DevOps
##* DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops).*
- DevOps = Dev+ IT Ops
- DevSecOps = DevOps + Security
- CI/CD = continuous integration (CI) + continuous delivery/deployment (CD)
Operations:
- Coding – code development and review, source code management tools, code merging.
- Building – continuous integration tools, build status.
- Testing – continuous testing tools that provide quick and timely feedback on business risks.
- Packaging – artifact repository, application pre-deployment staging.
- Releasing – change management, release approvals, release automation.
- Configuring – infrastructure configuration and management, infrastructure as code tools.
- Monitoring – applications performance monitoring, end-user experience.
Adoption of DevOps is being driven by:
- Use of agile and other development processes and methods;
- Demand for an increased rate of production releases – from application and business unit stakeholders;
- Wide availability of virtualized and cloud infrastructure – from internal and external providers;
- Increased usage of data center automation and configuration management tools;
- Increased focus on test automation and continuous integration methods;
- A critical mass of publicly available best practices.
IaC : Infrastructure as Code
Treat infrastructure like code. Model infrastructure with code by design, implement, and deploy application infrastructure with known software best practices
- Applicable to both software developers and IT infrastructure administrators.
- Use the same tools as any other software project would allow developers to rapidly deploy applications.
Methods:
- Pull:- the server to be configured will pull its configuration from the controlling server.
- Push:- controlling server pushes the configuration to the destination system
Types
| declarative (functional) | imperative (procedural). |
|---|---|
| focuses on what the eventual target configuration should be | focuses on how the infrastructure is to be changed to meet this |
| defines the desired state & system executes what needs to happen to achieve that desired state. | defines specific commands that need to be executed in the appropriate order |
Continuous configuration automation (CCA) too
| Tool | Released by | Method | Approach | Written in | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chef | Chef (2009) | Pull | Declarative and imperative | Ruby | - |
| Otter | Inedo | Push | Declarative and imperative | - | Windows-oriented |
| Puppet | Puppet (2005) | Pull | Declarative and imperative | C++ & Clojure since 4.0, Ruby | - |
| SaltStack | SaltStack | Push and Pull | Declarative and imperative | Python | - |
| CFEngine | Northern.tech | Pull | Declarative | C | - |
| Terraform | HashiCorp (2014) | Push | Declarative | Go | - |
| Ansible / Ansible Tower | Red Hat (2012) | Push | Declarative and imperative | Python | - |
Advantage:
- Less effort to setup infrastucture. Teams across the enterprise can work quickly and efficiently.
- Infrastructure automation enables speed through faster configuring infrastructure
- Removes the risk associated with human error like manual misconfiguration.
- Dcrease downtime and increase reliability.
IaC Variants
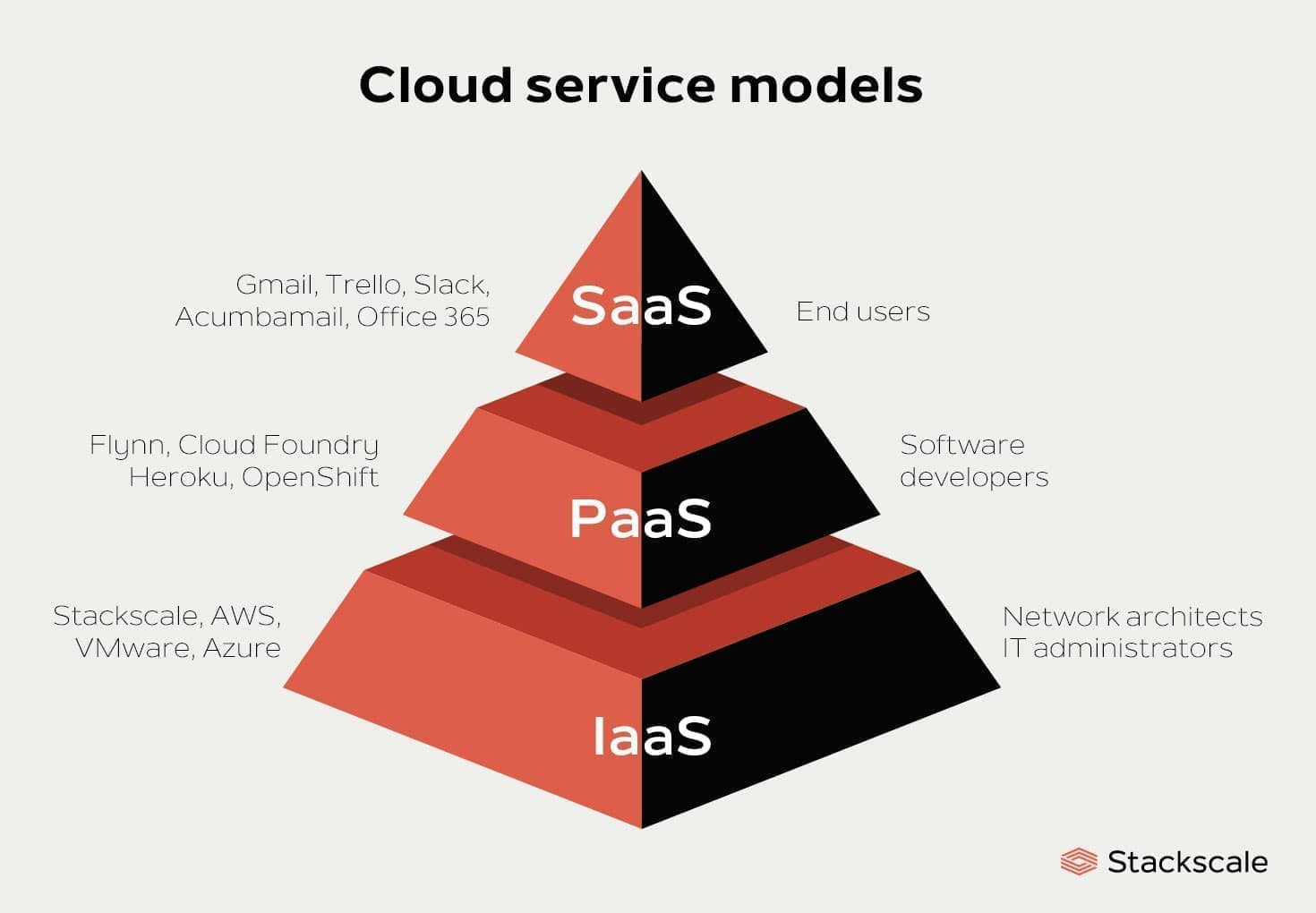
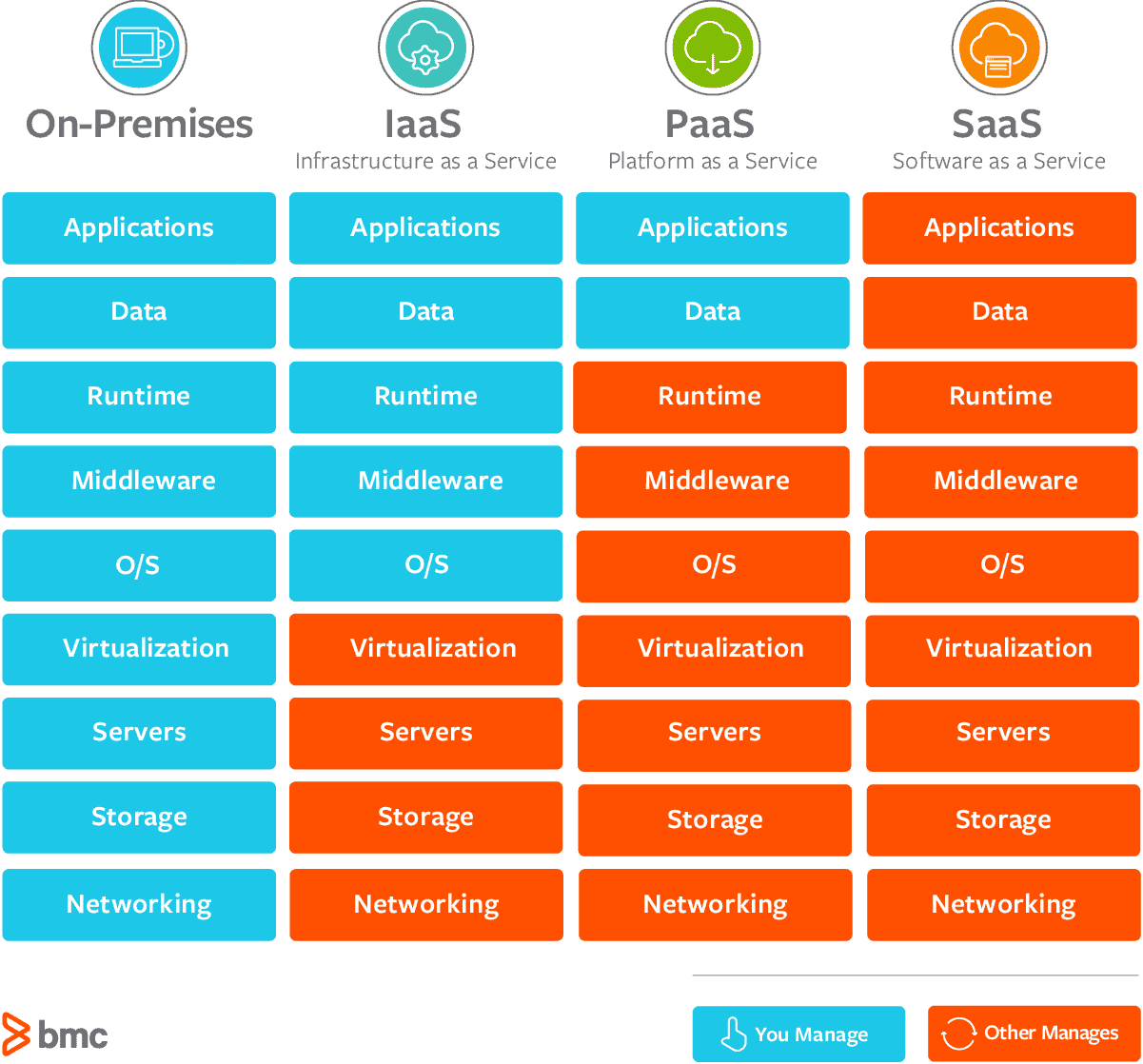
| Parameter | Software as a Service (SaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example: | Google Workspace, Dropbox, Salesforce, Cisco WebEx, Concur, GoToMeeting | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos, OpenShift | DigitalOcean, Linode, Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE) |
| Usage | Application | RunTime/ Middle ware | Storage/ Networking/ Vistualization |
| Control | No control over data & business logic | App can be deployed on public, private and hybrid cloud platform | online services that provide high-level APIs used to dereference various low-level details of underlying network infrastructure like physical computing resources, location, data partitioning, scaling, security, backup etc |
Virtualization:
Hypervisor/ virtual machine monitor, VMM/ virtualizer
Computer software, firmware or hardware that creates & runs virtual machines.
Hyper Visor = Supervisor of the Supervisors(Kernal)
- A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine.
The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems.
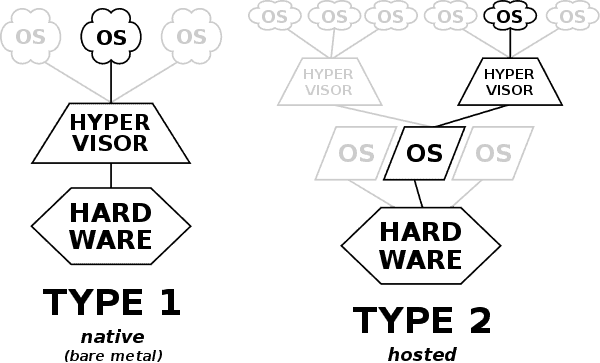
| Type-1, | Type-2 |
|---|---|
| native or bare-metal hypervisors | hosted hypervisors |
| run directly on the host's hardware to control the hardware and to manage guest operating systems. | run on a conventional operating system (OS) just as other computer programs do. |
| Microsoft Hyper-V and Xbox One system software, Oracle VM Server for SPARC, x86 POWER Hypervisor QNX Hypervisor,VMware ESXi (formerly ESX) | VirtualBox, VMware Player and VMware Workstation |
