- use case: production scenarios.
3. Premium
- Highest amount of storage and concurrent operations, enabling high-volume scenarios.
- Higher image throughput
- Geo-replication
- Content trust for image tag signing
- Private link with private endpoints to restrict access to the registry.
ACR Tasks
streamline building, testing, pushing, and deploying images in Azure.
Quick task
Build and push a single container image to a container registry on-demand, in Azure, without needing a local Docker Engine installation.
Automatically triggered tasks
- Automatically triggered tasks—Enable one or more triggers to build an image:
- Trigger on source code update
- Trigger on base image update
- Trigger on a schedule
Multi-step task
- Extend the single image build-and-push capability of ACR Tasks with multi-step, multi-container-based workflows
App Service
build and host web apps, background jobs, mobile back-ends, and RESTful APIs in the programming language of your choice without managing infrastructure.
-
PaaS: focus on the website and API logic while Azure handles the Indra to run and scale applications.
-
automatic scaling and high availability.
-
CI/CD: automated deployments from GitHub, Azure DevOps, or any Git repo.
-
Platform: Linux / Windows
Languages: - ASP.NET, ASP.NET Core, - Java, - Ruby, - Node.js, - PHP, - Python
General settings Ued to configure stack, platform, debugging, and incoming client certificate settings.
Logging
- Linux: support
Deployment logging
Feature a flag has two parts: a name and a list of one or more filters that are used to evaluate if a feature's state is on.
Types
1. Web apps
host web apps
2. API apps
host REST APIs
- Full Swagger support and the ability to package and publish API in Azure Marketplace.
- Consumed from any HTTP- or HTTPS-based client.
3. Mobile apps: back end for iOS and Android apps.
Store mobile app data in a cloud-based SQL database.
- Authenticate customers against common social providers, such as MSA, Google, Twitter, and Facebook.
- Send push notifications.
- Execute custom back-end logic in C# or Node.js.
- On the mobile app side, there's SDK support for native iOS and Android, Xamarin, and React native apps.
4. WebJobs: run background tasks as part of your application logic
- run a program (.exe, Java, PHP, Python, or Node.js) or script (.cmd, .bat, PowerShell, or Bash) in the same context as a web app, API app, or mobile app.
- They can be scheduled or run by a trigger
Configure application settings
In App Service, app settings are variables passed as environment variables to the application code. For Linux apps and custom containers, App Service passes app settings to the container using the --env flag to set the environment variable in the container.
App Service plan.
An App Service plan defines a set of compute resources for a web app to run.
App Service plan defines:
- Operating System (Windows, Linux)
- Region (West US, East US, etc.)
- Number of VM instances
- Size of VM instances (Small, Medium, Large)
- Pricing tier (Free, Shared, Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, PremiumV3, Isolated)
Hosting Pricing Tier
1. Shared tier
share the resource pools of app with the apps of other customer
- allocate CPU quotas to each app
- Resources can't scale out.
- Type:
Free, Shared - Use Case: Dev & Testing.
2. Dedicated compute tiers
run apps on dedicated Azure VMs.
Type: Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, PremiumV3
3. Isolated
runs dedicated Azure VMs on dedicated Azure Virtual Networks.
- Provides network & compute isolation
- Provides the maximum scale-out capabilities.
Type:
Isolated and IsolatedV2
4. Consumption
Only available to function apps.
- Scales the functions dynamically depending on workload.
Deployment Mode
Use deployment slots: Dev/test or Staging/ Production
- The swap between slots warms up the necessary worker instances to match production scale, thus eliminating downtime.
- By default, new slots are given a routing rule of
0% - To route traffic to deployment use:
x-ms-routing-name=stagingfor staging orx-ms-routing-name=selffor production
1. Automated deployment
Deploy Web Service directly form CI/CD Pipeline
- Sources:
Github, Azure DevOpes, Bitbucket
2. Manual Deployment
Manually push your code to Azure
- Sources:
Github, Azure CLI, Zip deploy using Curl, FTP/S
Authentication
out of the-box authentication with federated identity providers
-
Built directly into the platform and doesn’t require any particular language, SDK, security expertise, or even any code to utilize.
Network Feature
- By default, apps hosted in App Service are accessible directly through the internet and can reach only internet-hosted endpoints.
Deployment types
Network Feature Depends on Deployment type
1. Multi-tenant
service hosts App Service plans in the Free, Shared, Basic, Standard, Premium, PremiumV2, and PremiumV3 pricing SKUs.
| Control Inbound Network | Control Outbound Network |
|---|---|
| App-assigned address | Hybrid Connections |
| Access restrictions | Gateway-required virtual network integration |
| Service endpoints | Virtual network integration |
| Private endpoints |
2. Single-tenant App Service Environment (ASE)
hosts Isolated SKU App Service plans directly in Azure VNet.
Azure Virtual Desktop
desktop and application virtualization service that runs on the cloud.
- Cloud-hosted version of Windows from any location on any devices
- Connect using Azure Virtual Desktop client or modern Web Browser
- Support: Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and Linux.
- 1-3 YearAzure Reserved Virtual Machine Instances save 72 % versus pay-as-you-go pricing.
- You can pay for a reservation up front or monthly.
- Save cost by using existing Windows license
Security
- centralized security management for users' desktops with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
- secure access to data by assigning granular role-based access controls (RBACs) to users.
- User sessions are isolated in both single and multi-session environments.
Service Fabric
Distributed systems platform that makes it easy to package, deploy, and manage scalable and reliable microservices and containers.
-
Service Fabric is Microsoft's container orchestrator for deploying and managing microservices across a cluster of machines, benefiting from the lessons learned running Microsoft services at massive scale.
-
Can deploy applications in seconds, at high density with hundreds or thousands of applications or containers per machine.
-
Mix both services in processes and services in containers in the same application.
Enables low-touch workflows to provision, deploy, patch, and monitor applications lifecycle management.
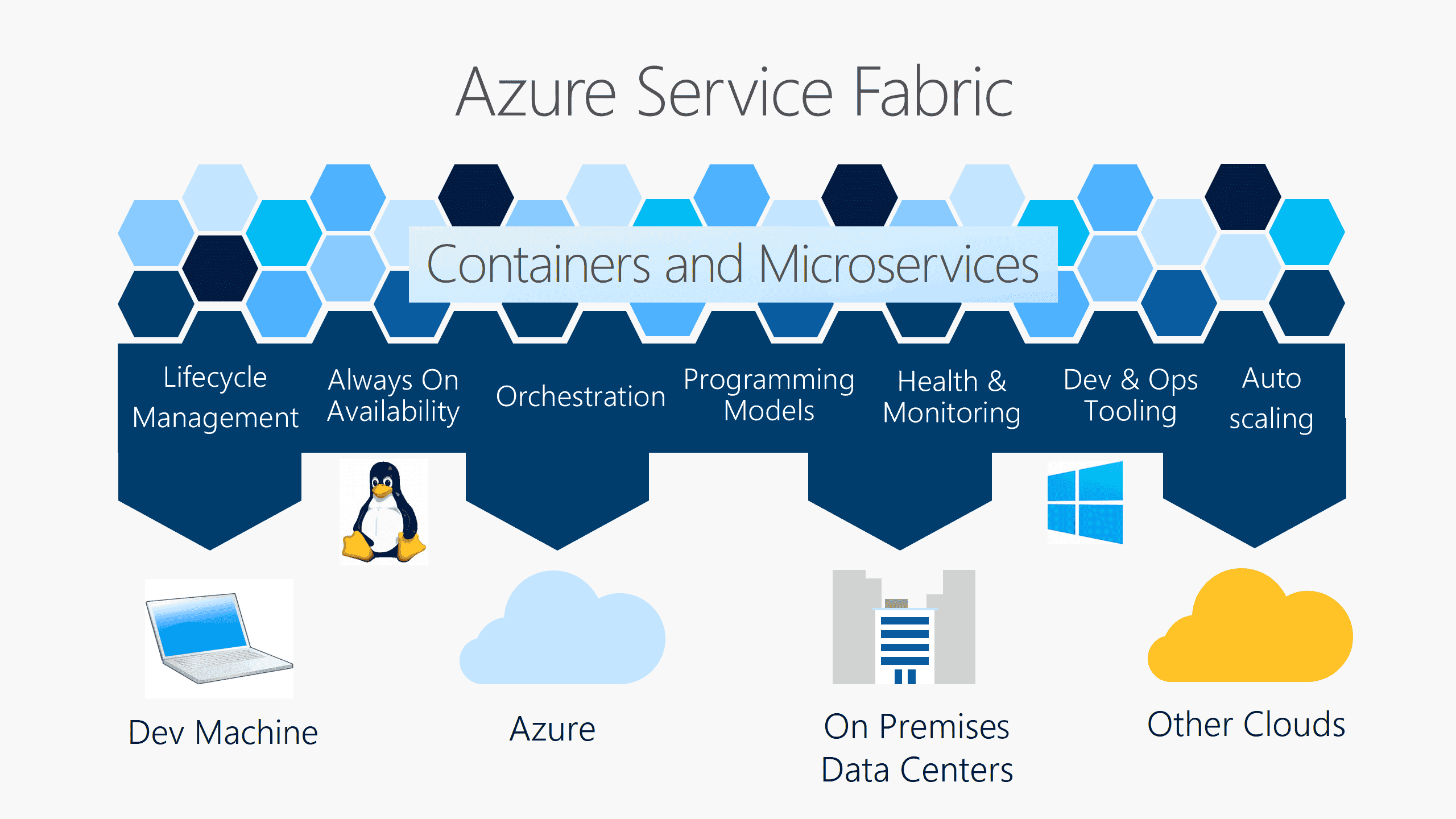
-
Supports the deployment of multiple application instances.
-
A service fabric cluster is a set of virtual machines into which your microservices are deployed and managed.
-
Build microservices and container-based applications using the programming language of your choice, including .NET Core 2.0, C #, and Java.
Supports two types of microservices:
Stateless
Doesn't maintain a mutable state outside a request and its response from the service such as protocol gateways and web proxies.
Stateful
Maintains a mutable, authoritative state beyond the request and its response.
Security
- Create or import a certificate using Azure Key Vault.
- Use Azure Firewall to complement your existing Network Security Group rules to control access to your cluster.
Pricing
- You are charged based on the number of vCPU and GBs of memory allocated to each VMs.
- You are charged based on the size, number of disks, and number of outbound data transfers.
Appendix
| Compute | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autoscaling | AWS EC2 Auto Scaling | Azure Autoscale, Azure virtual machine scale sets | Managed instance groups (MIGs) |
| Batch scheduling, executing and processing | AWS Batch | Azure Batch | Batch on GKE (preview), Cloud Scheduler |
| Functions as a service | AWS Lambda | Azure Functions | Cloud Functions |
| 5G-based infrastructure | AWS Wavelength | Azure Edge Zones | Global Mobile Edge Cloud (GMEC) |
| High performance computing cluster management | AWS ParallelCluster | Azure CycleCloud, Azure FXT Edge Filer | N/A |
| VM image builder | EC2 Image Builder | Azure VM Image Builder | N/A |
| Isolated servers | Dedicated Instances | Azure Dedicated Host | Sole-tenant Nodes, Shielded VMs |
| PaaS | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS | App Service, Azure Cloud Services, Azure Spring Cloud, Azure Red Hat OpenShift | App Engine |
| On-premises/edge devices | AWS Outposts, AWS Snow Family | Azure Modular Datacenter, Azure Stack Hub, Azure Stack HCI, Azure Stack Edge | N/A |
| Quantum computing | Amazon Braket | Azure Quantum (preview) | N/A |
| Virtual machines | Amazon EC2 | Virtual Machines | |
| Virtual private server | Amazon Lightsail | N/A | N/A |
| VMware integration | VMware Cloud on AWS | Azure VMware Solution | VMware Engine |