STORAGE
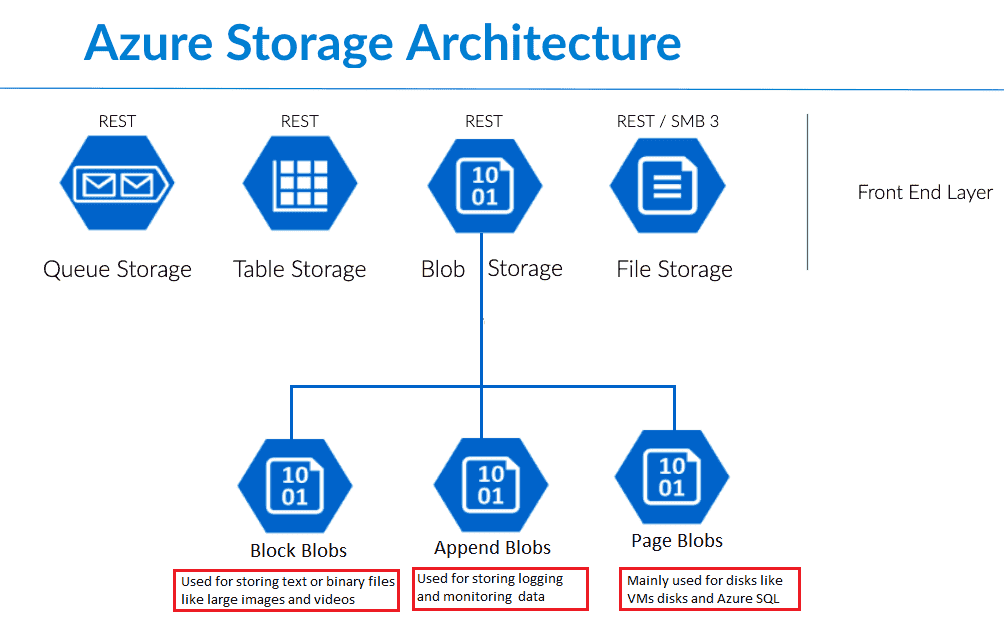
Azure storage account 
contains all of Azure Storage data objects: blobs, file shares, queues, tables, and disks.
- provides a unique namespace for Azure Storage data that's accessible from anywhere over HTTP or HTTPS.
- Data in storage account is durable and highly available, secure, and massively scalable.
Storage account names convention
- Storage account names must be between
3-24 characters in length - may contain numbers and lowercase letters only.
- must be unique within Azure. No two storage accounts can have the same name.
| Storage service | Endpoint | Usage | Redundancy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blob Storage | https:// | Very large objects | LRS, GRS, RA-GRS, ZRS |
| Azure Files | https:// | file server. | LRS, GRS |
| Queue Storage | https:// | Messages | LRS, GRS, RA-GRS |
| Table Storage | https:// | NoSQL data | LRS, GRS, LA-GRS |
| Data Lake Storage Gen2 | https:// |
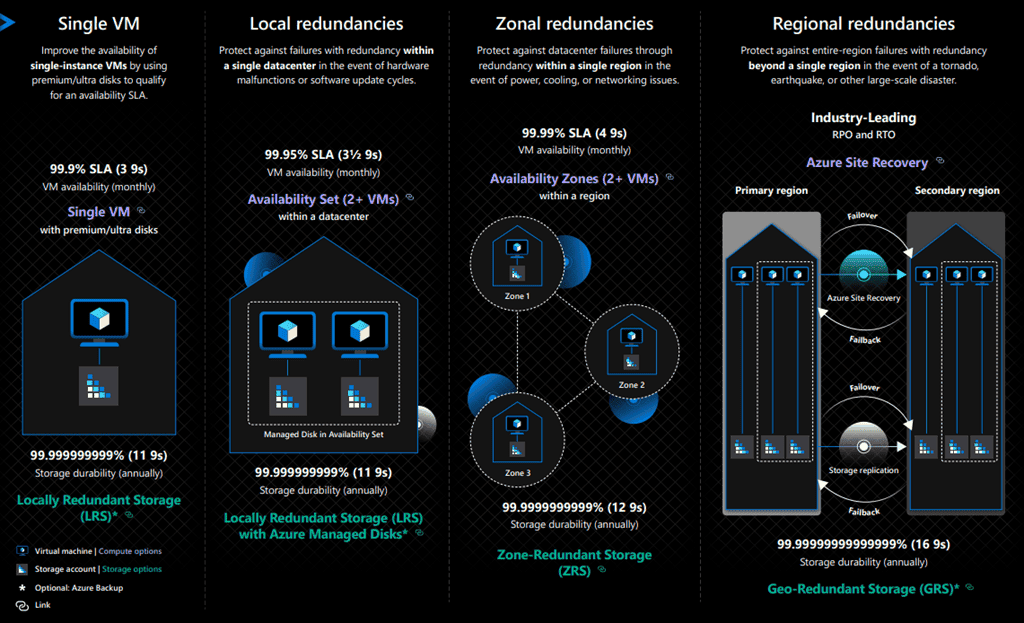
Redundancy Options
Data in an Azure Storage account is always replicated three times in the primary region.
1. Locally redundant storage (LRS)
3 copies of each file in one building but 3 different places
- Synchronously copies data 3X times within a single physical location in the primary region.
- lowest-cost redundancy option but offers the least durability
- Not recommended for data requiring high availability or durability
- 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability of objects over a given year.
2. Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
3 copies in one building, 3 copies in the other
- Synchronously copy data to 3X within a single physical location in the primary region using LRS.
- Asynchronously copies data to a single physical location in a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region.
- Write is first committed to the primary location and replicated using LRS.
- Update is then replicated asynchronously to the secondary region. When data is written to the secondary location, it's also replicated within that location using LRS.
- 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) over a given year.
2. Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
3 copies in 3 AVZ
- Synchronously copy across 3X Azure AVZ in the primary region.
- high availability: data is still accessible for R/W even if 1 zone becomes unavailable.
- 99.9999999999% (12 9's) durability for storage resources over a given year.
- Excellent performance, low latency
- May not protect your data against a regional disaster where
4. Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS)
3 copies in 3 AVZ X 2 Regions
- Redundancy across AVZ with protection from regional outages provided by geo-replication.
- Data is copied across 3X AVZ in the primary region & is replicated to a secondary geographic region for protection from regional disasters.
- Continue to R/W if 1 AVZ becomes unavailable or is unrecoverable.
- Data is also durable in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region isn't recoverable.
- Maximum consistency, durability, and availability, excellent performance, and resilience for disaster recovery.
- 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) durability of objects over a given year.
5. Read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) & Read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS)2
- When RA to the secondary is enabled, app can read from the secondary endpoint as well as from the primary endpoint.
- When RA is disabled, app can read from secondary only if Primary is failed
Availability in Outage Scenario
| Outage | LRS | ZRS | GRS/RA-GRS | GZRS/RA-GZRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Node in Data Center | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Entire Data Center / AVZ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Primary region | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| RA in sec region | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ (with RA-GRS) | ✅ (with RA-GZRS) |
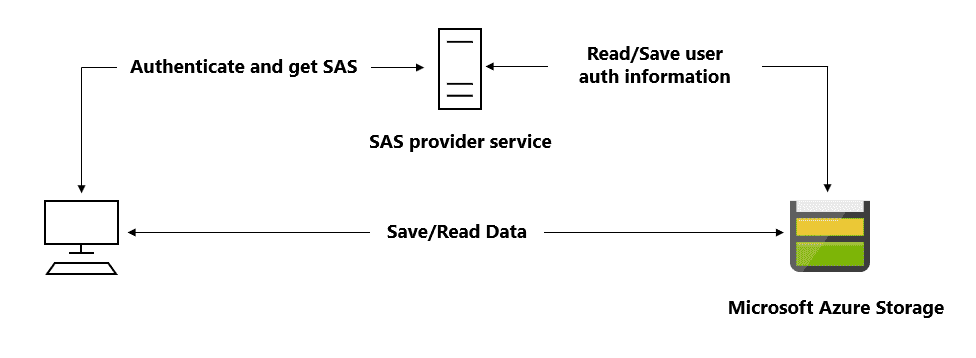
Shared Access Signatures(SAS)
pre-signed URI that points provide authorize access to one or more storage resources
Contain URL + SAS Token
https://medicalrecords.blob.core.windows.net/patient-images/patient-116139-nq8z7f.jpg?sp=r&st=2020-01-20T11:42:32Z&se=2020-01-20T19:42:32Z&spr=https&sv=2019-02-02&sr=b&sig=SrW1HZ5Nb6MbRzTbXCaPm%2BJiSEn15tC91Y4umMPwVZs%3D
- Token indicates how the resources may be accessed by the client.
| Param | Meaning | Values |
|---|---|---|
sp=acdlrw | Share Permission | a: add, c: create, d: delete, l: list, r: read, or w: write. |
| st=2020-01-20T11:42:32Z | share Time | |
| se=2020-01-20T19:42:32Z | Share Expiry Time | |
| sv=2019-02-02 | Share Version | |
| sr=b | storage resource | b: blob |
| sig=SrW1HZ5Nb6M | signature |
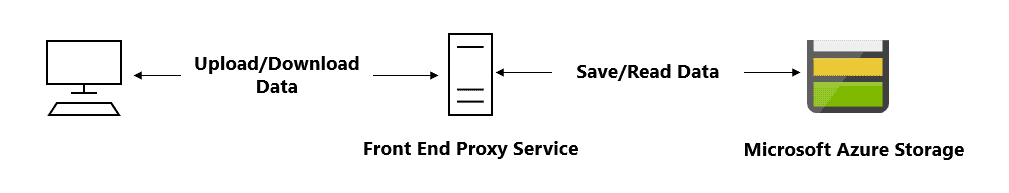
SAS mitigates the need for routing all data through the front-end proxy service.
SAS Signature Type
1. User delegation SAS
secured with AAD credentials and also by the permissions specified for the SAS.
- Blob storage only.
- Most secure SAS: use it wherever possible
2. Service SAS:
secured with the storage account key.
- Blob storage, Queue storage, Table storage, or Azure Files.
3. Account SAS
secured with the storage account key.
- delegates access to resources in one or more of the storage services.
Best practices
- Always use HTTPS.
- The most secure SAS is a user delegation SAS.
- Set expiration time to the smallest useful value.
- Only grant the access that's required.
- When there's an unacceptable risk of using a SAS, Create a middle-tier service to manage users and their access to storage for validation.
Stored access policy
provides an additional level of control over service-level SAS on the server side
- change the 3 Params or revoke it after it has been issued.
- start time
- expiry time
- permissions for a signature,
- maximum of 5 access policies may be set any given time.
- Works with:
Blob containers: Container ACLFile shares: Share ACLQueues: Queue ACLTables: Table ACL
Azure DISK STORAGE(DS) 
High-performance, durable block storage for Azure Virtual Machines
- Designed to be used with Azure Virtual Machines and Azure VMware Solution (in preview),
- High-performance: sub-millisecond latency for throughput and transaction-intensive workloads such as SAP HANA, SQL Server, and Oracle.
- Durable block storage for mission- and business-critical applications.
Terminology
IOPS; Number of requests that your application sends to the disks in one second.
Throughput/ data transfer rate(MBps). amount of data that application sends to the disks in a specified interval.
IOPS × I/O size = Throughput.
Latency time delay between request to the disk and receive a response.
VM I/O capping.: disk can manage throughput and IOPS requirement, but the VM can't accommodate these requirements.
disk I/O capping, disk can't meet the application demands.
Read caching: speed up data retrieval by caching frequent used data in fast cache and return from it.
Write caching: speed up write by adding data to Cached Queue for writing data later.
Disk bursting Increase performance for short interval
1. Credit-based bursting model :
Premium SSD <=512-GB, &Standard SSD <=1TB.- free and enabled by default on
- Use accumulated credit to burst disk for
30 MinuteMax
2. On-demand bursting model (preview):
Premium SSD >512 GB- paid service but no time limitation
Storage Tier
1. Ultra Disk Storage
Highest disk performance.
- performance depends on the size
4 GB-64TB.- independently configure the size, IOPS, and throughput of the disk.
- Can adjust the IOPS and throughput while disk is sill hot
Limitations
- Available only in a subset of Azure regions.
- Work only with VMs in AVZ
- Work only as data disks and as empty disks.
- Doesn't support disk snapshots, VM images, virtual machine scale sets, Azure Disk Encryption, Azure Backup, or Azure Site Recovery.
- Doesn't support cached R/W
2. Premium SSD
provide high throughput and IOPS with low latency
- Slightly lower performance vs Ultra Disk but don't have limitations of Ultra Disk
- Designed to provide consistent performance figures
- Available in all regions
- Work with VMs outside AVZ
- Need to detach from VM to change Throughput Performance
- Disk bursting: supported
- UseCase: when highest possible performance needed, but cant use Ultra Disk because of its current limitations.
3. Standard SSD
cost-effective storage option for VMs that need consistent performance at lower speeds
- provide single-digit millisecond (ms) latencies
- up to
6k IOPS & 750 MB/s of throughput. - Works with any VM
- Disk Bursting: supported on P30 disks and smaller disks.
- Use case: budgetary constraints and a workload that isn't performance-intensive.
4. Standard HDD
Use conventional magnetic disk drives that have moving spindles.
- write latencies under 10 ms and read latencies under 20 ms
- Works with any VM
- Use case: minimize costs for less critical workloads and development or test environments.
 Azure FILE STORAGE
Azure FILE STORAGE
Simple, secure and serverless enterprise-grade cloud file shares
- Can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit using
SMB 3.0and HTTPS. - Must have access to
port 445 - Can be cached on Windows Servers with
Azure File Syncfor fast access near where the data is being used.
Protocol Support
1. Server Message Block (SMB) protocol
- Windows, Linux, & macOS .
2. Network File System (NFS) protocol
- Linux or macOS
Storage Tiers
If you created either a premium or a standard file share, you cannot automatically convert it to the other tier.
1. Standard file shares (HDD)
- Reliable performance for IO workloads which are less latency-sensitive.
- LRS, ZRS, GRS, GZRS
- 5 TiB by default, 100 TiB for LRS or ZRS storage accounts.
2. Premium file shares (SSD)
- High performance & low latency, within single-digit milliseconds for most IO operations.
- For IO-intensive workloads.
- LRS, ZRS
- upto 100 TiB.
Azure NetApp Files
Enterprise file storage, powered by NetApp
Azure Table Storage
A NoSQL key-value store for large semi-structured dataset
- replicated 3X within a region using geo-redundant storage
Entity: Building block of table max1MBin size.- Scale automatically as demand grow
- Use Case: Store data sets that do not require complex joins, foreign keys, or stored procedures, and can be denormalized for fast access.
 Azure Queue Storage
Azure Queue Storage
storing large numbers of messages which can be access messages from anywhere in the world via authenticated calls using HTTP or HTTPS
- Use case: Asynchronous message queueing to communicate between components of the application.
Queue: A queue contains a set of messages.
- The queue name must be all lowercase
Message: In any format, of up to 64 KB.
- Default TTL:
7 days. - Max TTL:
7 dayBefore version 2017-07-29. Version 2017-07-29 or later be any positive number or-1indicating that the message doesn't expire.
 Azure BLOB STORAGE (Binary Large OBject)
Azure BLOB STORAGE (Binary Large OBject)
Massively scalable and secure object storage for cloud-native workloads
- Accessible over
HTTP/S - Access by:
Azure Storage REST API, Azure PowerShell, Azure CLI, or an Azure Storage client library. - Use Case:Stores all types of files:
- image, video, audio,
- log files backups, disaster recovery, and archiving.
Versioning
Identified by a version ID
- Enable versioning and restore an earlier version of a blob to recover your data.
- If you disable the versioning of the blob, it does not delete existing blobs, versions, or snapshots. Azure simply wont add versions to new files
Terminology
Storage Account: Unique namespace in Azure for your dataContainer: hold blobs directory in a file system.
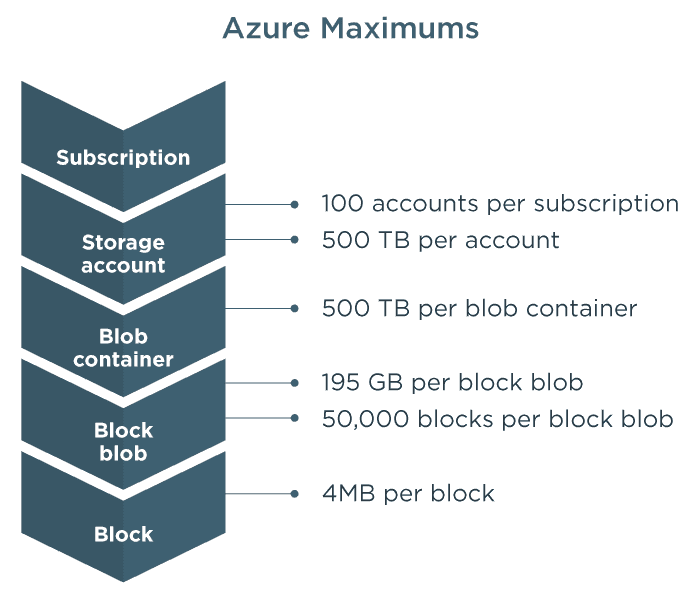
Blob Types
1. Standard
Standard general-purpose v2account
- UseCase:: for most scenarios using Azure Storage.
2. Premium
Higher performance by SSD
- UseCase:: High transactions rates, or scenarios that use smaller objects or require consistently low storage latency.
2.1. Block
- Store binary and text data up to
4.7 TB. - Preview larger block blobs up to 190.7 TiB
2.2 Append
- Ideal for logging data from virtual machines
2.3. Page
- Random Access files
- Upto:
8 TBin size - Store
virtual hard drive (VHD)files
BLOB Access Tiers
Data storage limits are set at the account level and not per access tier. You can choose to use all of your limit in one tier or across all three tiers.
1. Hot
Frequently accessed objects
- Most cost-effective, while storage costs are higher
- Default in new Storage Accounts
2. Cool
Infrequently accessed data
- More cost-effective, but higher access cost than hot tier
- Storage Duration: at least
30 days
3. Archive
Rarely accessed files for archiving.
- Lowest cost for storing data
- Highest access cost: To read data in archive storage, you need to change the blob tier to hot or cold first.
- Immutable: Data cant be overridden
- Storage Duration: at least
180 days - Can be copied within the same storage account.
- Encrypted at rest & transit using HTTPS & AES 256
- Use case: Long-term backup, secondary backup, and archival datasets
Rehydrate Archive
To read data in archive storage, you need to change the blob tier to hot or cold first.
Two options for rehydrating a blob:
1. Copy Blob or Copy Blob from URL
Copy an archived blob to new hot or cool tier blob.
- Microsoft recommends this option for most scenarios.
2. Set Blob Tier operation.
Change a blob's access tier to an online tier.
- Set Blob Tier request is initiated, it cannot be canceled.
Rehydrate Priority
1. Standard (Default)
- take up to
15 hours.
2. High
1 hourfor objects under10 GBin size.
Lifecycle Management Policy
Collection of rules/policy in a
JSONdocument. Can be added using:
- Azure portal
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure CLI
- REST APIs
Features
- Transition blobs to a cooler storage tier (hot to cool, hot to archive, or cool to archive)
- Delete blobs at the end of lifecycles
- Define rules to be run once per day at the storage account level
- Apply rules to containers or a subset of blobs (using prefixes as filters)
Rules
filter set: limits rule actions to a certain set of objects within a container or objects names.
action set applies the tier or delete actions to the filtered set of objects.:
{
"rules": [
{
"name": "ruleFoo",
"enabled": true,
"type": "Lifecycle",
"definition": {
"filters": {
"blobTypes": [ "blockBlob" ],
"prefixMatch": [ "container1/foo" ]
},
"actions": {
"baseBlob": {
"tierToCool": { "daysAfterModificationGreaterThan": 30 },
"tierToArchive": { "daysAfterModificationGreaterThan": 90 },
"delete": { "daysAfterModificationGreaterThan": 2555 }
},
"snapshot": {
"delete": { "daysAfterCreationGreaterThan": 90 }
}
}
}
}
]
}
Other Storage Options
Azure Data Lake Storage 
Massively scalable and secure data lake for your high-performance analytics workloads
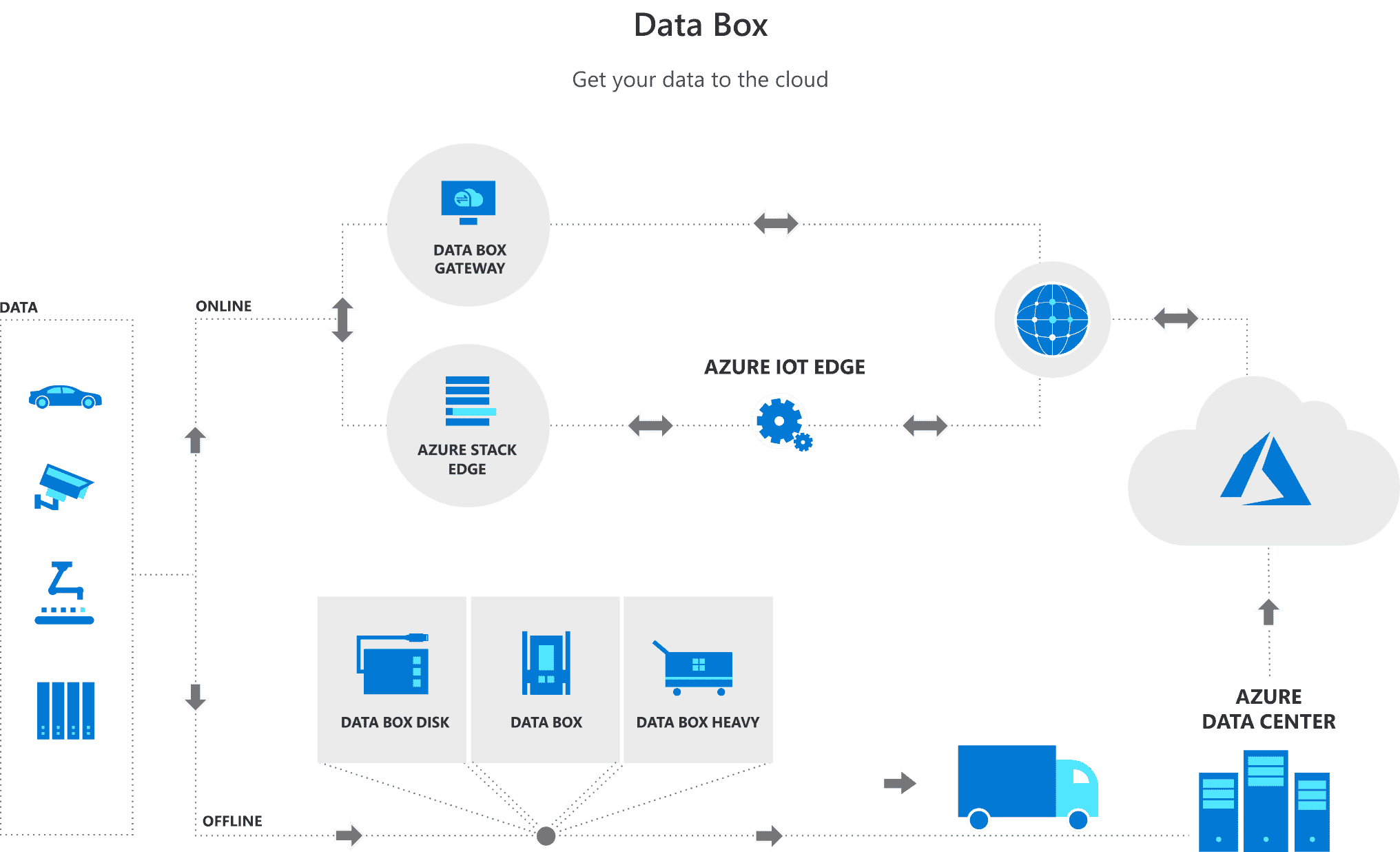
Data Box 
Brifcase to move terrabyte/petabyte of data to Azure and edge compute

Data Box
This ruggedized device with
100-TBcapacity uses standard NAS protocols and common copy tools.
- It features AES 256-bit encryption for safer transit.
Data Box Disk
Our
8-TB SSDwith a USB/SATA interface has 128-bit encryption.
- Packs of up to five for a total of 40 TB.
Data Box Heavy
This ruggedized, self-contained device is designed to lift
1 PBof data to the cloud.
Data Box Gateway
Transfers data to and from Azure—but it’s a virtual appliance.
Microsoft Azure Confidential Ledger
Store unstructured data that is completely tamper-proof and can be cryptographically verified
Appendix
| Storage | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Archival storage | S3 Glacier, S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Archive Storage | Archive Storage |
| Backup | AWS Backup | Azure Backup | N/A |
| Block storage | Amazon Block Store (EBS) | Azure Disk Storage | Persistent Disk, Local SSD |
| File storage | Amazon Elastic File Service (EFS), Amazon FSx for Windows File Server, Amazon FSx for Lustre | Avere vFXT for Azure, Azure Files, Azure NetApp Files, Azure FXT Edge Filer | Filestore |
| Object storage | Amazon S3 | Azure Blob Storage | Cloud Storage, Cloud Storage for Firebase |
