Serverless Computing
Azure takes care of managing the server infrastructure and the allocation and deallocation of resources based on demand.
-
Abstraction of servers: Serverless computing abstracts the servers you run on. Infrastructure isn't your responsibility.
-
No need reserve capacity. Scaling and performance are handled automatically.
-
Pay as go: billed only for the exact resources you use.
-
Event-driven scale: excellent fit for workloads that respond to incoming events.
- Timers: run task in timely manner
- HTTP: run task in respond to API and webhook scenarios.
- Queues: order processing.
Functions
run a small piece of code to do a task in response to an event (often via a REST request), timer, or message from another Azure service,
-
A single task is performed for each invocation.
-
Each function execution can run on a different compute instance. This execution context is transparent to the code.
-
Supported languages:
C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, and PowerShell
Features
-
Serverless: meant to be short-lived and stateless tasks
-
Scalable & Highly Available: The platform automatically schedules the function to run and scales the number of compute instances based on the rate of incoming events.
-
Micro-billing: With serverless computing, pay only for the time code runs. .
-
UseCase: when that work can be completed quickly, within seconds or less eg Image or order processing, file maintenance, or for any tasks that you want to run on a schedule
Components:
The Function contains both code and metadata about its triggers and bindings.
Function = Code + Config file
Function app
provides an execution context in Azure in which your functions run.
- it is the unit of deployment and management for your functions. A way to organize and collectively manage your functions.
- Comprised of one or more individual functions that are managed, deployed, and scaled together.
- All of the functions in a function app share the same pricing plan, deployment method, and runtime version.
Config function.json file
define the function's trigger, bindings, and other configuration settings.
-
The runtime uses this config file to determine the events to monitor and how to pass data into and return data from a function execution.
{ "bindings": [ {"type": "queueTrigger", "direction": "in", "name": "order", "queueName": "myqueue-items", "connection": "MY_STORAGE_ACCT_APP_SETTING" }, {"type": "table", "direction": "out", "name": "$return", "tableName": "outTable", "connection": "MY_TABLE_STORAGE_ACCT_APP_SETTING" } ]}
Triggers
Triggers are what cause a function to run. A trigger defines how a function is invoked.
-
payload: associated data with trigger provided to function.
-
1:1 : Every function has one and only one trigger.
Bindings
provide a declarative way to connect to services from within the code.
-
bindings may be connected as input bindings
in, output bindingsout, or bothinout. -
Data from bindings is provided to the function as parameters.
-
"name": custom binding name
-
"type": Trigger type,
-
"direction": determine binding is used for receiving/sending data to/from the function.
Host Config host.json file
contains runtime-specific configurations and is lies in the root folder of the function app.
Scaling options
- Support GA on both Linux and Windows VMs.
- Scaling is depend on Hosting Plan
functionAppScaleLimit- Sets Max number of instances: 0 or null = unrestricted,- New instance rate: rate of allocation of new Instances
- For HTTP triggers: atmost Once/Sec
- For non-HTTP triggers: at most once/ 30Sec.
Scale controller
monitor the rate of events and determine whether to scale out or scale in.
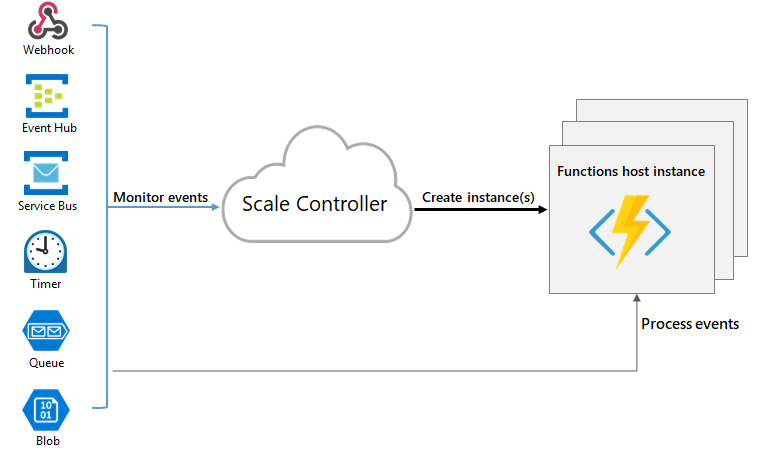
1. Consumption plan
- Default Option
- pay as go.
- Scales automatically: Functions host Instances are dynamically added and removed based on the number of incoming events.
Limits
1.5 GBRAM & 1 CPU- 10 minutes for a single execution
- Scale up to 200 Instances
2. Functions Premium plan
- Always ready instances: Avoid cold starts with perpetually warm instances
- Unlimited execution duration, with 60 minutes guaranteed.
- Virtual network connectivity.
- Premium instance sizes: one core, two core, and four core instances.
- More predictable pricing, compared with the Consumption plan.
- High-density app allocation for plans with multiple function apps.
Limit
- Scale up to 100 Instances
- Processing power depend on Plan
| SKU | Cores | Memory Storage |
|---|---|---|
| EP1 1 | 3.5GB | 250GB |
| EP2 2 | 7GB | 250GB |
| EP3 4 | 14GB | 250GB |
3. App service (Dedicated) plan
Run functions within an
App Serviceplan at regular App Service plan rates.
Predictive scaling and costs
- Scale Automatic or Manual but Auto scaling rate is lower than other 2 plans
- Run functions within an
App Serviceplan at regular App Service plan rates.
Best for long-running scenarios where Durable Functions can't be used.
- Reuses existing, underutilized VMs running other App Service instances.
- Predictive scaling and costs are required.
Running Function in Isolation:
For highest amount of control and isolation
1. App Service Environment (ASE)
Provides a fully isolated and dedicated environment for securely running
App Serviceapps at high scale.
- Very high scale.
- Full compute isolation and secure network access.
- High memory usage.
2. Kubernetes
Fully isolated and dedicated environment running on Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaling(
KEDA)
- Custom hardware requirements.
- Isolation and secure network access.
- Ability to run in hybrid or multi-cloud environment.
- Run alongside existing Kubernetes applications and services.
Managing State
Function App requires Azure Storage account(Blob, Queue, Files, and Table storage) for logging function, triggers and bindings to store your application data.
- Function code files are stored on Azure Files shares on the function's main storage account.Function code files cant be recovered after deleting the main storage.
1. Stateless(Default):
they behave as if they're restarted every time they respond to an event.
2. Stateful (Durable Functions)
An extension lets manages state, checkpoints, and restarts
- a context is passed through the function to track prior activity.
Allows defining stateful workflows by writing orchestrator functions and stateful entities by writing entity functions using the Azure Functions programming model.
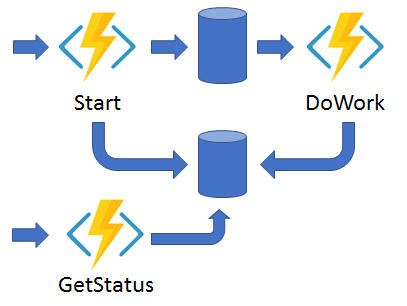
1. Function chaining:
The Output of one Fn is applied to the input of another Fn.

2. Fan in /out
Execute multiple functions in parallel and then wait for all functions to finish

3. Async HTTP APIs
Coordinating the state of long-running operations and respond back to Client
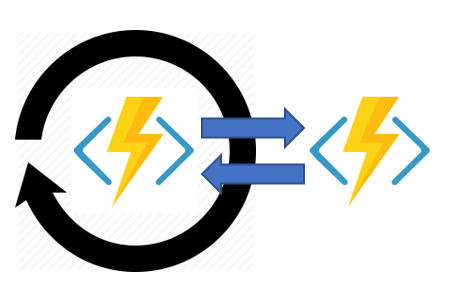
4. Monitor
Polling until specific conditions are me
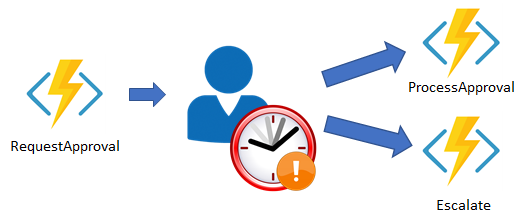
5. Human interaction
wait for human input or escalate
Durable function types
1. Orchestrator functions
functions describe how actions are executed and the order in which actions are executed.
- Written in
C# or JavaScript - Code must follow Constrains
- triggered by an orchestration trigger binding
2. Activity functions
basic unit of work in orchestration function
- Can have only a single value passed to them. To pass multiple values, you must use tuples, arrays, or complex types.
- may be executed serially, in parallel, or some combination of both.
- Uses an activity trigger
3. Entity functions
define operations for reading and updating small pieces of state
- manage state explicitly into stateful entities
- triggered by an entity trigger binding.
3. Client functions
Triggers Orchestrator and entity functions triggers
WebJobs SDK
Code-first integration service that is designed for developers.
Azure Functions is built on the WebJobs SDK but function provider better features
| feature | Functions | WebJobs |
|---|---|---|
| Serverless with AutoScaling | Yes | No |
| Develop/test in browser | Yes | No |
| Pay-per-use | Yes | No |
| Logic Apps Integration | Yes | No |
| Trigger | Timer, Storage queues and blobs, Service Bus queues and topics, Cosmos DB, Event Hubs, HTTP/WebHook (GitHub Slack), Azure Event Grid | Timer, Storage queues and blobs, Service Bus queues and topics, Cosmos DB, Event Hubs, File system |
Logic App
Allows you to automate your workflows without writing a single line of code
- integration platform as a service (iPaaS): built on a containerized runtime.
- Deploy and run Logic Apps anywhere to increase scale and portability while automating business-critical workflows anywhere.
Logic app designer: Visual designer on the Azure portal or in Visual Studio to create workflows which will be
persisted as a JSON.
Actions steps that happen after the trigger and perform tasks in the workflow of your logic app.
- It Can include data conversions and flow controls, such as conditional statements, switch statements, loops, and branching.
Workflow helps creating a series of Actions
Trigger is the first step to run your logic app.
Managed connectors allows to access and work with your data.
Enterprise Integration Pack allows you to create an automated, scalable enterprise integration workflow.
| Param | Functions | Logic Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Code-first (imperative) | Designer-first (declarative). |
| Purpose | write code to complete each step. | Use a GUI to define the actions and how they relate to one another. |
| State | Stateful Steless(Default) & Stateful | Stateful |
| Connectivity | built-in 10+ binding types, custom bindings. | Large collection of connectors. Enterprise Integration Pack for B2B scenarios. |
| custom bindings. | yes | yes |
| Actions | Each activity is an Azure function. Write code for activity functions | Large collection of ready-made |
| Monitoring | Azure Application Insights | Azure portal, Log Analytics. |
| Management | REST API, Visual Studio. | REST API, Visual Studio. PowerShell, Azure portal, |
| Execution context | Can run locally or in the cloud | Runs only in the cloud. |
