Azure Networking & Content Delivery
Overview of AWS Networking & Content Delivery Services with: Region, Availability Zone, Edge Location, VPC, Subnet, Route Table, NAT Gateway, VPN Gateway, Direct Connect, CloudFront, API Gateway, etc.
NETWORKING
 Azure Traffic Manager
Azure Traffic Manager
A DNS-based traffic load balancer.
Improves the responsiveness of your applications by sending the request to the closest endpoint.
- Reduce Latency: direct traffic to the endpoint with the lowest latency.
- Highly Available: It is resilient to failure.
- Health Checks: provides health monitoring for every endpoint to route traffic to healthy end points
- Failover: Offers automatic failover when an endpoint goes down.
Traffic Manager endpoints:
- Azure
- External
- Nested
Routing Methods
Combine multiple traffic-routing methods using nested traffic manager profiles.
1. Priority
allows you to set a primary endpoint for all traffic.
2. Weighted
distribute traffic according to weights.
3. Performance
routes users to the closest endpoint.
4. Geographic
direct users to a specific endpoint for data sovereignty mandates, localization of content
5. Multivalue
endpoints for IPv4/IPv6 addresses return all healthy endpoints.
6. Subnet
map a group of end-user IP address range to a specific endpoint.
Pricing
- You are charged based on the number of DNS queries received.
- You are also charged for each monitored endpoint.
- You can reduce your DNS query charges by configuring a larger TTL.
- You are charged for the number of data points used in the traffic view.
Virtual network (VNet)
A virtual network (VNet) allows to specify an IP address range for the VNet, add subnets, associate network security groups, & configure route tables.
When you create a VNet, you must specify a range of IPv4 addresses for the VNet in the form of a CIDR block (example: 10.0.0.0/16).
- A CIDR block must not overlap with any existing CIDR block that’s associated with your VNet.
- The 5 reserved addresses in each CIDR block is not available for you to use, and cannot be assigned to any virtual machines.
- You can add multiple subnets in each Availability Zone of your VNet’s region.
Subnet:
A subnet is a range of IP addresses in VNet.
- You can launch Azure resources into a specified subnet.
- Use a public subnet for resources that need to connect to the Internet
- private subnet for resources that won’t be connected to the Internet.
- To protect the Azure resources in each subnet, use network security groups.
Types of subnets:
- Public subnet
- Private subnet
- Gateway subnet
The CIDR block size of an IPv4 address is between a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses) and /29 netmask (8 IP addresses).
You can delegate a subnet to be used by a dedicated service.
Network Security Groups
Allow/Deny incoming/outgoing traffic of Azure resources.
-
Rules to allow or block traffic, based on factors
- such as source and destination IP address
- port
- protocol.
-
The rules are processed from lowest to highest numbers.
-
Rule number between 100 and 4096.
-
When you create a network security group, Azure assigns default security rules for inbound and outbound traffic.
Troubleshooting
- IP flow verify of Azure Network Watcher: check which network security rule allows or denies the traffic.
- VNet service endpoint policy: you can filter the egress VNet traffic to Azure Storage.
Network virtual appliances
Specialized VM that can be compared to a hardened network appliance.
- A network virtual appliance carries out a particular network function,
- running a firewall
- performing wide area network (WAN) optimization.
Between Azure resources
- A VM in Azure can connect to the internet by default using public IP of Load Balancer.
- Can be connected using Azure CLI, Remote Desktop Protocol, or Secure Shell.
1. Virtual network
can connect to other VMs, & other Azure resources
2. Service endpoints
Connect to other Azure resource types. This approach enables you to link multiple Azure resources to virtual networks to improve security and provide optimal routing between resources.
With on-premises resources
1. VPN Gateway
Sends encrypted traffic between an Azure virtual network and an on-premises location over the public Internet
Active-Standby Mode:
one IPsec tunnel is active and the other tunnel is in standby.
-
- public IP
- Traffic flows through the active tunnel, and if some issue happens with this tunnel, the traffic switches over to the standby tunnel.
Active-Active Mode
data flowing through both tunnels at the same time.
-
- public IPs.
- higher throughput.
VPN Gateway type
Policy-based vs. route-based VPN devices differ in how the IPsec traffic selectors are set on a connection
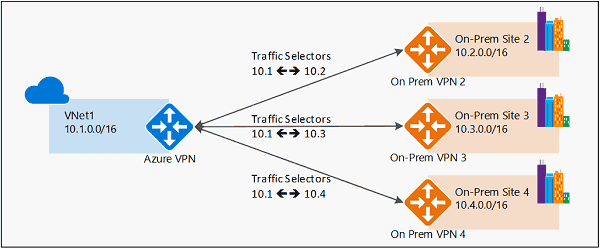
1. Policy-based routing (PBR)
a technique that forwards and routes data packets based on policies or filters.
- Network Admin can selectively apply policies based on
- source and destination IP address,
- source or destination port
- traffic type
- protocols
- access list, packet size,
- Used to segregate the traffic for deep inspection or analysis.
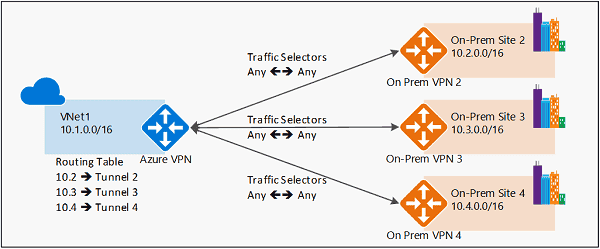
2. Route Based Routing (RBR)
any-to-any (wildcard) traffic selectors, and let routing/forwarding tables direct traffic to different IPsec tunnels.
- Use Routing table
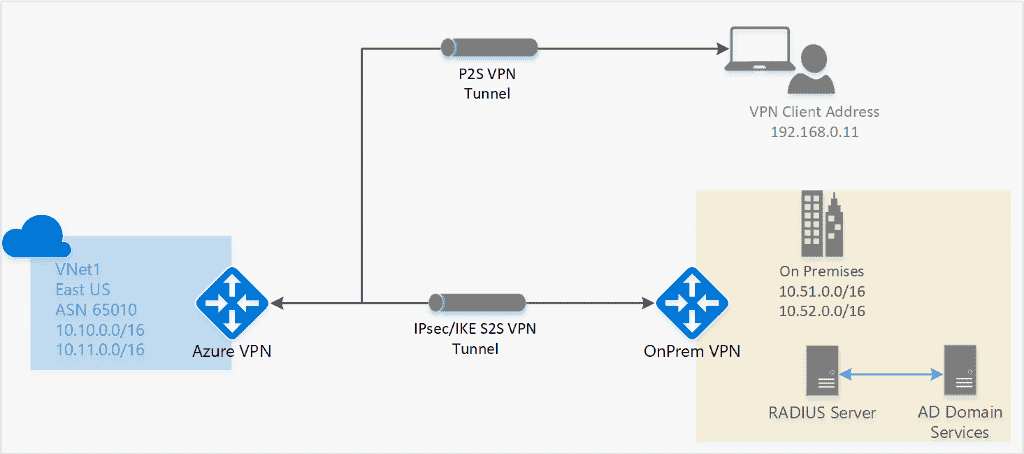
1.1 Point-to-site VPN (P2S)
secure connection to virtual network from an individual client computer
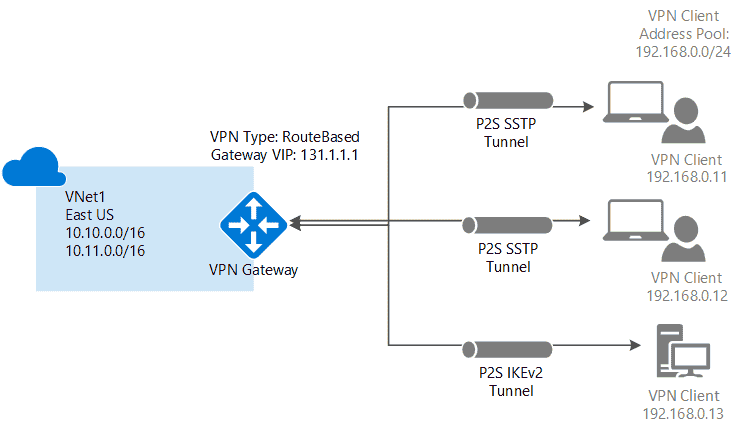
Protocol
OpenVPN® Protocol: an SSL/TLS based VPN protocol for Android, iOS (versions 11.0 and above), Windows, Linux, and Mac devices (macOS versions 10.13 and above).Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP): a proprietary TLS-based VPN protocol for Windows that have SSTP and support TLS 1.2 (Windows 8.1 and later).IKEv2 IPsec: connect from Mac devices (macOS versions 10.11 and above).
1.2. Site-to-site VPN
Links on-premises VPN device or gateway to the Azure VPN gateway in a virtual network.
- Devices in Azure can appear as being on the local network.
- The connection is encrypted and works over the internet.
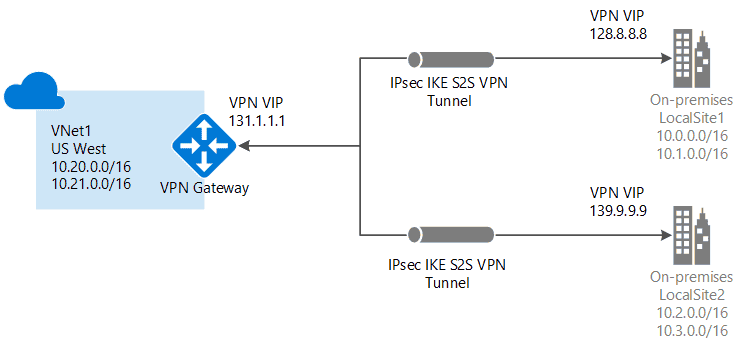
Protocol:
IPsec/IKE (IKEv1 or IKEv2)
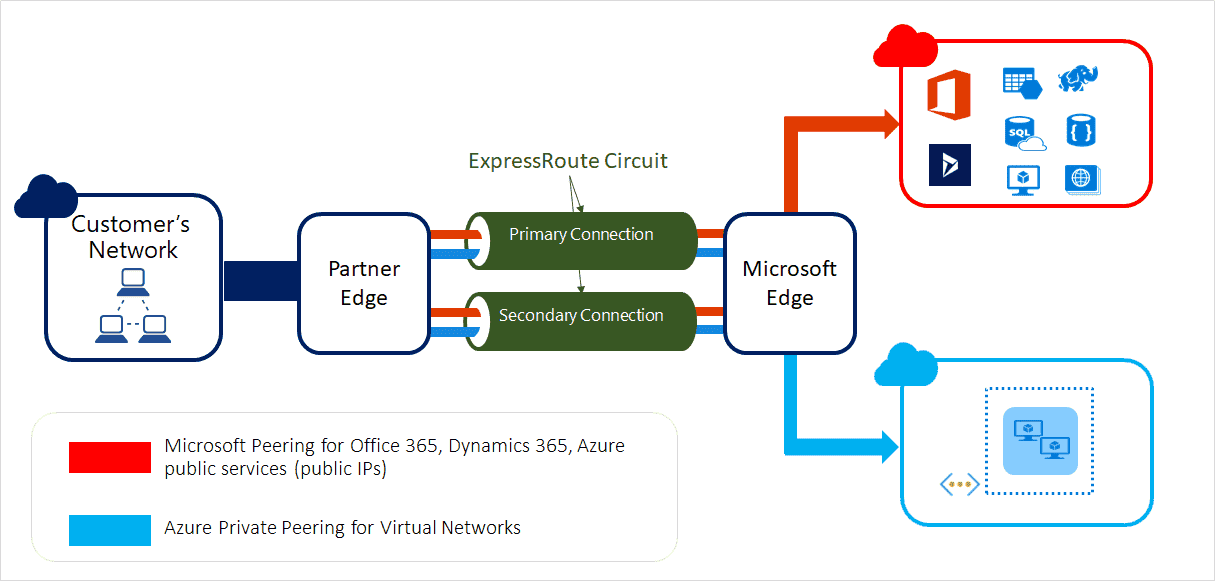
 2. Azure ExpressRoute
2. Azure ExpressRoute
Dedicated private connectivity to Azure that doesn't travel over the internet.
- Give greater bandwidth and even higher levels of security.
- The connection is redundant in every peering location for higher reliability.
- enable access to Microsoft Azure services and Microsoft Office 365 services from your on-premises network.
- Upto 100Gbps connectivity
- Supports Active/Active scale connectivity.
Use Cases
- Transferring large data sets.
- Real-time data feeds.
- regulatory requirements mandating the use of private connectivity.
| Param | Point-to-Site | Site-to-Site | ExpressRoute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure Supported Services | Cloud Services and Virtual Machines | Cloud Services and Virtual Machines | Services list |
| Typical Bandwidths | Based on the gateway SKU | Typically < 1 Gbps aggregate | 50 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps, 500 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps |
| Protocols Supported | SSTP, OpenVPN & IPsec | IPsec | Direct connection over VLANs, NSP's VPN technologies (MPLS, VPLS,...) |
| Routing | RouteBased (dynamic) | support PolicyBased (static routing) and RouteBased (dynamic routing VPN) | BGP |
| Connection resiliency | active-passive | active-passive or active-active | active-active |
| Typical use case | Secure access to Azure virtual networks for remote users | Dev / test / lab scenarios and small to medium scale production workloads for cloud services and virtual machines | Access to all Azure services (validated list), Enterprise-class and mission critical workloads, Backup, Big Data, Azure as a DR site |
 Azure Front Door
Azure Front Door
A service that uses Microsoft’s global network to improve the availability and performance of applications to your local and global users.
- provides fast, reliable, and secure access between users and your applications’ static and dynamic web content across the globe.
- Works at the HTTP/HTTPS layer & uses a split TCP-based anycast protocol
- Supports a range of traffic-routing methods and backend health monitoring options for various application needs and automatic failover models.
URL-based routing
Routes the traffic to backend pools based on URL paths of the request.
- Redirect traffic based on protocol, hostname, path, and query string with URL redirect.
- You can configure more than one website on the same Front Door with multiple-site hosting.
- Front Door supports end-to-end IPv6 connectivity and HTTP/2 protocol.
Session affinity
- Use cookie to redirect the user session to the same application backend.
- URL rewrite allows you to configure a Custom Forwarding Path that will copy any part of the incoming path that matches a wildcard path to the forwarded path.
Security
- If you need your domain name to be visible in your Front Door URL, you must have a custom domain. Front Door also supports managed certificates or custom TLS/SSL certificates.
- You can create custom rules to protect your HTTP/HTTPS workload from exploitation using Azure Web Application Firewall.
Pricing
- Inbound and outbound data transfers
- The number of routing rules
Routing
By default, Azure routes traffic between subnets on any connected virtual networks, on-premises networks, and the internet.
- Route tables
Allows you to define rules about how traffic should be directed.
- Creates custom route tables that control how packets are routed between subnets.
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Propagate on-premises BGP routes to Azure virtual networks.
- works with Azure VPN gateways, Azure Route Server, or ExpressRoute
Load Balancers
| Service | Load Balancer | Application Gateway | Traffic Manager | Front Door |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service | Network load balancer. | Web traffic load balancer | DNS-based traffic load balancer. | Global application delivery |
| Network Protocols | Layer 4 (TCP or UDP) | Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) | Layer 7 (DNS) | Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) |
| Type | Internal and Public | Standard and WAF | – | Standard and Premium |
| SKU | Basic and Standard | Standard and WAF (v1 & v2) | – | Standard and Premium |
| Routing | Hash-based, Source IP affinity | Path-based | Performance, Weighted, Priority, Geographic, MultiValue, Subnet | Latency, Priority, Weighted, Session Affinity |
| Global/Regional Service | Global | Regional | Global | Global |
| Recommended Traffic | Non-HTTP(S) | HTTP(S) | Non-HTTP(S) | HTTP(S) |
| Endpoints | NIC (VM/VMSS), IP address | IP address/FQDN, Virtual machine/VMSS, App services | Cloud service, App service/slot, Public IP address | App service, Cloud service, Storage, Application Gateway, API Management, Public IP address, Traffic Manager, Custom Host |
| Endpoint Monitoring | Health probes | Health probes | HTTP/HTTPS GET requests | Health probes |
| Redundancy | Zone redundant and Zonal | Zone redundant | Resilient to regional failures | Resilient to regional failures |
| SSL/TLS Termination | – | ✅ | – | ✅ |
| Web Application Firewall | – | ✅ | – | ✅ |
| Sticky Sessions | ✅ | ✅ | – | ✅ |
| VNet Peering | ✅ | ✅ | – | – |
| Pricing | Standard Load Balancer – charged based on the number of rules and processed data | Charged based on Application Gateway type, processed data, outbound data transfers, and SKU. | Charged per DNS queries, health checks, measurements, and processed data points. | Charged based on outbound/inbound data transfers, and incoming requests from client to Front Door POPs. |
# **Appendix**
| Networking | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Build, deploy and manage APIs | Amazon API Gateway | Azure API Apps, API Management | Apigee API Management Platform |
| Content delivery network | Amazon CloudFront | Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Cloud CDN |
| Dedicated fiber connection | AWS Direct Connect | Azure ExpressRoute | Cloud Interconnect |
| Domain name system | Amazon Route 53 | Azure DNS | Cloud DNS |
| Load balancing | Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) | Application Gateway, Load Balancer, Traffic Manager | Cloud Load Balancing |
| Network accelerator | AWS Global Accelerator | Accelerated Networking | Premium Network Service Tier |
| Network area translation | NAT Gateway | Virtual Network NAT, Azure Route Server (preview) | Cloud NAT |
| Satellite ground station | AWS Ground Station | Azure Orbital (preview) | N/A |
| Service discovery | Amazon ECS, AWS Cloud Map | N/A | GKE |
| Traffic control plane | AWS App Mesh | Azure Front Door, Azure Service Fabric | Traffic Director |
| Virtual WAN | N/A | Virtual WAN | N/A |
| VPC | Amazon VPC | Azure Virtual Network | Virtual Private Cloud |
| VPC/VM secure connector | AWS Transit Gateway, AWS VPN | Azure Bastion, Azure Private Link, Azure VPN gateway | Cloud VPN, Direct Peering, VPC Service Controls |
