IDENTITY MANAGEMENT
Azure AD 
An identity and access management service that helps you access internal and external resources.
Authentication : the process of establishing the identity of a person or service that wants to access a resource.
Authorization: the process of establishing what level of access an authenticated person or service has. It specifies what data they're allowed to access and what they can do with it.
AD licenses
1. Free
- user and group management in your on-premises directory.
- Basic reports, self-service password change for cloud users
SSOacross Azure, Microsoft 365, and many popular SaaS apps.
2. Premium P1
- Included with Microsoft 365
- Allows access to both on-premises and cloud resources.
- Conditional Access for MFA
$6 user/month
3. Premium P2
- Included with Microsoft 365
- Add feature to
P1: risk-based Conditional Access, Identity Protection &
Privileged Identity Management(
PIM) $9 user/month*
4.Pay as you go
- offers a feature called Azure AD B2C
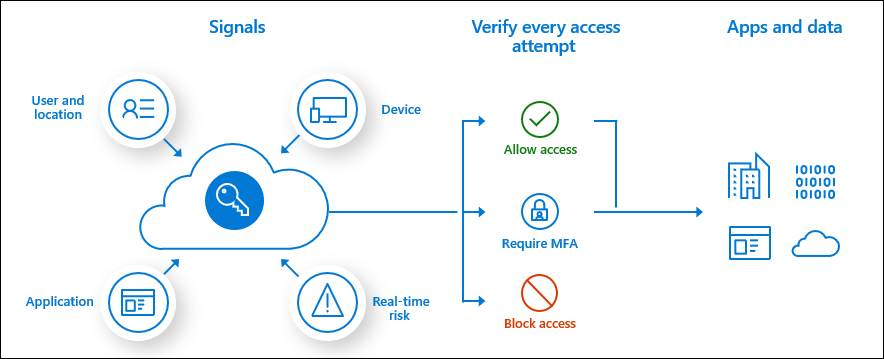
Conditional Access 
tool that Azure AD uses to allow (or deny) access to resources based on identity signals.
- Works with Azure AD Premium P1 or P2 license
These signals include
- who the user is
- where the user is: IP Location
- what device the user is requesting access from.
Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
additional security for identities by requiring two or more elements to fully authenticate.
- Verify user based on
- Something you know, typically a password.
- Something you have, such as a trusted device that's not easily duplicated, like a phone or hardware key.
- Something you are - biometrics like a fingerprint or face scan.
- Can Verify using:
- Microsoft Authenticator app
- OATH hardware token
- SMS or Voice call
Azure AD Device Management
allows you to manage and configure device identities.
Self-service password reset (SSPR)
allow users to change or reset their password, with no administrator or help desk involvement.
Single sign-on (SSO)
enables a user to sign in one time and use that credential to access multiple resources and applications.
Authenticate External User
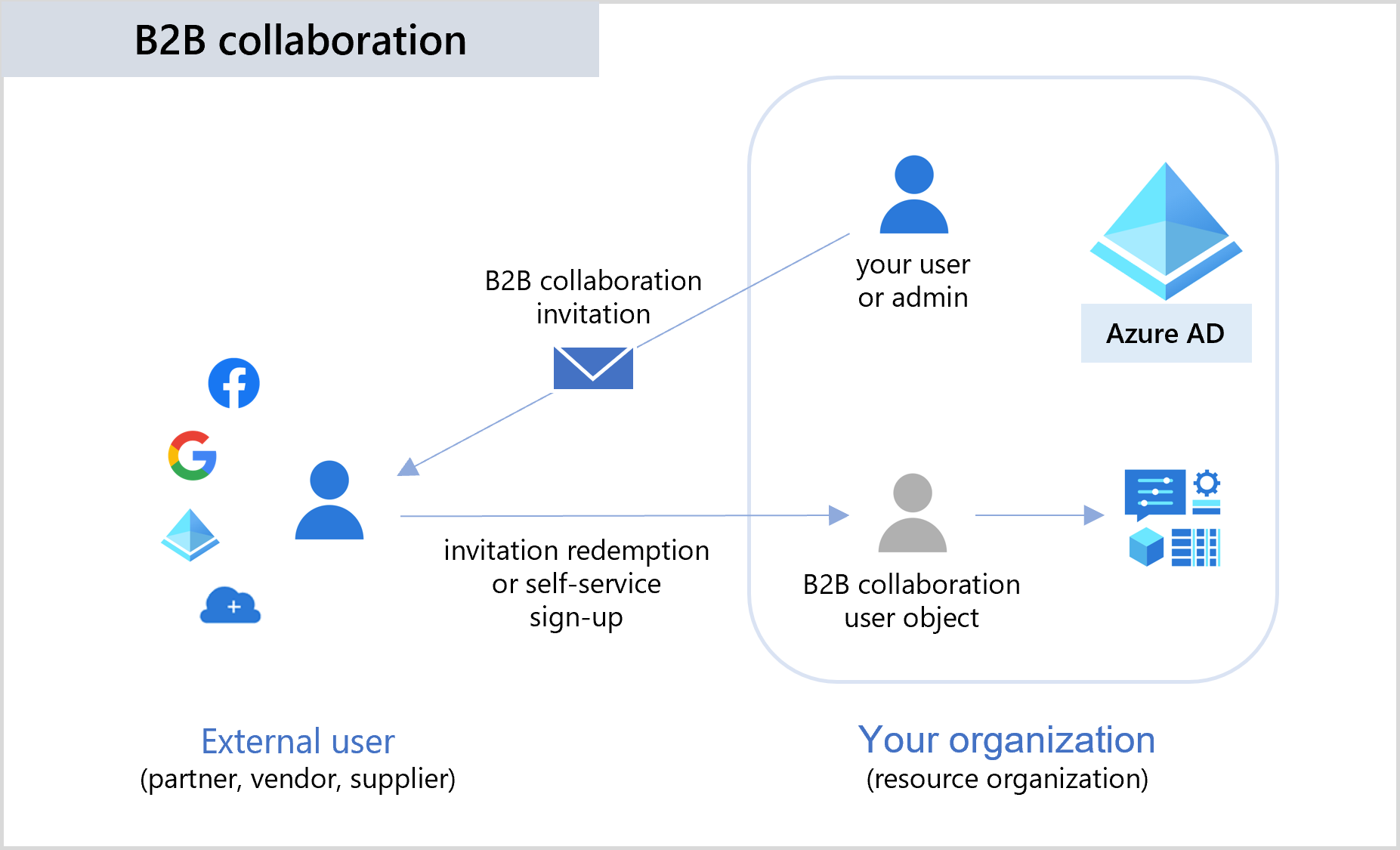
1. Azure AD B2B collaboration
A simple invitation and redemption process lets partners use their own credentials to access your company's resources.
- securely share your company's applications and services with external users, while maintaining control over your own corporate data
2. Azure AD B2C
allow customers to use their preferred social, enterprise, or local account identities to get single sign-on access to your applications and APIs.
- Allows businesses to build customer facing applications by allowing anyone to sign up into with no restrictions on user account.

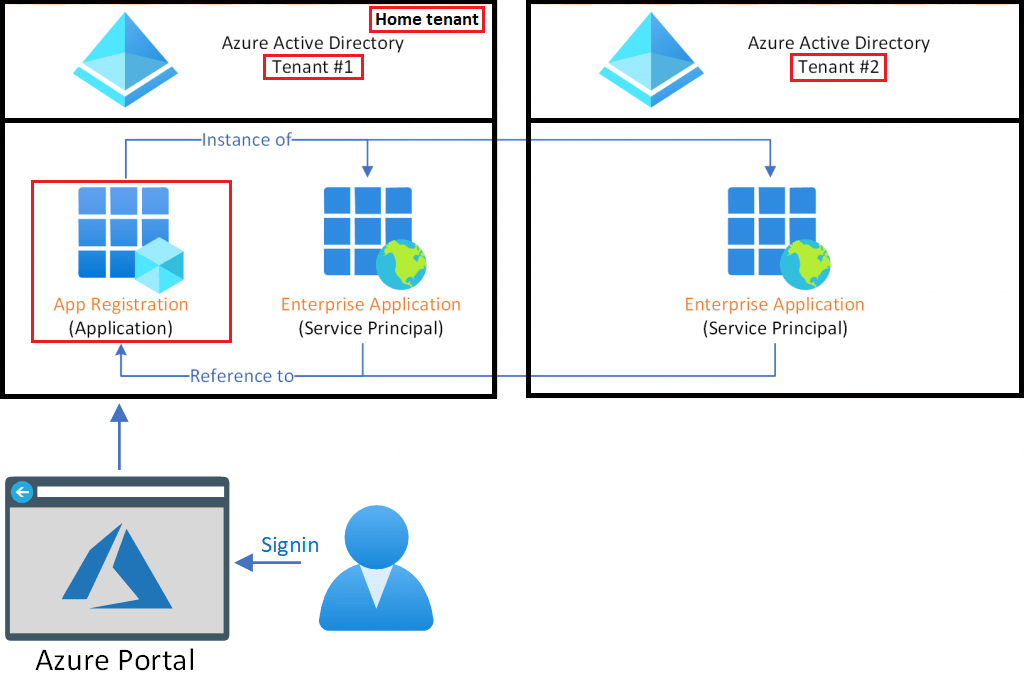
Azure tenant
A dedicated and trusted instance of Azure AD representing a single organization.
- Automatically created when your organization signs up for a Microsoft cloud service subscription
- Microsoft Azure
- Microsoft Intune
- Microsoft 365.
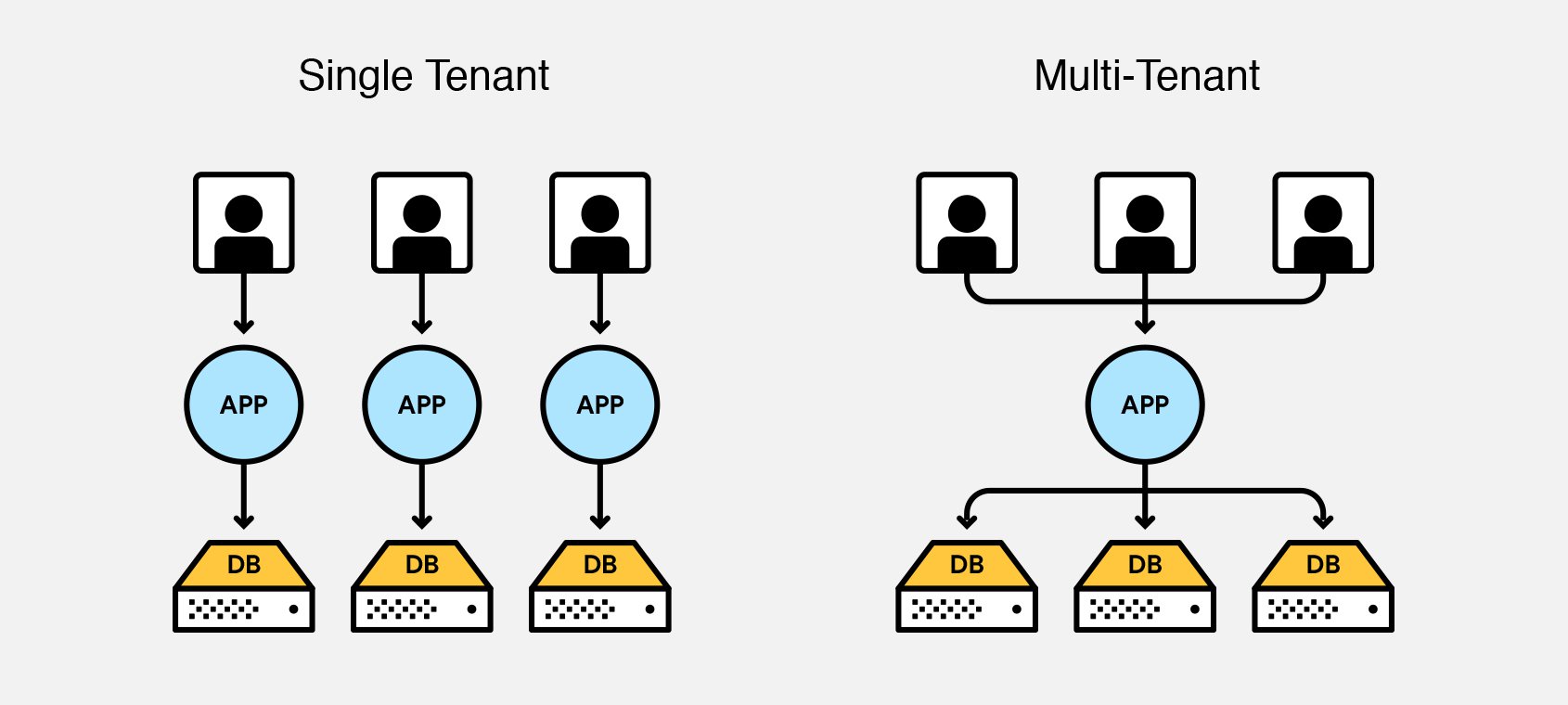
1. Single tenant
Access other services in a dedicated environment are considered single tenant.
- A single-tenant application has only one
service principal (in its home tenant), created and consented for use during application registration.
2. Multi-tenant 
Azure tenants that access other services in a shared environment, across multiple organizations
- A multi-tenant application also has a service principal created in each tenant where a user from that tenant has consented to its use.
Application objects
Global representation of application for use across all tenants.
-
Azure AD application is defined by its one and only application object, which resides in the Azure AD tenant where the application was registered (known as the application's
"home" tenant). -
serves as the template from which common and default properties are derived for use in creating corresponding
service principalobjects. -
1:1relationship with the software application -
1:manyrelationship with its corresponding service principal object(s).
Service Principal
Local representation of application for use in a specific tenant.
- A service principal must be created in each tenant where the application is used
- Service Principal give Identity for sign-in and/or access to resources being secured by the tenant
service principal Type
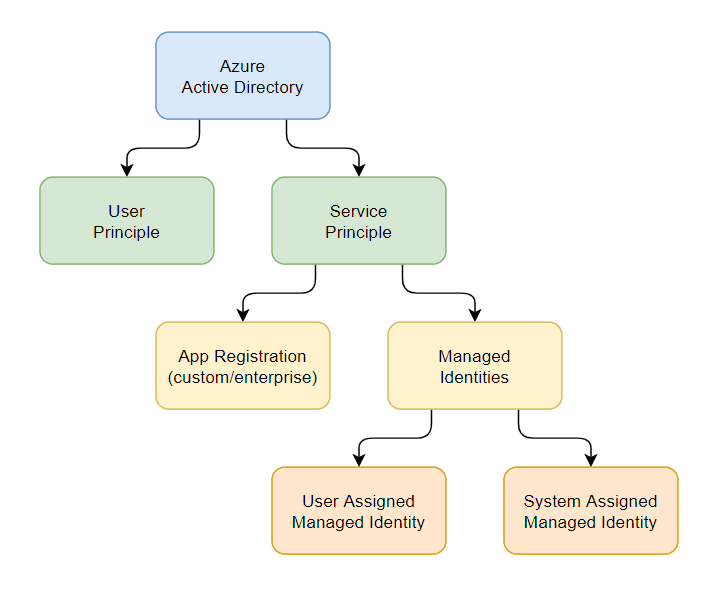
1. Application
The type of service principal is the local representation, or application instance, of a global application object in a single tenant or directory.
- A service principal is created in each tenant where the application is used and references the globally unique app object.
- The service principal object defines what the app can actually do in the specific tenant, who can access the app, and what resources the app can access.
2. **Managed identity
**
This type of service principal is used to represent a managed identity.
- Used for linking a Service Principal security object to an Azure Resource like a Virtual Machine, Web App, Logic App or similar.
Provide an identity for applications to use when connecting to resources that support Azure AD authentication.
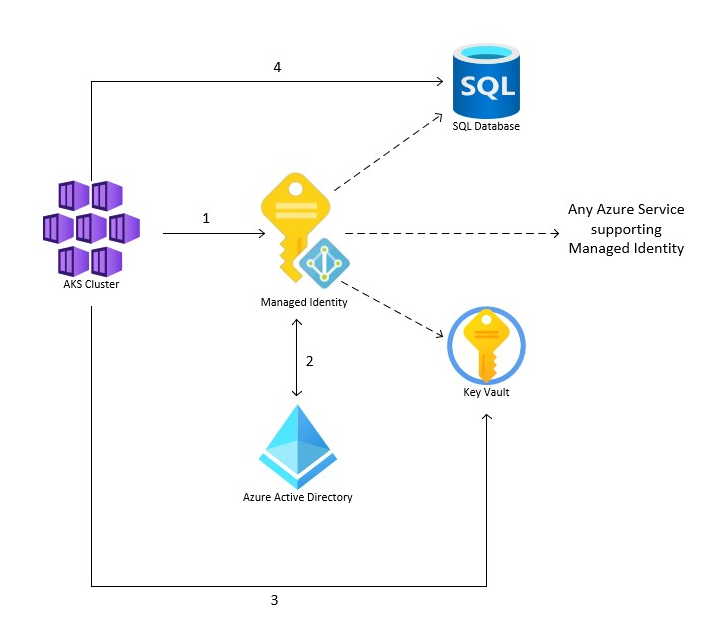
- When a managed identity is enabled a service principal representing that managed identity is created in your tenant.
- Service principals representing managed identities can be granted access and permissions, but cannot be updated or modified directly.
.png)
Managed Identity Types
2.1 System-assigned managed identity
Created as part of an Azure resource (for example, an Azure virtual machine or Azure App Service)
- When the identity is enabled, Azure creates an identity for the instance in the Azure AD tenant that's trusted by the subscription of the instance.
- After the identity is created, the credentials are provisioned onto the instance.
- Sharing: 1-1 Cannot be shared, it can only be associated with a single Azure resource.
- LifeCycle : directly tied to the Azure service instance that it's enabled on.
- Deletion: If the instance is deleted, Azure automatically cleans up the credentials and the identity in Azure AD.
2.2 User-assigned managed identity
Created as a standalone Azure resource.
- Azure creates an identity in the Azure AD tenant that's trusted by the subscription in use.
- After the identity is created, the identity can be assigned to one or more Azure service instances.
- Sharing: 1 - Many: Can be shared,Can be associated with more than one Azure resource.
- Lifecycle: managed separately from the lifecycle of the Azure service instances to which it's assigned.
- Deletion: Must be explicitly deleted.
3. Legacy
This type of service principal represents a legacy app, which is an app created before app registrations were introduced or an app created through legacy experiences.
- A legacy service principal can have credentials, service principal names, reply URLs, and other properties that an authorized user can edit, but does not have an associated app registration.
- The service principal can only be used in the tenant where it was created.
MS Identity platform
Helps you build applications your users and customers can sign in to using their Microsoft identities or social accounts, and provide authorized access to your own APIs or Microsoft APIs like Microsoft Graph.
Does 2 Jobs:
- Allow sign in using Microsoft identities or social accounts
- Provide authorization to own APIs or Microsoft APIs
Permission types
1. Delegated permissions
Used by apps that have a signed-in user present.
- User or an Admin can consents to app permissions.
- The app is delegated with the permission to act as a signed-in user when it makes calls to the target resource.
2. Application permissions
used by apps that run without a signed-in user present, for example, apps that run as background services or daemons.
- Only an Admin can consent to app permissions.
Components of Identity Platform
1. OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect
Allow third-party app to access web-hosted resources on behalf of a user.
Any web-hosted resource that integrates with the Microsoft identity platform has a resource identifier, or application ID URL
OAuth authenticate several identity types:
AD: Login using Work or school accountsAD B2C: Login using Social or local accounts,- Personal Microsoft account: Login using Skype, Xbox, and Outlook.com: ,
2. Application management portal
A registration and configuration experience in the Azure portal
- along with the other Azure management capabilities.
3. Application configuration API and PowerShell
Use Microsoft Graph API and PowerShell to automate DevOps tasks.
Microsoft Graph
Gateway to data and intelligence in Microsoft 365.
Provides a unified programmability model that can access the data in Microsoft 365, Windows 10, and Enterprise Mobility + Security.
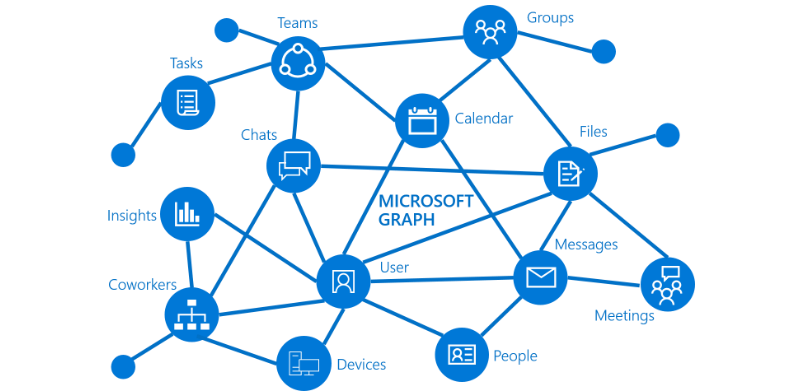
Exposes REST APIs and client libraries to access data on the following Microsoft cloud services
Microsoft 365
Office package in the cloud and also on the desktop
MS Graph API
Offers a single endpoint: https://graph.microsoft.com.
- Allow Accessing Data using:
REST APIs or SDKs - Microsoft Graph also includes a powerful set of services that manage user and device identity, access, compliance, security, and help protect organizations from data leakage or loss.
Microsoft Graph connectors
bring data that is external to the Microsoft cloud into Microsoft Graph. .
- sources: Google Drive, Jira, and Salesforce.
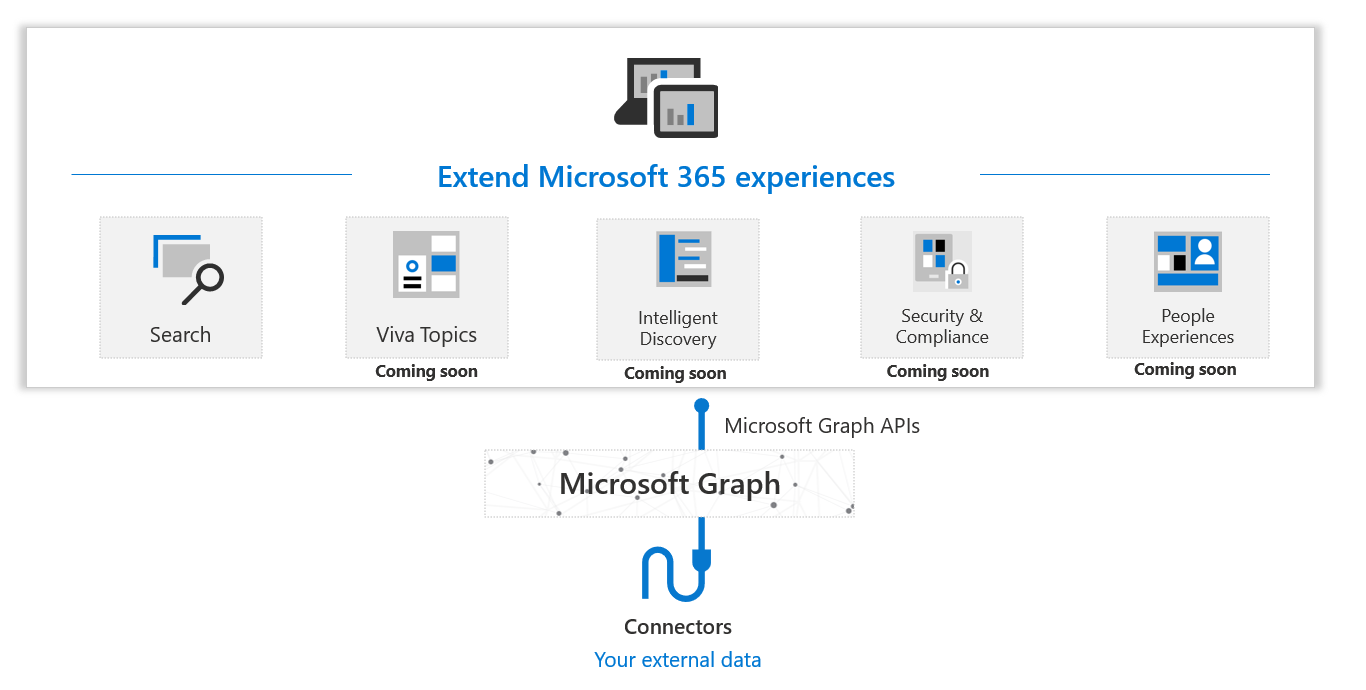
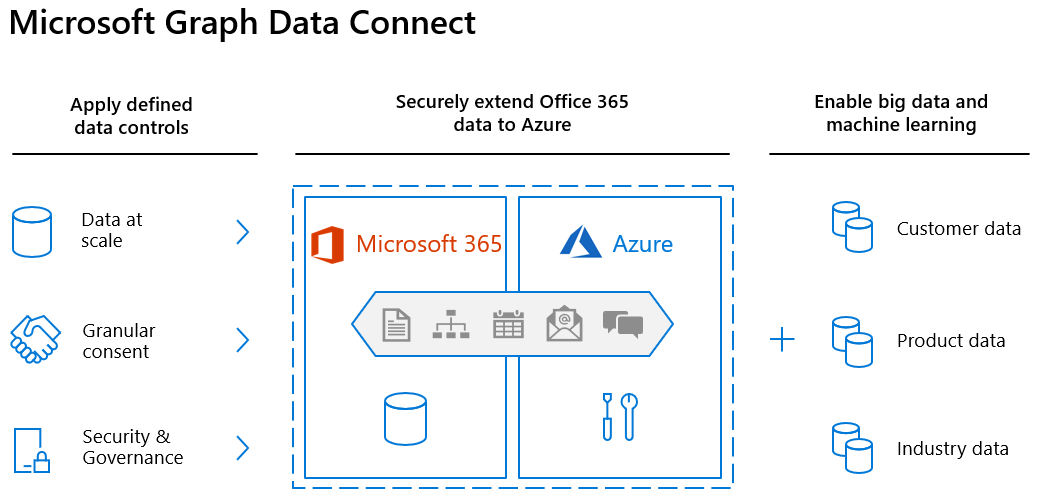
Microsoft Graph Data Connect
Allows developing App for analytics, intelligence, and business process optimization by extending Microsoft 365 data into Azure
- Ideal for big data and machine learning
4. Open-source libraries
Microsoft Authentication Libraries (
MSAL) and support for other standards-compliant libraries
Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL)
enables developers to acquire tokens from the Microsoft identity platform in order to authenticate users and access secured web APIs.
-
fundamental part of the Microsoft identity platform . MSAL simplifies token retrieval, management, caching, and updating while leveraging best practices for resiliency
-
MSAL is conceptually designed to be a secure solution without developers having to worry about the implementation details.
-
Support:
JavaScript, Java, Node, Go, React, Angular, Python, Android, iOS, .NET,
No need to directly use the OAuth libraries or code against the protocol in application
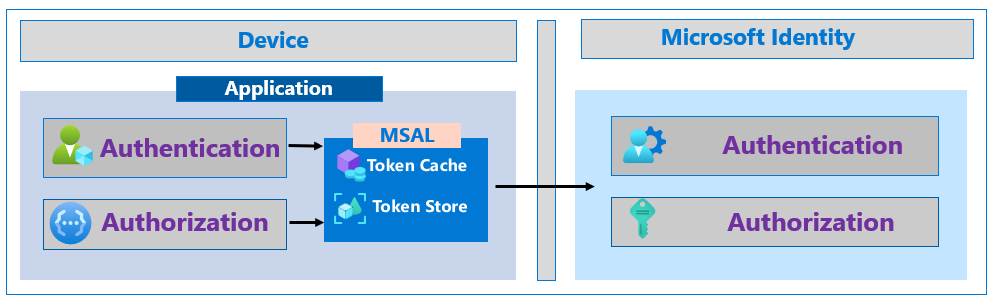
- Acquires tokens on behalf of a user or application.
- Cache Token & refreshes expired tokens.
- Troubleshoot by exposing actionable exceptions, logging, and telemetry.
