☁️ Terraform Cloud capabilities - 6%
- 9a Explain how Terraform Cloud helps to manage infrastructure
- 9b Describe how Terraform Cloud enables collaboration and governance
Terraform Cloud
Cloud service on https://app.terraform.io/app/Hassium/workspaces for running Terraform runs in a consistent and reliable cloud environment instead of on your local machine.
TF Tiers
1. FREE
- Pricing: Free up to 500 resources/month
- Hosting: Cloud
2. STANDARD
For professional individuals or teams adopting infrastructure as code provisioning.
- Pricing: FREE Tier + $0.00014 per hour/resource
- Hosting: Cloud
- Support: Enterprise support included
3. PLUS
For enterprises standardizing and managing infrastructure automation and lifecycle, with scalable runs.
- Pricing: Custom Plan
- Hosting: Cloud
- Support:Enterprise support included
- Additional feature: Audit logging, Drift detection, Continuous validation
4. Terraform ENTERPRISE
For enterprises with special security, compliance, and additional operational requirements.
On premise private TF cloud by providing self hosted instance of TF
- Pricing: Custom Plan
- Hosting:: Self-managed Private Server
- Support:Enterprise support included
- Additional feature: PLUS TIER +
- No resource limit
- SAML/SSO login
TF Cloud Workflow
Terraform Cloud supports three workflows for Terraform runs:
1. The CLI-driven workflow
uses Terraform's standard CLI tools to execute runs in Terraform Cloud.
- Trigger remote Terraform runs from your local command line.
2. The UI/Version Control System(VCS): Most common
VCS driven workflow, in which changes pushed to version control repositories trigger runs in the associated workspace.
- Store Terraform configuration in a git repository, and trigger runs based on pull requests and merges.
3. The API-driven workflow: (More advanced option)
which allows you to create tooling to interact with the Terraform Cloud API programmatically.
- Integrate Terraform into a larger pipeline using the Terraform API.
TF Cloud supported VCS providers
When workspaces are linked to a VCS repository, TF Cloud can automatically initiate Terraform runs when changes are committed to the specified branch.
- Webhooks TF Cloud uses webhooks to monitor new commits and pull requests.
- GitHub
- GitHub App for TF
- GitHub.com (OAuth)
- GitHub Enterprise
- GitLab.com
- GitLab EE and CE
- Bitbucket Cloud
- Bitbucket Server
- Azure DevOps Server
- Azure DevOps Services-
Workspaces(
terraform.tfstate.d.)
Terraform Cloud manages infrastructure collections with workspaces instead of directories.
-
Terraform stores the workspace states in a directory called
terraform.tfstate.d. This directory should be treated similarly to local-onlyterraform.tfstate. -
A workspace contains everything Terraform needs to manage a given collection of infrastructure
-
separate workspaces acts like completely separate working Directories.
-
Terraform starts with a single,
defaultworkspace that can not be deleted. -
Terraform CLI Workspace refer to separate instances of state data inside the same Terraform working directory
We Can include the name of the current workspace using the ${terraform.workspace}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
count = "${terraform.workspace == "default" ? 5 : 1}"
# ... other arguments
}
| command | use |
|---|---|
terraform workspace new dev | create a new workspace |
terraform workspace select dev | change to the selected workspace |
terraform workspace list | list out all workspaces |
terraform workspace delete dev | delete workspaces |
Local vs Remote State
| Component | Local Terraform | Terraform Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Terraform configuration | On disk | In linked version control repository, or periodically uploaded via API/CLI |
| Variable values As | .tfvars files, as CLI arguments, or in shell environment | In workspace |
| State | On disk or in remote backend | In workspace |
| Credentials and secrets | In shell environment or entered at prompts | In workspace, stored as sensitive variables |
Terraform Run
TF Cloud performs Terraform runs on its own disposable virtual machines, using that workspace's configuration, variables, and state.
TF Cloud keeps additional data for each workspace:
-
State versions
Each workspace retains backups of its previous state files for tracking changes over time or recovering from problems.
-
Run history
When Terraform Cloud manages a workspace's Terraform runs, it retains a record of all run activity, including summaries, logs, a reference to the changes that caused the run, and user comments. |
Sentinel
Policy as code framework for HashiCorp Enterprise Products.
- Only after a successful
terraform plan, Terraform Cloud checks whether the plan obeys policy to determine whether it can be applied.
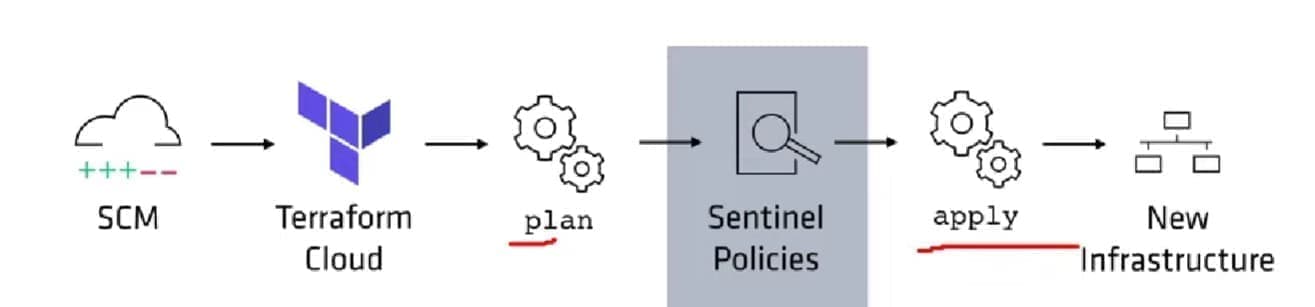 Sentinel language: All Sentinel policies are written using
the Sentinel language so all Sentinel-enabled applications share the same policy language.
Sentinel language: All Sentinel policies are written using
the Sentinel language so all Sentinel-enabled applications share the same policy language.
Development. Sentinel provides a CLI for development and testing. This local CLI can be used to verify policies before deploying them to a system.
Testing. Sentinel provides a test framework designed specifically for automation. This allows developers and CI systems to further verify policies.
import "time"
# Validate time is between 8 AM and 4 PM
valid_time = rule { time.now.hour >= 8 and time.now.hour < 16 }
# Validate day is M - Th
valid_day = rule {
time.now.weekday_name in ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"]
}
main = rule { valid_time and valid_day }
Sentinel has three enforcement levels:
Advisory: The policy is allowed to fail. However, a warning should be shown to the user or logged.
- Advisory is the default enforcement level.
-
Soft Mandatory: The policy must pass unless an override is specified. The semantics of "override" are specific to each Sentinel-enabled application. -
Hard Mandatory: The policy must pass no matter what. The only way to override a hard mandatory policy is to explicitly remove the policy.
Terraform Cloud Sentinel Imports
A policy can include imports that enable a policy to access reusable libraries, external data, and functions.
Terraform Cloud provides four imports to define policy rules for the plan, configuration, state, and run associated with a policy check.
-
tfplan- Access a Terraform plan, which is the file created as a result of the terraformplancommand. -
tfconfig- Access a Terraform configuration. The configuration is the set of.tf filesthat describe the desired infrastructure state. -
tfstate- Access the Terraform state. Terraform uses state to map real-world resources to your configuration. -
tfrun- Access data associated with arunin Terraform Cloud. For example, you could retrieve the run's workspace.
Terraform Cloud Agents
Paid feature that allows Terraform Cloud to communicate with isolated, private, or on-premises infrastructure.
- allow you to run Terraform operations from a Terraform Cloud workspace on private infrastructure.
Agents do not support:
- Connecting to private infrastructure from Sentinel policies using the http import.
Consul
Distributed, highly available, and data center aware solution to connect and configure applications across dynamic, distributed infrastructure.
Runs on Linux, macOS, FreeBSD, Solaris, and Windows and includes an optional browser based UI.
Packer
open source tool for creating identical machine images for multiple platforms from a single source configuration.
- Packer is lightweight, runs on every major operating system, and is highly performant, creating machine images for multiple platforms in parallel.
- Packer is able to use tools like Chef or Puppet to install software onto the image.
A machine image is a single static unit that contains a pre-configured operating system and installed software which is used to quickly create new running machines. Machine image formats change for each platform. Some examples include AMIs for EC2, VMDK/VMX files for VMware, OVF exports for VirtualBox, etc.
Vault
Manage secrets and protect sensitive data with Vault
